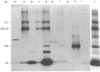
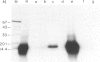
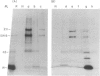
Abstract
Children from an area of Africa endemic for the large roundworm of humans, Ascaris lumbricoides, were found to vary considerably in the specificity of their serum IgG response to the internal antigens of the parasite. This was particularly noticeable for responses to a 14-kD protein (ABA-1) of the parasite that has previously been shown to be the subject of a strong IgE antibody response in infected animals. The possibility that this heterogeneity in immune repertoire has a genetic basis was explored in inbred mice infected with Ascaris suum. This showed that no strain responded to all the potential antigens, that the recognition profiles of strains bearing independent haplotypes were unique, and only H-2-identical strains had responses of similar specificities. Major histocompatability complex (MHC) restriction was confirmed using H-2-congenic animals on BALB and B10 backgrounds, which responded according to their H-2 haplotype. It is likely, therefore, that it is the MHC which controls the repertoire to Ascaris antigens in infected people. If this is so, then there will be implications for immunopathology associated with ascariasis, and possibly also for resistance and susceptibility to infection.
Full text
PDF
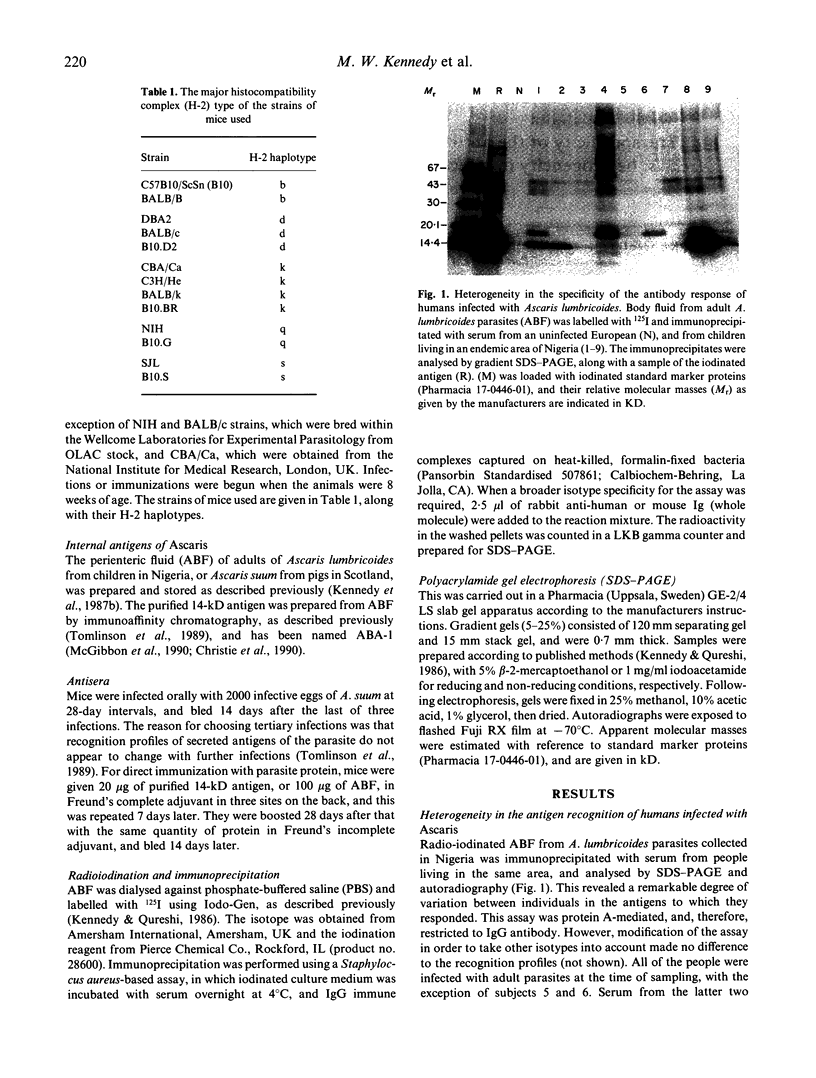



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almond N. M., Parkhouse R. M., Chapa-Ruiz M. R., Garcia-Ortigoza E. The response of humans to surface and secreted antigens of Trichinella spiralis. Trop Med Parasitol. 1986 Dec;37(4):381–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anders R. F. Multiple cross-reactivities amongst antigens of Plasmodium falciparum impair the development of protective immunity against malaria. Parasite Immunol. 1986 Nov;8(6):529–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1986.tb00867.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. M. The population dynamics and epidemiology of intestinal nematode infections. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1986;80(5):686–696. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(86)90367-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundy D. A. Population ecology of intestinal helminth infections in human communities. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Oct 31;321(1207):405–420. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1988.0100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkins D. B., Haswell-Elkins M., Anderson R. M. The epidemiology and control of intestinal helminths in the Pulicat Lake region of Southern India. I. Study design and pre- and post-treatment observations on Ascaris lumbricoides infection. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1986;80(5):774–792. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(86)90384-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenspon L. W., White J., Shields R. L., Fügner A., Gold W. M. Purification of Ascaris suum antigen: its allergenic activity in vitro and in vivo. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1986 Mar;77(3):443–451. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(86)90178-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haswell-Elkins M. R., Elkins D. B., Anderson R. M. Evidence for predisposition in humans to infection with Ascaris, hookworm, Enterobius and Trichuris in a South Indian fishing community. Parasitology. 1987 Oct;95(Pt 2):323–337. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000057772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haswell-Elkins M. R., Kennedy M. W., Maizels R. M., Elkins D. B., Anderson R. M. The antibody recognition profiles of humans naturally infected with Ascaris lumbricoides. Parasite Immunol. 1989 Nov;11(6):615–627. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1989.tb00925.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett E. E., Miller H. R. Production and activities of IgE in helminth infection. Prog Allergy. 1982;31:178–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. P., Murphy D. B., McDevitt H. O. Variable synthesis and expression of E alpha and Ae (E beta) Ia polypeptide chains in mice of different H-2 haplotypes. Immunogenetics. 1981;12(3-4):321–337. doi: 10.1007/BF01561674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. W. Genetic control of the immune repertoire in nematode infections. Parasitol Today. 1989 Oct;5(10):316–324. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(89)90122-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. W., Gordon A. M., Tomlinson L. A., Qureshi F. Genetic (major histocompatibility complex?) control of the antibody repertoire to the secreted antigens of Ascaris. Parasite Immunol. 1987 Mar;9(2):269–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1987.tb00506.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. W., Qureshi F., Fraser E. M., Haswell-Elkins M. R., Elkins D. B., Smith H. V. Antigenic relationships between the surface-exposed, secreted and somatic materials of the nematode parasites Ascaris lumbricoides, Ascaris suum, and Toxocara canis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Mar;75(3):493–500. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. W., Qureshi F., Haswell-Elkins M., Elkins D. B. Homology and heterology between the secreted antigens of the parasitic larval stages of Ascaris lumbricoides and Ascaris suum. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Jan;67(1):20–30. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. W., Qureshi F. Stage-specific secreted antigens of the parasitic larval stages of the nematode Ascaris. Immunology. 1986 Jul;58(3):515–522. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizels R. M., Selkirk M. E., Sutanto I., Partono F. Antibody responses to human lymphatic filarial parasites. Ciba Found Symp. 1987;127:189–202. doi: 10.1002/9780470513446.ch13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzinger P. A one-receptor view of T-cell behaviour. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):497–501. doi: 10.1038/292497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. B., Jones P. P., Loken M. R., McDevitt H. O. Interaction between I region loci influences the expression of a cell surface Ia antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5404–5408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odunjo E. O. Helminthic anaphylactic syndrome (HAS) in children. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1970;35(1):220–223. doi: 10.1159/000162233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinder M., Dupont A., Egwang T. G. Identification of a surface antigen on Loa loa microfilariae the recognition of which correlates with the amicrofilaremic state in man. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2480–2486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard D. I., Behnke J. M., Carr A., Wells C. The recognition of antigens on the surface of adult and L4 Necator americanus by human and hamster post-infection sera. Parasite Immunol. 1986 Jul;8(4):359–367. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1986.tb00852.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roach T. I., Wakelin D., Else K. J., Bundy D. A. Antigenic cross-reactivity between the human whipworm, Trichuris trichiura, and the mouse trichuroids Trichuris muris and Trichinella spiralis. Parasite Immunol. 1988 May;10(3):279–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1988.tb00221.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. H. A clonal deletion model for Ir gene control of the immune response. Scand J Immunol. 1978;7(1):3–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00420.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson L. A., Christie J. F., Fraser E. M., McLaughlin D., McIntosh A. E., Kennedy M. W. MHC restriction of the antibody repertoire to secretory antigens, and a major allergen, of the nematode parasite Ascaris. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 1;143(7):2349–2356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakelin D. Genetic control of immunity to helminth infections. Parasitol Today. 1985 Jul;1(1):17–23. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(85)90101-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassom D. L., Wakelin D., Brooks B. O., Krco C. J., David C. S. Genetic control of immunity to Trichinella spiralis infections of mice. Hypothesis to explain the role of H-2 genes in primary and challenge infections. Immunology. 1984 Apr;51(4):625–631. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]