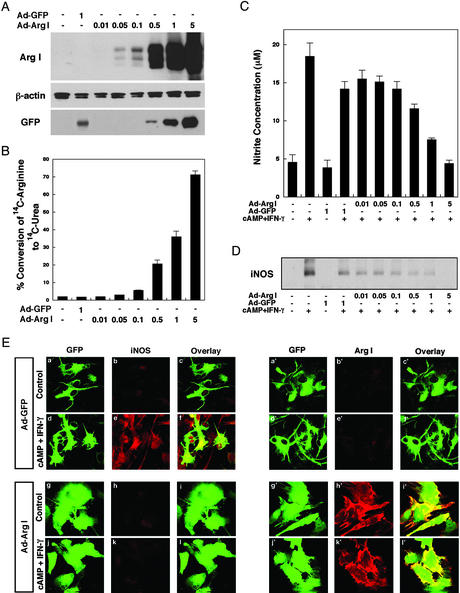
Figure 2.
(A) Increased expression of arginase I in astrocytes by using an adenoviral vector. Rat astrocytes were infected with an adenoviral vector containing arginase I (Ad-Arg I) or vector control (Ad-GFP) for 48 h. Whole-cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with antibodies specific for arginase I, β-actin, or GFP. (B) Increased arginase activity in virally transfected astrocytes. Rat astrocytes were infected with the indicated moi of Ad-Arg I or Ad-GFP for 48 h. Arginase activity reflects percent conversion of [14C]arginine added to the culture medium to 14C urea. Results are mean ± SD of triplicate experiments. (C) Overexpression of arginase I in astrocytes can decrease cytokine-induced NO levels in astrocytes. Rat astrocytes were infected with the indicated moi of Ad-Arg I or Ad-GFP for 24 h and then further treated with cAMP (1 mM) and IFN-γ (100 units/ml) to induce NO product. After 16 h, NO levels were quantified by measuring the accumulation of nitrite in the culture medium of astrocytes with the Griess reagent. (D) Overexpression of arginase I in astrocytes can decrease cytokine-induced iNOS protein levels. Rat astrocytes were infected with Ad-Arg I or Ad-GFP (vector control) for 24 h and subsequently treated with cAMP (1 mM) and IFN-γ (100 units/ml) for 16 h. Immunoblot analysis of iNOS in whole-cell lysates is shown. (E) For confocal microscopy cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and incubated with rabbit anti-iNOS (b, e, h, and k) or rabbit anti-arginase I (b′, e′, h′, and k′) antibody. The adenovirus transfer vector used in these studies has a double expression cassette, and GFP has been subcloned into Ad-GFP (a, a′, d, and d′) or Ad-Arg I (g, g′, j, and j′) to monitor vector-derived expression.