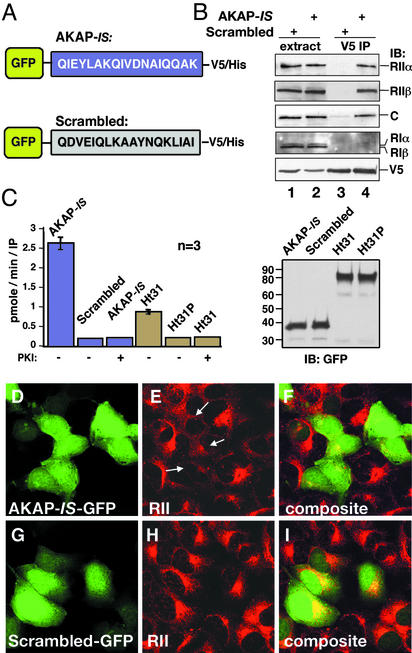
Figure 4.
AKAP-IS interacts with PKA inside cells. (A) Schematic representation of GFP fusion proteins with the AKAP-IS (Upper) and scrambled (Lower) peptides used in the cell-based studies. Sequences are given by the single-letter amino acid codes. (B) HEK293 cells were transfected with either construct, and immune complexes were immunoprecipitated from cell extracts (extract) with a V5 antibody (V5 IP). Copurification of PKA holoenzyme subunits was detected by immunoblotting (IB) using antibodies against the RIIα (top blot), RIIβ (second blot), C subunit (third blot), or RI subunits (fourth blot). The GFP fusion proteins were detected by immunoblotting using the V5 antibody (bottom blot). (C) The specific activity (pmol/min per IP) of PKA C subunit coprecipitating with chimeric AKAP fusion proteins (indicated above each column) was measured by a filter paper binding assay using the Kemptide as a substrate. PKA activity was blocked when PKI-(5–24) peptide (10 μM) was added to the reaction mixture. The accumulated data from three independent experiments are shown (Left). Immunoblot shows that equal amounts of the GFP fusion proteins were used in these experiments (Right). (D–I) Cells transiently transfected with plasmids expressing AKAP-IS or the scrambled peptide for 24 h were fixed, and immunocytochemical techniques were used to detect intrinsic GFP fluorescence (green; D and G). The subcellular location of RII (red; E and H) was detected with a monoclonal anti-RII antibody and Texas red-conjugated secondary antibody. Arrows indicate the mislocalization of RII from the Golgi/centrosomal area in AKAP-IS-expressing cells. Composite images (F and I) are presented.