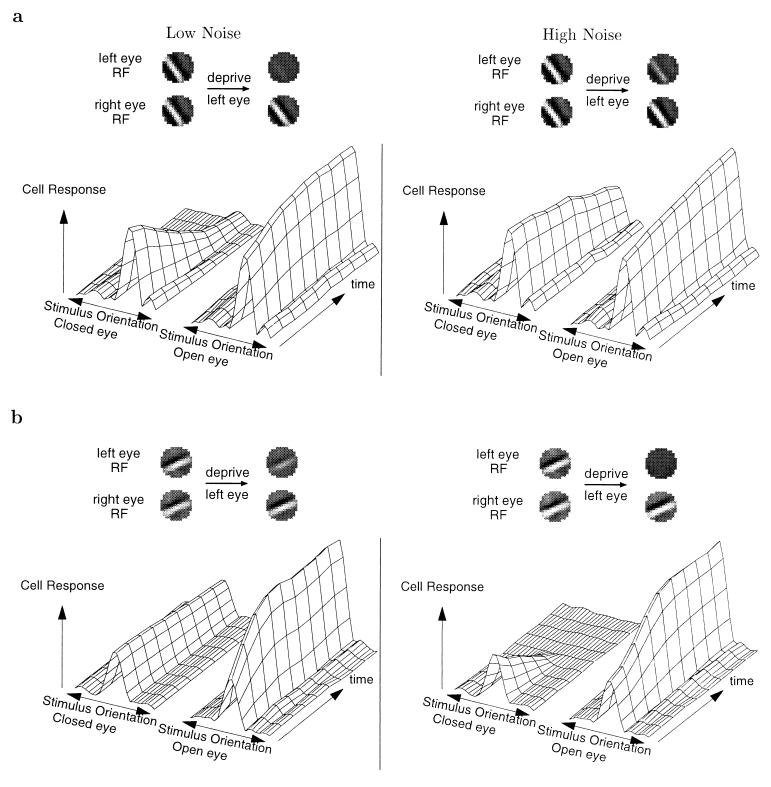
Figure 1.
The effect of noise from the closed eye on the disconnection of the closed eye in MD. (a) The heterosynaptic rule. K2, as described in Blais et al. (10) and Learning Rules, is used to train a neuron in the natural scene environment to obtain binocular, oriented receptive fields (RF). Shown are the results of monocular deprivation starting from the binocular state. Left and right receptive fields (Upper), before and after depriving the left eye. Each pixel represents a point in space over the retina, where white and black correspond to strong and weak synaptic strengths, respectively, from that retinal input. The responses of the cell to oriented sine gratings (Lower) as a function of time during deprivation in a low-noise environment (Lower Left) and a high-noise environment (Lower Right). (b) The homosynaptic rule, BCM, is used to train a neuron. All of the conventions are the same as a. The two rules have the opposite dependence on the noise from the closed eye of the rate of disconnection of the closed eye in MD.