Abstract
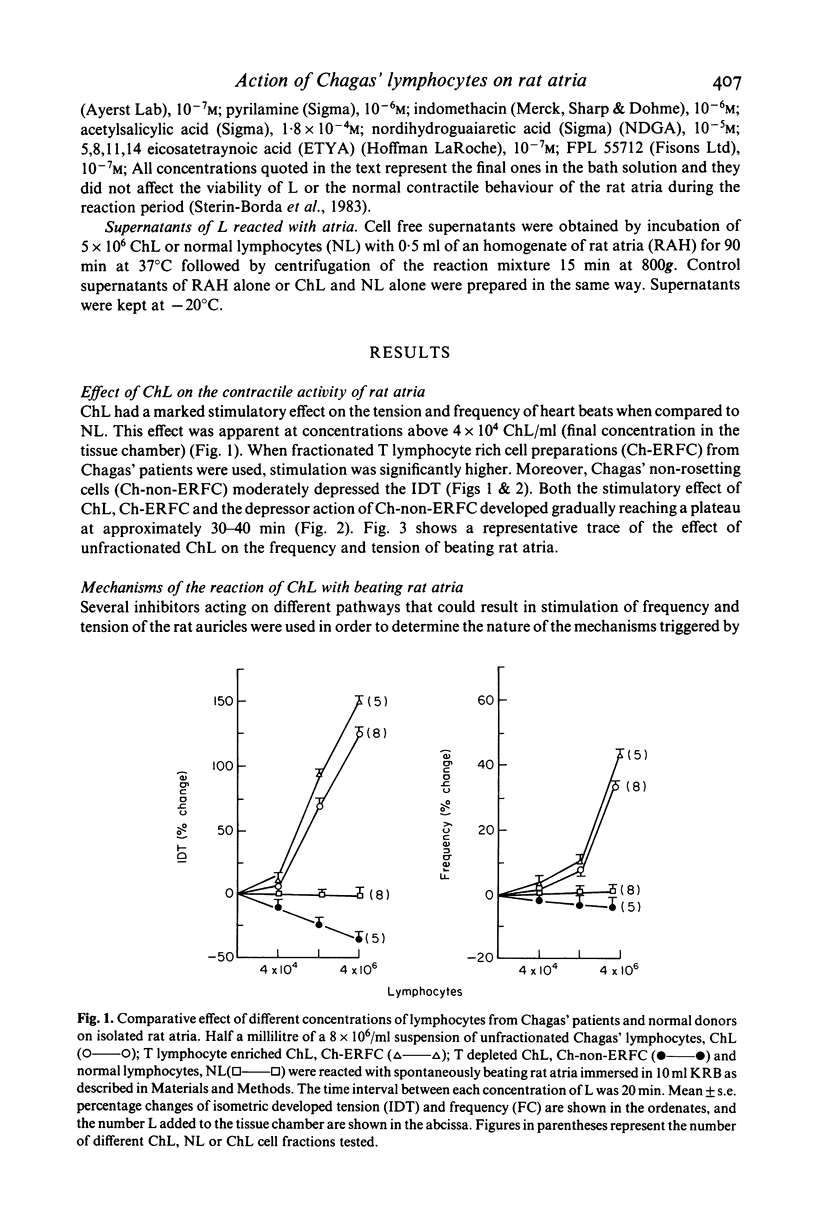
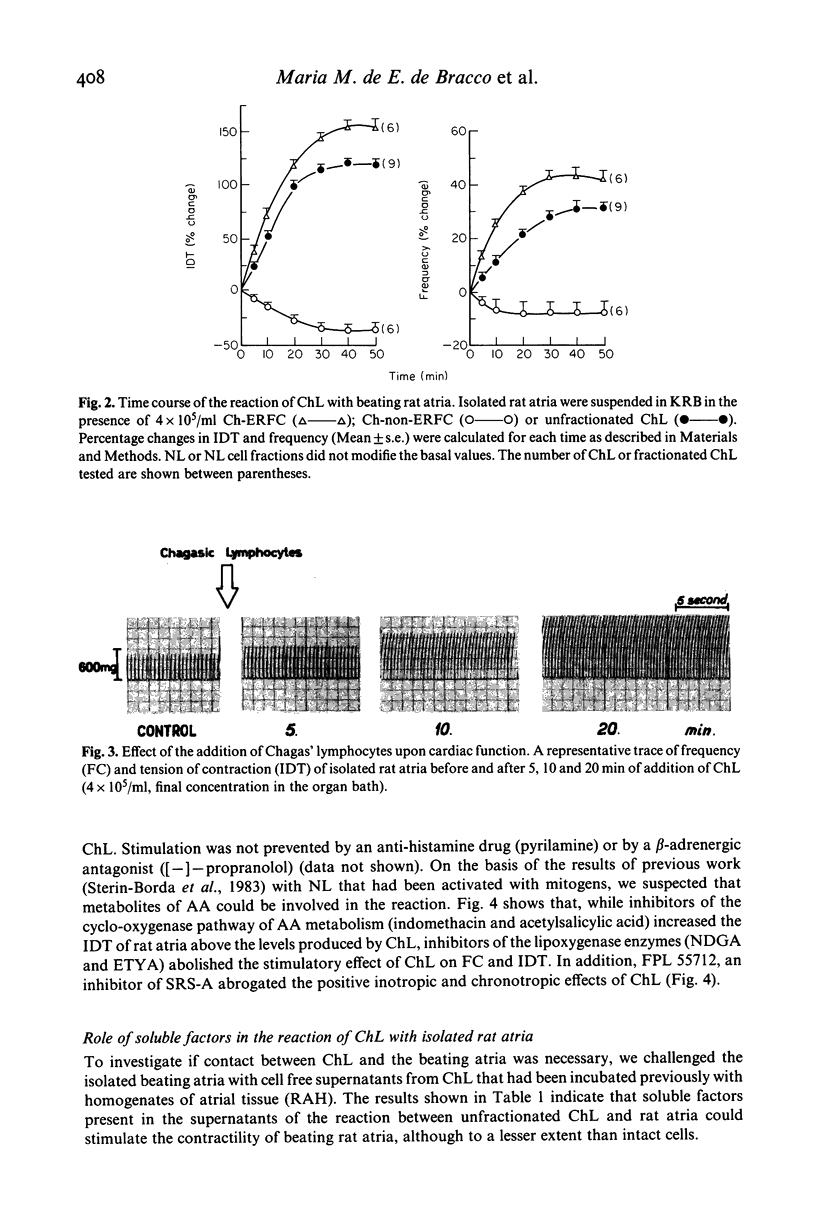
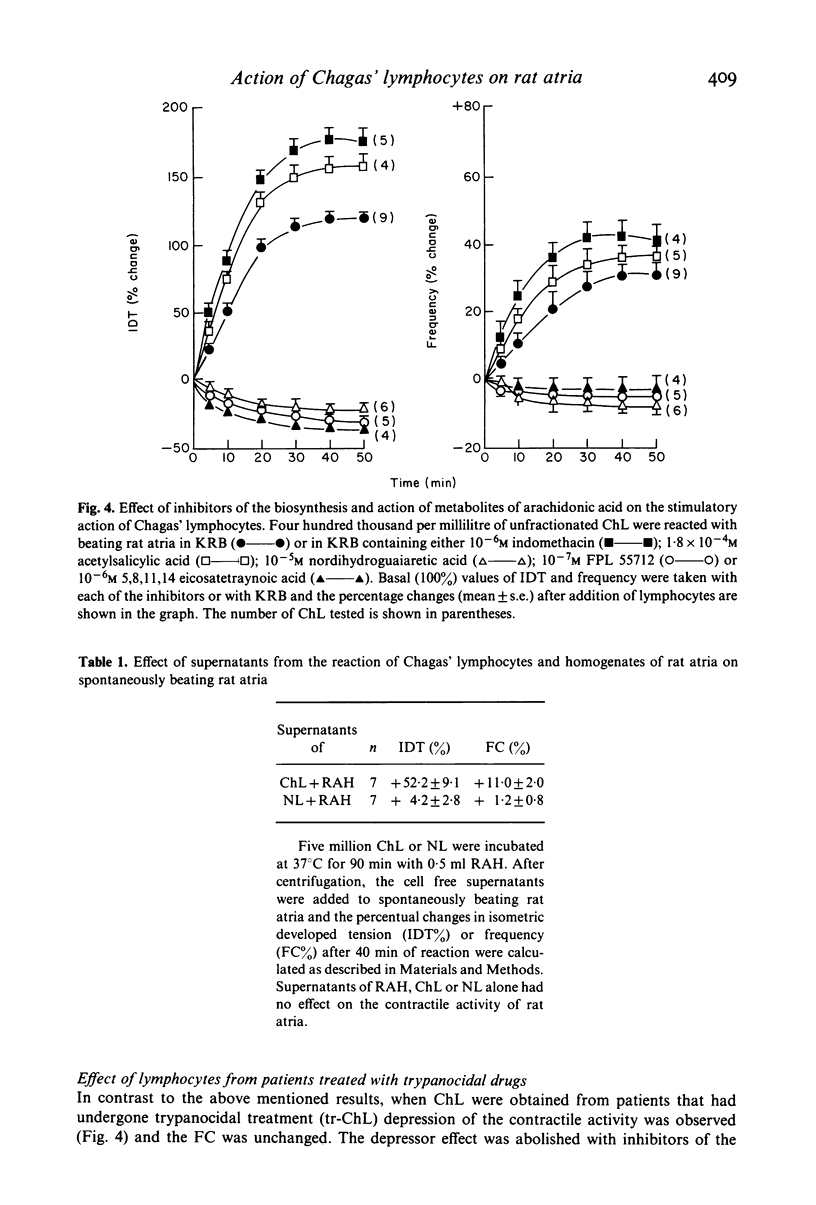
The aim of this work was to study the effect of lymphocytes from individuals infected with Trypanosoma cruzi (Chagas' patients) on the contractile behaviour of living heart tissue. Chagas' lymphocytes (ChL) reacted with isolated rat atria preparations increasing the isometric development tension (IDT) and frequency of contractions (FC) in a dose-dependent manner. The maximal stimulatory effect was reached after 30-40 min of contract. In contrast, normal lymphocytes (NL) did not alter the basal IDT and FC values. beta-adrenergic antagonists, anti-histamine agents and inhibitors of the synthesis and action of arachidonic acid (AA) products were used to study the mechanisms of the reaction. (-)-propranolol (10(-7)M) and pyrilamine (10(-6)M) had no effect ruling out the participation of beta-adrenergic agonists or histamine. However, indomethacin (10(-6)M) and acetylsalicylic acid (1.8 X 10(-4)M) enhanced the effect of ChL. Inhibitors of the lipoxygenase pathway (5,8,11,14-eicosatetraynoic acid, 10(-7)M; nordihydroguairetic acid, 10(-5)M) and FPL55712, an antagonist of one of its terminal products: the slow reacting substance of anaphilaxis (SRS-A), abolished the reaction. Therefore, a fundamental role for SRS-A in the production of the stimulatory effect is postulated. Lymphocytes of the T cell lineage (E rosette forming cells, ERFC) are the effector cells involved in this reaction, whereas non-rosetting ChL depressed IDT. T ascertain if effector cells could be replaced by soluble factors, ChL were reacted with homogenates of rat atria and the cell free supernatants were added to beating rat atria. Positive ino- and chronotropic effects were obtained, indicating that soluble factors generated during the reaction can substitute for the intact effector cells. On the other hand if the effector cells were purified from Chagas' patients that had been treated 1 month to 6 years before the assay with trypanocidal drugs (3-methyl-4-(5'-nitrofurfurylidene-amino)-tetrahydro-4H-1, 4-tiazine-1, 1-dioxide, nifurtimox or N-benzyl-2-nitro-imidazolacetamide, benznidazole) only depressor effects were found. The depressor inotropic action of lymphocytes from treated patients (tr-ChL) was abolished with indomethacin and acetyl salicylic acid indicating that products of the cyclooxygenase pathway of AA were involved. While this work provides additional evidence for the hypothesis that lymphocytes from T. cruzi infected patients may react with heart tissue and alter its contractile behaviour, the results should not be extrapolated to the in vivo situation.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

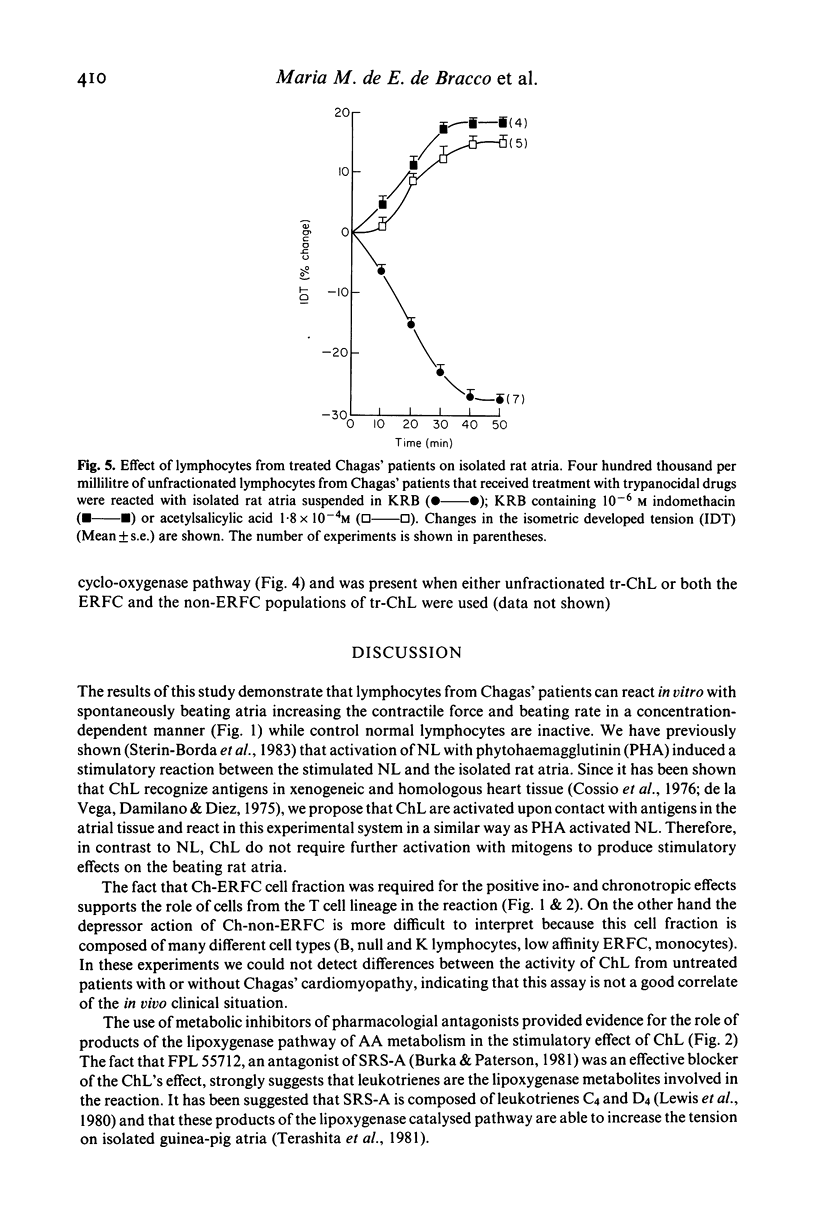


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burka J. F., Paterson N. A. The effects of SRS-A and histamine antagonists on antigen-induced contraction of guinea pig trachea. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Apr 9;70(4):489–499. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90360-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossio P. M., Damilano G., De la Vega M. G., Laguens M. T., Cabeza Meckert P., Diez C., Arana R. M. In vitro interaction between lymphocytes of Chagasic individuals and heart tissue. Medicina (B Aires) 1976;36(4):287–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossio P. M., Diez C., Laguens R. P., Arana R. M. Inmunopatología de la enfermedad de Chagas. Hechos y perspectivas. Medicina (B Aires) 1980;40 (Suppl 1):222–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bracco M. M., Isturiz M. A., Manni J. A. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Characterization of the effector cells. Immunology. 1976 Mar;30(3):325–333. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lelchuk R., Cardoni R. L., Fuks A. S. Cell-mediated immunity in Chagas' disease: Alterations induced by treatment with a trypanocidal drug (nifurtimox). Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Dec;30(3):434–438. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lelchuk R., Cardoni R. L., Levis S. Nifurtimox-induced alterations in the cell-mediated immune response to PPD tin guinea-pigs. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Dec;30(3):469–473. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. A., Austen K. F., Drazen J. M., Clark D. A., Marfat A., Corey E. J. Slow reacting substances of anaphylaxis: identification of leukotrienes C-1 and D from human and rat sources. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3710–3714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterin-Borda L., Borda E., Fink S., de Bracco M. M. Effect of phytohemagglutinin-stimulated human lymphocytes on isolated rat atria. Participation of lipoxygenase products of arachidonic acid metabolism. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1983 Sep;324(1):58–63. doi: 10.1007/BF00647839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterin-Borda L., Canga L., Pissani A., Gimeno A. L. Inotropic effect of PGE1 and PGE2 on isolated rat atria. Influence of adrenergic mechanisms. Prostaglandins. 1980 Nov;20(5):825–836. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(80)90136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterin-Borda L., Cossio P. M., Gimeno M. F., Gimeno A. L., Diez C., Laguens R. P., Meckert P. C., Arana R. M. Effect of chagasic sera on the rat isolated atrial preparation: immunological, morphological and function aspects. Cardiovasc Res. 1976 Nov;10(6):613–622. doi: 10.1093/cvr/10.6.613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterin-Borda L., Fink S., Diez C., Cossio P., DeBracco M. D. beta-Adrenergic effect of antibodies from chagasic patients and normal human lymphocytes on isolated rat atria. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Dec;50(3):534–540. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Vega M. T., Damilano G., Diez C. Leukocyte migration inhibition test with heart antigens in American trypanosomiasis. J Parasitol. 1976 Feb;62(1):129–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]