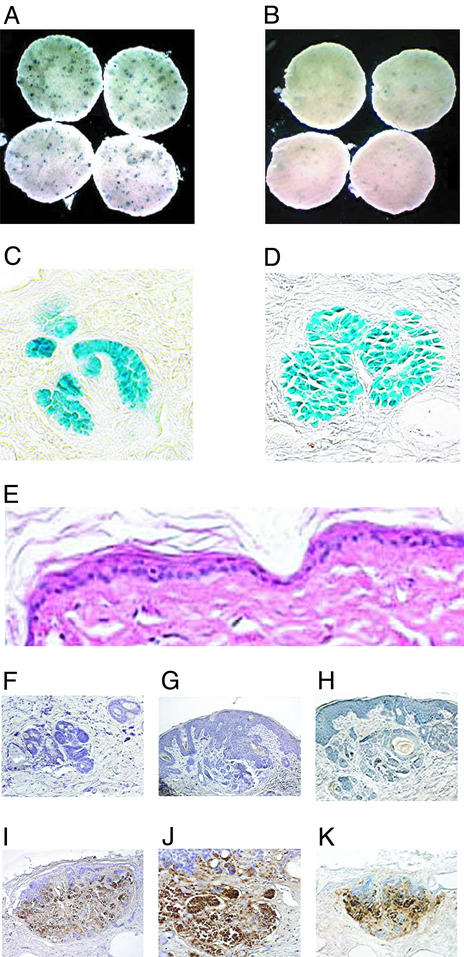
Figure 4.
CUR61414 induces regression of basaloid lesions in skin punches from UV-irradiated Ptch+/−-heterozygous mice. (A and B) Whole-mount X-gal staining of punches from UV-treated skin. After 6 days in culture, punches were treated for an additional 4 days with vehicle (0.5% DMSO) (A) or CUR61414 (5 μM) (B). This resulted in a significant reduction of the number of microscopic lesions (blue spots; see also Table 2). (C and D) Histological analysis of sections from the X-gal-stained skin punches, after UV-treatment: eosin counterstaining of sections from skin punches before (C) and after (D) culture in vitro. (E) H&E staining of a section from a CUR61414-treated skin punch; no overtoxicity is observed. (F–K) TUNEL staining of sections from vehicle-treated (F–H) or CUR61414-treated (I–K) skin punches, containing UV-induced basaloid lesion. A significant increase in apoptosis is observed after CUR61414 treatment.