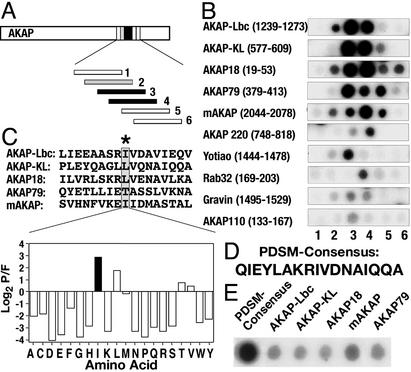
Figure 1.
Derivation of PDSM consensus sequence. (A) Schematic representation of how the RII-binding sequences within AKAPs were defined. Peptide arrays of 20-mer peptides (each offset by three residues) from 10 individual AKAPs were screened for RII binding by the overlay procedure. (B) Autoradiographs of RII-binding peptides from 10 anchoring proteins. The name of each AKAP and segment of sequence analyzed is indicated. (C Upper) Alignment of the five highest-affinity RII-binding sequences by using the MEME software. An AKAP-specific position-dependent scoring matrix (PDSM) was calculated by the log (base 2) of the probability that an amino acid is found at a given position in the alignment divided by the frequency that this amino acid is found in the nonredundant protein database (P/F). (C Lower) Values derived for position 9 in the PDSM sequence represented as a graphical output. Isoleucine (black bar) is the highest-scoring amino acid. Amino acids are indicated by their single-letter codes. (D) The MEME-derived PDSM consensus sequence. (E) RII overlay autoradiograph of a peptide array containing the PDSM consensus sequence and five high-affinity AKAPs (indicated above each lane).