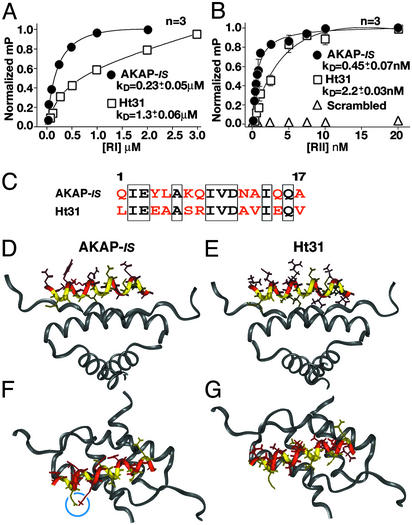
Figure 3.
Biochemical and structural analysis of AKAP-IS. Dissociation constants (Kd) of AKAP-IS (●) and Ht31 (□) peptides were determined by fluorescence polarization. Saturation binding curves were generated with increasing concentrations of RIα (A) or RIIα (B). Polarization values (mP) were determined at equilibrium and normalized to the highest value of saturation. Nonlinear regression analysis was used to derive Kd values from three independent experiments. Interaction of RII was not detected when a scrambled peptide (▵) of amino acid composition identical to that of the AKAP-IS sequence was used. (C) Alignment of the AKAP-IS and Ht31 sequences. Identical (boxed) and dissimilar (red) residues are indicated. (D–G) Molecular modeling of the AKAP-IS–RIIα complex used coordinates from the NMR structure of the Ht31/RIIα complex. The core peptide (yellow) and sites of divergence between AKAP-IS and Ht31 (red) are indicated. A side view reveals a change in RII contact side chains at positions 14 and 17 in AKAP-IS (D) compared with the Ht31 (E). Top view of AKAP-IS (F) reveals the formation of a salt bridge formed by residues E3 and K7 (blue circle) that is not found in Ht31 (G).