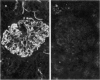
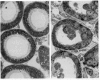
Abstract
In active Heymann nephritis, antibodies directed against the brush border membrane of proximal tubules are able, when deposited in vivo, to cause substantial damage to the tubule epithelium. Prominent features of the lesion include fragmentation and loss of microvilli and proliferation of epithelial cells. Passive transfer of anti-brush border serum to appropriate proteinuric recipients also leads to proximal tubule pathology. In experiments reported here, full expression of the damage was observed in complement deficient recipients of passively transferred anti-brush border serum. A complement-independent process initiated by cross-linking of membrane determinants, which is analogous to the stimulation of B cell proliferation following cross-linking of Ig receptors by appropriate ligands, could account for the pathogenicity of anti-brush border serum.
Full text
PDF


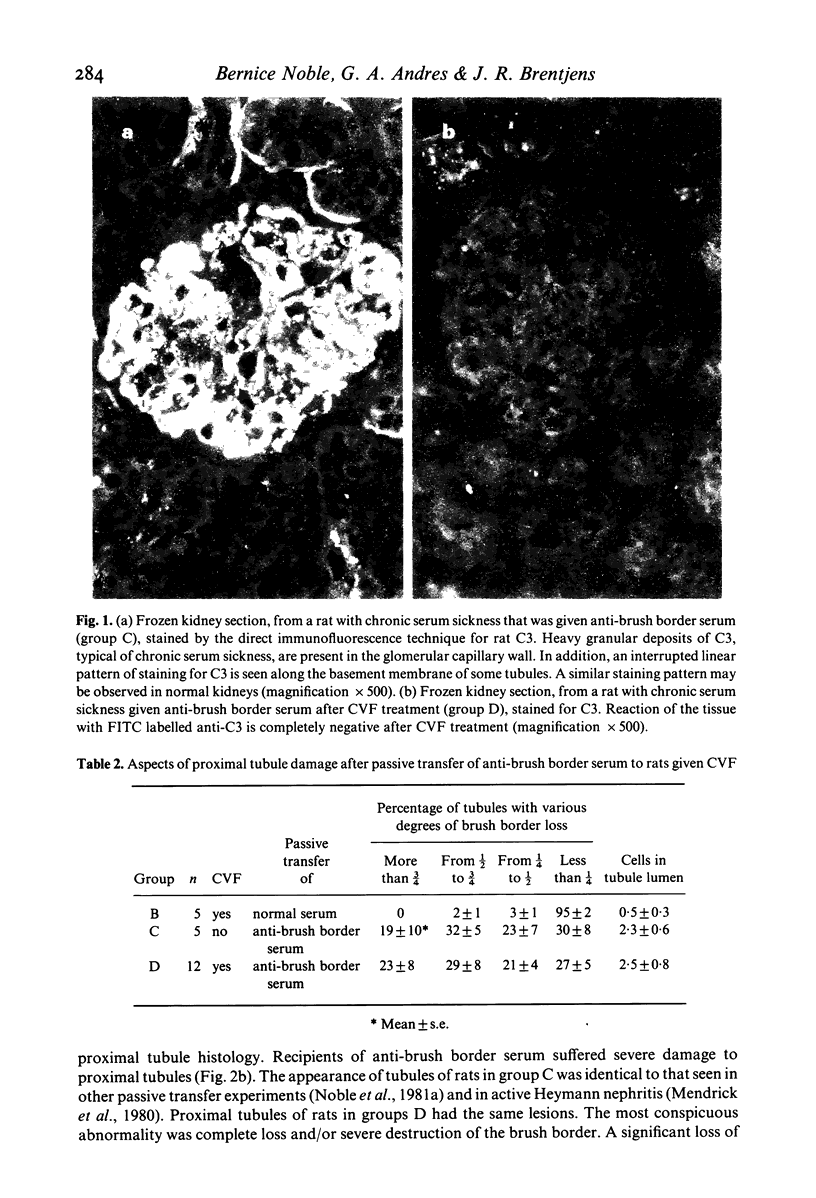
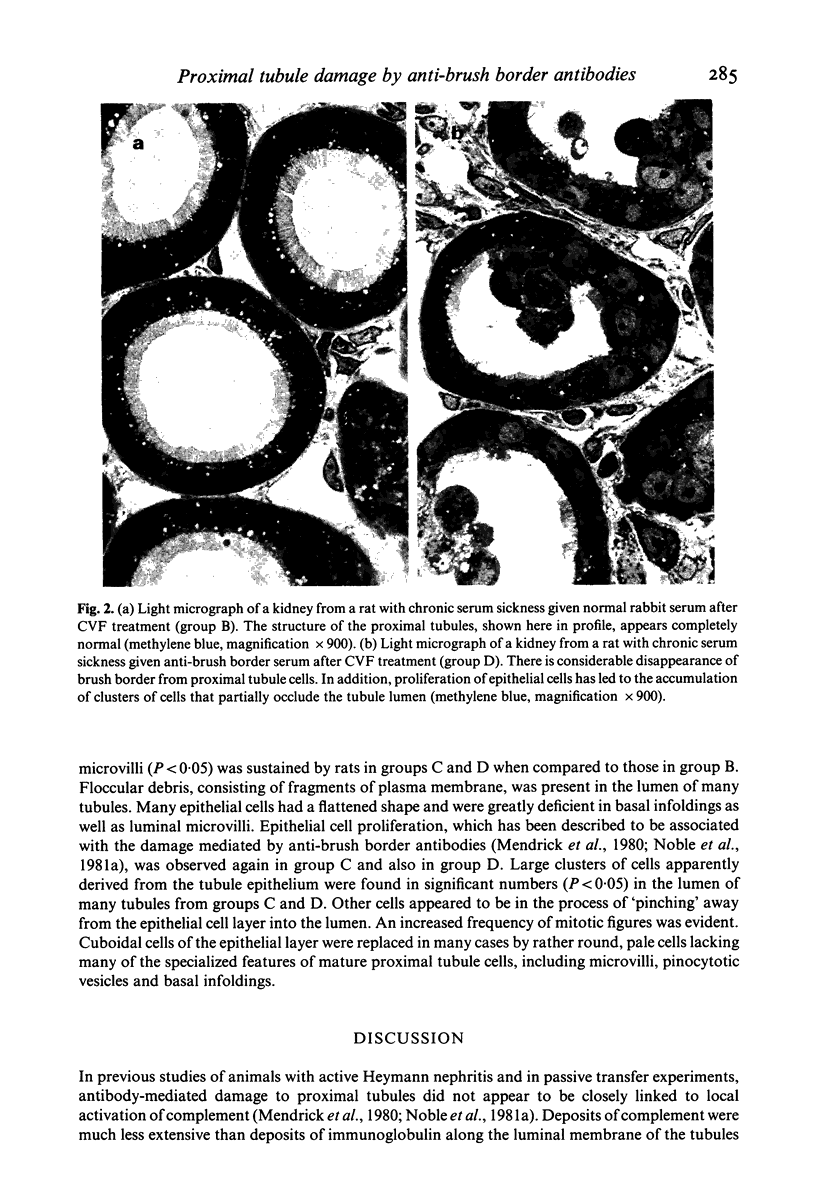



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barba L. M., Caldwell P. R., Downie G. H., Camussi G., Brentjens J. R., Andres G. Lung injury mediated by antibodies to endothelium. I. In the rabbit a repeated interaction of heterologous anti-angiotensin-converting enzyme antibodies with alveolar endothelium results in resistance to immune injury through antigenic modulation. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):2141–2158. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.2141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartolotti S. R., Peters D. K. Delayed removal of renal-bound antigen in decomplemented rabbits with acute serum sickness. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 May;32(2):199–206. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Unanue E. R. B lymphocyte biology studied with anti-Ig antibodies. Immunol Rev. 1980;52:3–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00328.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Unanue E. R. Surface immunoglobulin and the lymphocyte cytoskeleton. Fed Proc. 1983 May 15;42(8):2446–2451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron M., Bascou C., Vial M. C., Grossetete J., Hinglais N., Girard J. F., Druet P. Effects of decomplementation on mercuric chloride-induced glomerulonephritis in Brown-Norway rats. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Sep;49(3):611–617. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drachman D. B., Angus C. W., Adams R. N., Kao I. Effect of myasthenic patients' immunoglobulin on acetylcholine receptor turnover: selectivity of degradation process. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3422–3426. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgington T. S., Glassock R. J., Dixon F. J. Autologous immune complex nephritis induced with renal tubular antigen. I. Identification and isolation of the pathogenetic antigen. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):555–572. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgington T. S., Glassock R. J., Watson J. I., Dixon F. J. Characterization and isolation of specific renal tubular epithelial antigens. J Immunol. 1967 Dec;99(6):1199–1210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engers H. D., Unanue E. R. The fate of anti-Ig-surface Ig complexes on B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1973 Feb;110(2):465–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grupe W. E., Kaplan M. H. Demonstration of an antibody to proximal tubular antigen in the pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune nephrosis in rats. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Sep;74(3):400–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEYMANN W., HACKEL D. B., HARWOOD S., WILSON S. G., HUNTER J. L. Production of nephrotic syndrome in rats by Freund's adjuvants and rat kidney suspensions. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Apr;100(4):660–664. doi: 10.3181/00379727-100-24736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Farquhar M. G. Immunocytochemical localization of the Heymann nephritis antigen (GP330) in glomerular epithelial cells of normal Lewis rats. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):667–686. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendrick D. L., Noble B., Brentjens J. R., Andres G. A. Antibody-mediated injury to proximal tubules in Heymann nephritis. Kidney Int. 1980 Sep;18(3):328–343. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble B., Mendrick D. L., Brentjens J. R., Andres G. A. Antibody-mediated injury to proximal tubules in the rat kidney induced by passive transfer of homologous anti-brush border serum. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1981 May;19(2):289–301. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(81)90071-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble B., Milgrom M., Van Liew J. B., Brentjens J. R. Chronic serum sickness in the rat: influence of antigen dose, route of antigen administration and strain of rat on the development of disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Dec;46(3):499–507. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble B., Van Liew J. B., Andres G. A., Brentjens J. R. Factors influencing susceptibility of LEW rats to Heymann nephritis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1984 Feb;30(2):241–254. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(84)90059-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salant D. J., Belok S., Madaio M. P., Couser W. G. A new role for complement in experimental membranous nephropathy in rats. J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;66(6):1339–1350. doi: 10.1172/JCI109987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Liew J. B., Brentjens J. R., Noble B. Relationship of kidney function to immunopathology in chronic serum sickness of rats. Kidney Int. 1983 Aug;24(2):160–169. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner N. L. Membrane immunoglobulins and antigen receptors on B and T lymphocytes. Adv Immunol. 1974;19(0):67–216. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60252-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]