Abstract
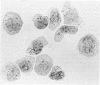
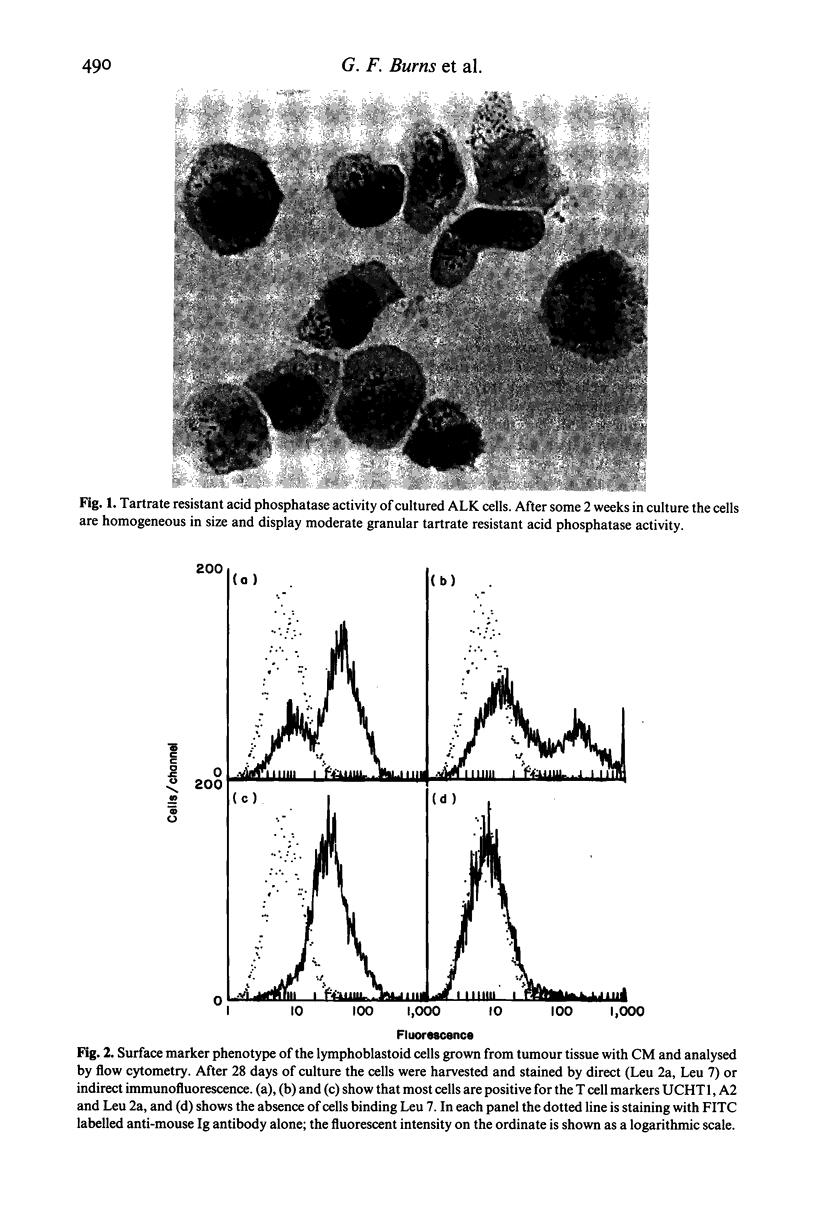
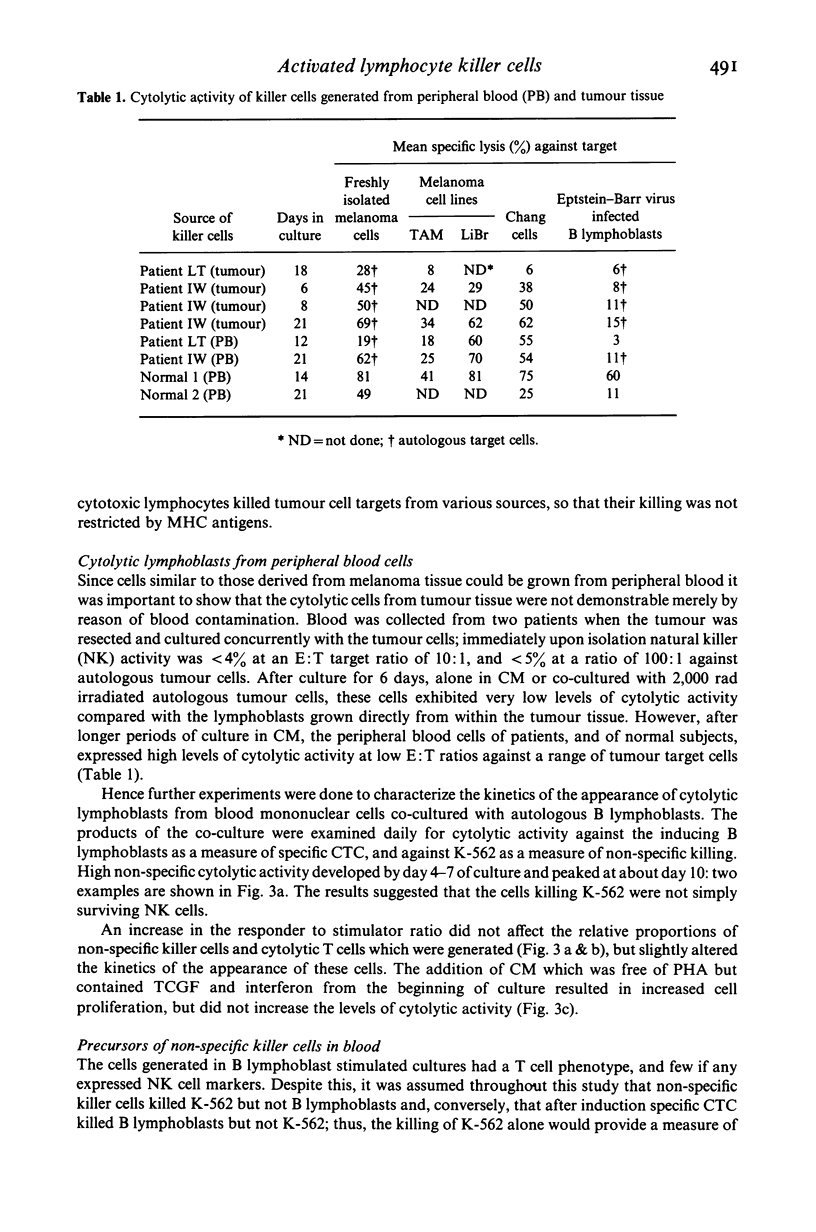
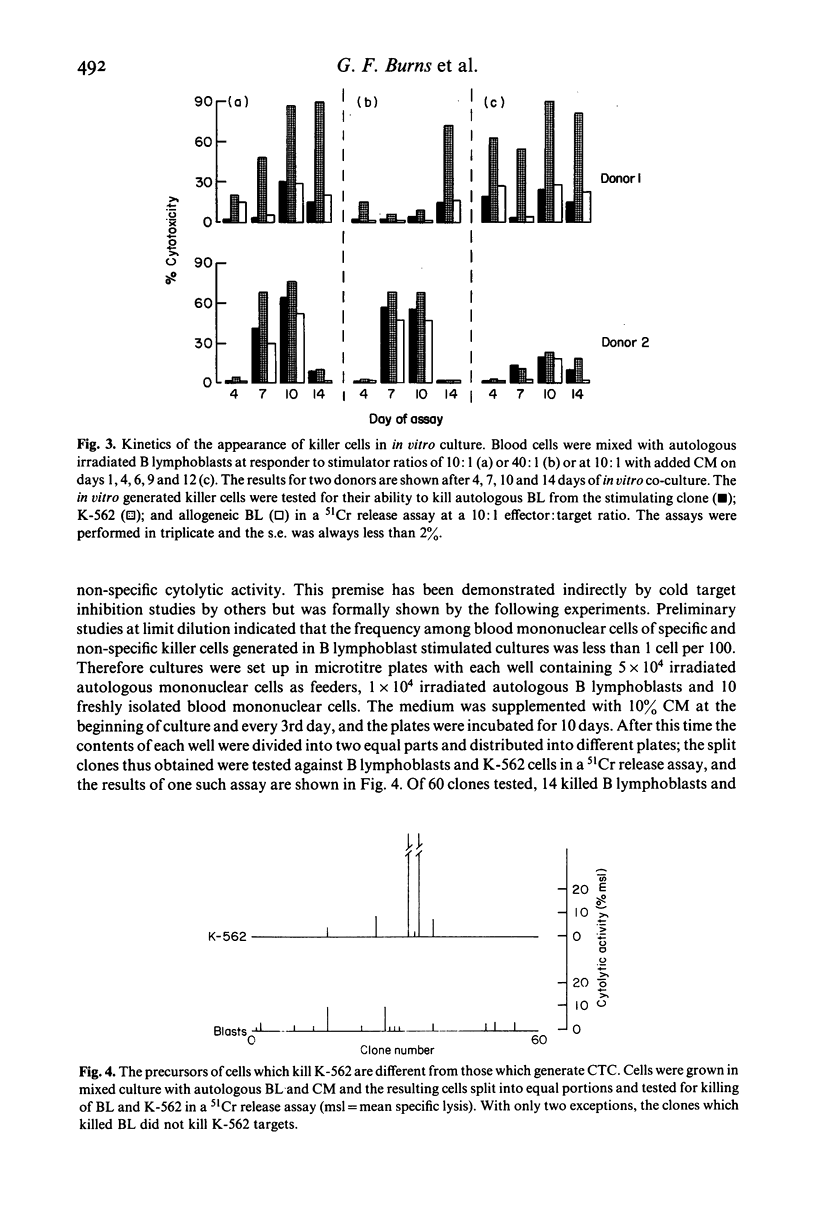
Lymphoid cells infiltrating metastatic melanomas were grown directly from cell suspensions of tumour tissue by the addition of T cell growth factor. Lymphoid cells grew out at the expense of tumour cells in six of seven freshly excised tumours, and cells from two cultures were expanded for in vitro testing of cytolytic function against different target cells. Early in culture the tumour derived lymphocytes killed fresh autologous melanoma cells and, particularly later in culture, were highly and non-specifically cytolytic for cultured melanoma and non-melanoma cells. Cultured peripheral blood lymphocytes from patients with melanoma, and from normal subjects, were cytolytic to the same degree as tumour derived lymphocytes, and also resembled cells grown from tumour tissue in possessing acid phosphatase activity which was resistant to tartrate. Cultured lymphoblasts from both tumour and peripheral blood had a T cell phenotype when analysed with monoclonal antibodies. An in vitro co-culture system was employed to study the kinetics and the precursors of these non-specific killer cells among blood mononuclear cells. Blood mononuclear cells cultured with irradiated B lymphoblasts led to the generation of non-specific cytolytic cells, referred to as activated lymphocyte killer (ALK) cells, after 7-10 days of culture and the progenitors of these ALK cells were demonstrated to be distinct from those of specific cytolytic T cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo T., Cooper M. D., Balch C. M. Characterization of HNK-1+ (Leu-7) human lymphocytes. I. Two distinct phenotypes of human NK cells with different cytotoxic capability. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1752–1757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez J. M., de Landazuri M. O., Bonnard G. D., Herberman R. B. Cytotoxic activities of normal cultured human T cells. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1270–1275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asano S., Goodyear M., Burns G. F., Bartlett P. F., MacKay I. R. Colony formation by T-lymphocytes infiltrating human tumours. Immunol Lett. 1981 Apr;3(1):17–19. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(81)90089-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asano S., Riglar C. Colony growth in agar by human melanoma cells. Cancer Res. 1981 Mar;41(3):1199–1204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks C. G. Reversible induction of natural killer cell activity in cloned murine cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Nature. 1983 Sep 8;305(5930):155–158. doi: 10.1038/305155a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns G. F., Battye F. L., Goldstein G. Surface antigen changes occurring in short-term cultures of activated human T lymphocytes: analysis by flow cytometry. Cell Immunol. 1982 Jul 15;71(1):12–26. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90492-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns G. F., Boyd A. W., Beverley P. C. Two monoclonal anti-human T lymphocyte antibodies have similar biologic effects and recognize the same cell surface antigen. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1451–1457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm E. A., Ramsey K. M., Mazumder A., Wilson D. J., Djeu J. Y., Rosenberg S. A. Lymphokine-activated killer cell phenomenon. II. Precursor phenotype is serologically distinct from peripheral T lymphocytes, memory cytotoxic thymus-derived lymphocytes, and natural killer cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Mar 1;157(3):884–897. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.3.884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayhoe F. G., Burns G. F., Cawley J. C., Stewart J. W. Cytochemical, ultrastructural and immunological studies of circulating Reed-Sternberg cells. Br J Haematol. 1978 Apr;38(4):485–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1978.tb01073.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masucci M. G., Klein E., Argov S. Disappearance of the NK effect after explantation of lymphocytes and generation of similar nonspecific cytotoxicity correlated to the level of blastogenesis in activated cultures. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2458–2463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawelec G. P., Hadam M. R., Ziegler A., Lohmeyer J., Rehbein A., Kumbier I., Wernet P. Long-term culture, cloning, and surface markers of mixed leukocyte culture-derived human T lymphocytes with natural killer-like cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1892–1896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeley J. K., Golub S. H. Studies on cytotoxicity generated in human mixed lymphocyte cultures. I. Time course and target spectrum of several distinct concomitant cytotoxic activities. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1415–1422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortman K., Wilson A., Scollay R., Chen W. F. Development of large granular lymphocytes with anomalous, nonspecific cytotoxicity in clones derived from Ly-2+ T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2728–2732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strassmann G., Bach F. H., Zarling J. M. Depletion of human NK cells with monoclonal antibodies allows the generation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes without NK-like cells in mixed cultures. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1556–1560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tötterman T. H., Häyry P., Saksela E., Timonen T., Eklund B. Cytological and functional analysis of inflammatory infiltrates in human malignant tumors. II. Functional investigations of the infiltrating inflammatory cells. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Dec;8(12):872–875. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830081209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vose B. M., Bonnard G. D. Human tumour antigens defined by cytotoxicity and proliferative responses of cultured lymphoid cells. Nature. 1982 Mar 25;296(5855):359–361. doi: 10.1038/296359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vose B. M., Vánky F., Klein E. Human tumour--lymphocyte interaction in vitro. V. Comparison of the reactivity of tumour-infiltrating, blood and lymph-node lymphocytes with autologous tumour cells. Int J Cancer. 1977 Dec 15;20(6):895–902. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910200612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vánky F., Gorsky T., Gorsky Y., Masucci M. G., Klein E. Lysis of tumor biopsy cells by autologous T lymphocytes activated in mixed cultures and propagated with T cell growth factor. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):83–95. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]