Abstract
Porcine hyaline articular cartilage (HAC) has been used to investigate the interaction of bovine serum albumin (BSA) and anti-BSA with articular collagenous tissues in vitro. There was a marked retention of 125I-labelled BSA by plugs of HAC (a) exposed to rabbit anti-BSA for 1-2 h at 37 degrees C prior to a similar incubation with the antigen, or (b) exposed to the antigen and then to antibody. The specifically retained radiolabelled BSA was localized in or at the articular surface of the plugs. In the absence of specific antibody a relatively small amount of the antigen was retained. Exposure of HAC to multiple cycles of antibody and antigen treatment resulted in an increased retention of the 125I-BSA. There was a concomitant increase in the retention of the anti-BSA and the capacity of the treated plugs to fix complement. The forces that maintained the labelled antigen in the tissue were not readily reversed by excess unlabelled BSA. Pre-formed, soluble BSA/anti-BSA complexes did not appear to penetrate the tissue unless the HAC was first exposed to anti-BSA. The results suggest that the antibody-mediated, surface oriented retention of 125I-BSA results from the formation of immune complexes in the tissue.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cooke T. D., Hurd E. R., Ziff M., Jasin H. E. The pathogenesis of chronic inflammation in experimental antigen-induced arthritis. II. Preferential localization of antigen-antibody complexes to collagenous tissues. J Exp Med. 1972 Feb 1;135(2):323–338. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.2.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke T. D., Jasin H. E. The pathogenesis of chronic inflammation in experimental antigen-induced arthritis. I. The role of antigen on the local immune response. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 Jul-Aug;15(4):327–337. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke T. D., Maeda M. Polymorphonuclear cell interactions with immune complexes in cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Dec;22(12):1416–1416. doi: 10.1002/art.1780221221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke T. D., Richer S., Hurd E., Jasin H. E. Localization of antigen-antibody complexes in intraarticular collagenous tissues. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 13;256:10–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb36032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollister J. R., Mannik M. Antigen retention in joint tissues in antigen-induced synovitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Apr;16(4):615–627. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasin H. E. Mechanism of trapping of immune complexes in joint collagenous tissues. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Dec;22(3):473–485. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G., Garvey J. S. Improved methods for separation and purification by affinity chromatography. J Immunol Methods. 1977;15(1):29–37. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno O., Tateishi H., Cooke T. D. Pathogenesis of chronic inflammation in experimental ferritin-induced arthritis. IV. Immuno-electron microscopic techniques in the study of articular collagenous tissues. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Jan-Feb;21(1):81–91. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
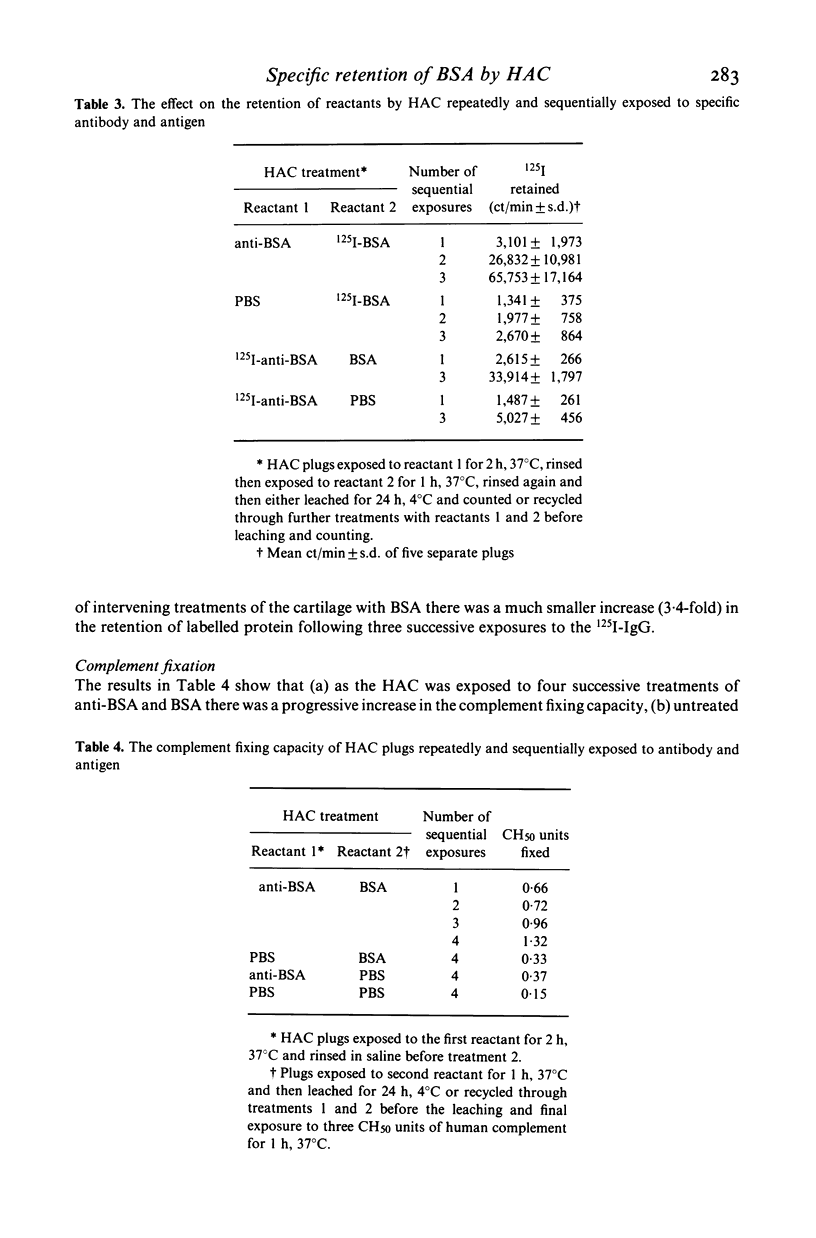
- Randall N., Cooke T. D., Aston W. P. Complement and antigen retention by articular collagenous tissues in antigen-induced arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1982 Jan-Feb;9(1):159–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teuscher C., Donaldson D. M. The deposition and formation of immune complexes in collagenous tissues. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1979 May;13(1):56–66. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(79)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


