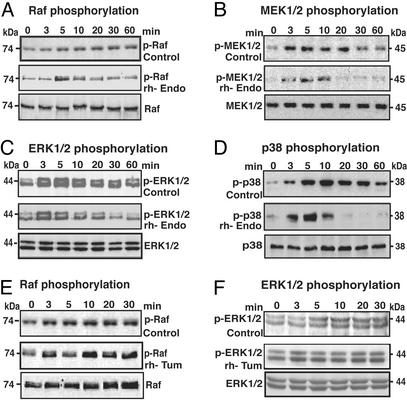
Figure 5.
Effects of rhEndo and rhTum on ERK and p38 MAP kinase signal transduction pathways. Serum-starved HUVEC were plated on fibronectin in incomplete medium containing 10 μg/ml rhEndo (A–D) or rhTum (E and F) and lysed at the indicated times (0–60 min). The levels of phosphorylated proteins after incubation with rhEndo or rhTum (Middle) were compared with untreated controls (Top) by immunoblot. (Bottom) The total signaling protein levels in rhEndo or rhTum-treated HUVEC. (A and E) Raf phosphorylation. Immunoblots for phopho-Raf indicate that sustained phosphorylation of Raf (p-Raf) (A and E, Upper) was inhibited by treatment with rhEndo (A Middle) but not with rhTum (E Middle). (B) MEK1/2 phosphorylation. The prolonged phosphorylation of MEK1/2 (B Top), downstream of Raf, was significantly inhibited by rhEndo (B Middle). (C and F) ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Immunoblots for phosphorylated ERK1/2 (p-ERK) indicate sustained phosphorylation of ERK1 (Upper) and ERK2 (Lower) after HUVEC were seeded on fibronectin (C and F, Upper). Treatment with rhEndo inhibited phosphorylation of ERK1 but had no significant effect on ERK2 phosphorylation (C Middle). Treatment with rhTum had no effect on phosphorylation of ERK1/2 (F). (D) p38 phosphorylation. Immunoblots for phosphorylated 38 MAP kinase (p-p38) indicate that prolonged phosphorylation of p38 (D Top) was decreased after treatment with rhEndo (D Middle).