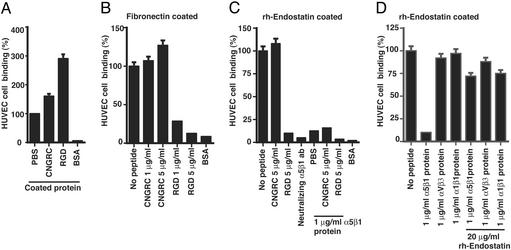
Figure 3.
Cell attachment assays. The graphs display results of three independent experiments, presented as relative percentage compared with PBS control. (A) Attachment of HUVEC was increased to plates that were coated with synthetic peptides CNGRC (25 μg/ml) or RGD-4C (25 μg/ml) compared with uncoated control plates. (B) Attachment of HUVEC on fibronectin-coated plates was significantly inhibited by preincubation of the cells with RGD-4C peptide (73% at 1 mg/ml; 89% at a concentration of 5 μg/ml), whereas preincubation of with CNGRC-peptide had no effect on adhesion of HUVEC. (C) Attachment of HUVEC on rhEndo-coated plates was significantly inhibited by RGD cyclic peptide or α5β1 blocking antibodies, whereas CNGRC peptide had no significant effect. Addition of soluble α5β1 integrin protein into the wells significantly inhibited attachment of PBS or CNGRC peptide treated HUVEC, whereas it had no additional effect when the cells were pretreated with RGD cyclic peptide. (D) Attachment of HUVEC on rhEndo-coated plates was significantly inhibited by incubation with α5β1 soluble protein, whereas αvβ3 or α1β1 integrins had no significant effect. α5β1 integrin-induced inhibition was reversed by addition of soluble rhEndo to the culture media.