Abstract
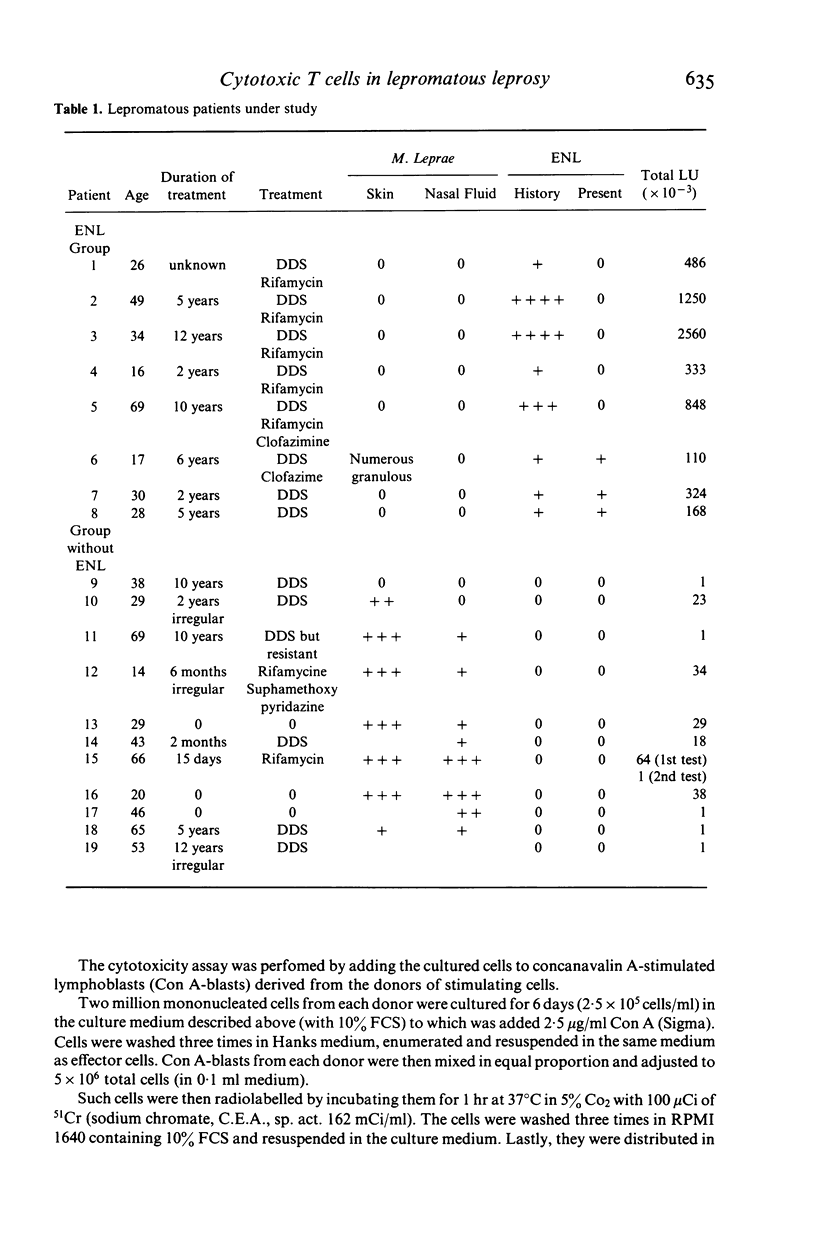
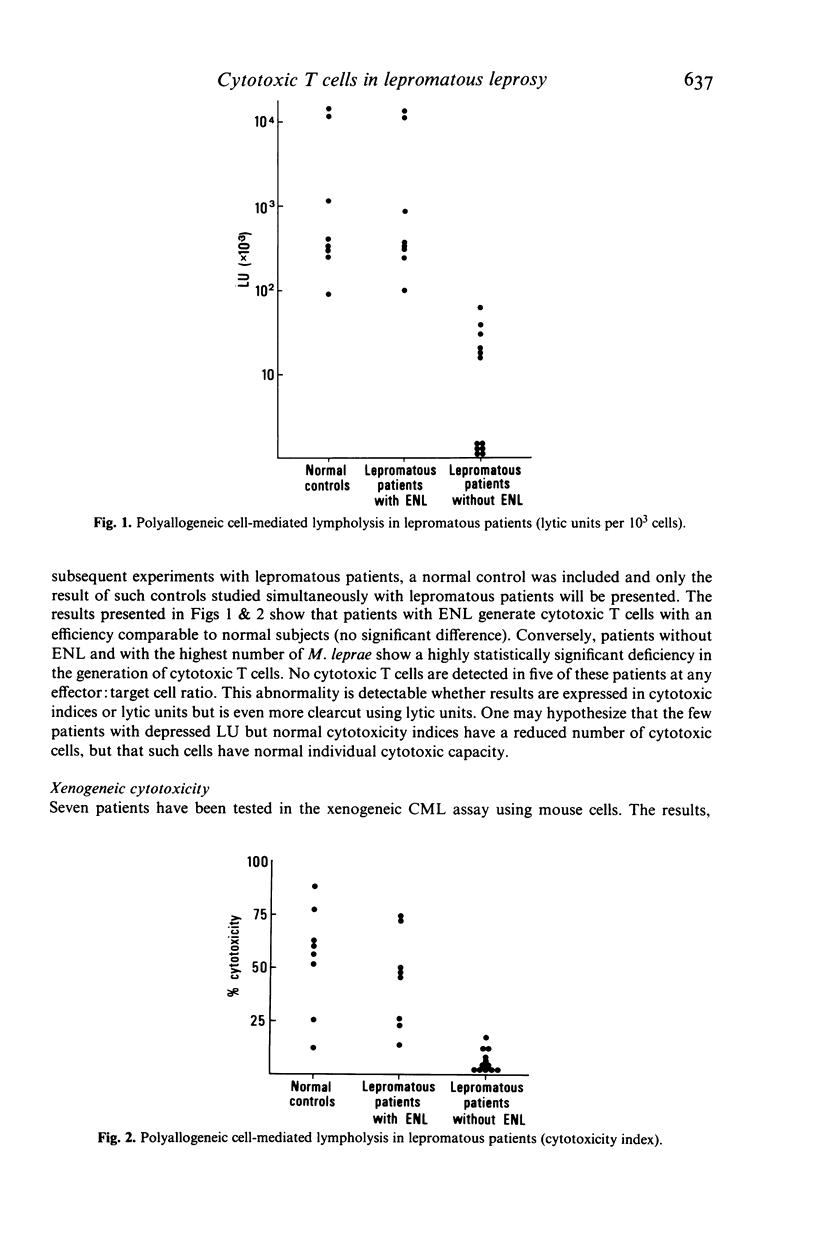
Cytotoxic T cells are consistently produced in normal individuals after in vitro stimulation by a pool of mitomycin-treated normal lymphocytes. Patients suffering from lepromatous leprosy (LL), presenting with large amounts of Mycobacterium leprae and without a history of erythema nodosum leprosum (ENL) are unable to generate such cytotoxic T cells, while lepromatous patients with ENL which, in the present study were all deprived of M. leprae, react normally.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach M. A., Chatenoud L., Wallach D., Phan Dinh Tuy F., Cottenot F. Studies on T cell subsets and functions in leprosy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Jun;44(3):491–500. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beiguelman B., Pisam R. C. Effect of DDS on phytohemagglutinin-induced lymphocyte transformation. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1974 Oct-Dec;42(4):412–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock W. E., Carlson E. M., Gershon R. K. The evolution of immunosuppressive cell populations in experimental mycobacterial infection. J Immunol. 1978 May;120(5):1709–1716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock W. E., Evans P. E., Filomeno A. R. Impairment of cell-mediated immune responses by infection with Mycobacterium lepraemurium. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):157–164. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.157-164.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock W. E. Immunology and the therapeutics of leprosy. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Sep;91(3):482–484. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-3-482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock W. E., Jr, Fasal P. Studies of immune mechanisms in leprosy. 3. The role of cellular and humoral factors in impairment of the in vitro immune response. J Immunol. 1971 Apr;106(4):888–899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock W. E., Jr Perturbation of lymphocyte circulation in experimental murine leprosy. I. Description of the defect. J Immunol. 1976 Oct;117(4):1164–1170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock W. E., Jr Perturbation of lymphocyte circulation in experimental murine leprosy. II. Nature of the defect. J Immunol. 1976 Oct;117(4):1171–1178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnaud C., Fadaï-Ghotbi M., Lesavre P., Bach J. F. Education of human lymphocytes against mouse cells: specific recognition of H-2 antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Feb;7(2):81–85. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830070206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charpentier B., Carnaud C., Bach J. F. Selective depression of the xenogeneic cell-mediated lympholysis in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1979 Aug;64(2):351–360. doi: 10.1172/JCI109469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Convit J., Pinardi M. E., Rojas F. A. Some considerations regarding the immunology of leprosy. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1971 Apr-Jun;39(2):556–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer J. M., Bullock W. E., Fields J. P. Disturbance of the blood T:B lymphocyte ratio in lepromatous leprosy. Clinical and immunologic correlations. N Engl J Med. 1973 May 17;288(20):1036–1039. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197305172882002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han S. H., Weiser R. S., Kau S. T. Prolonged survival of skin allografts in leprosy patients. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1971 Jan-Mar;39(1):1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herscowitz H. B., McKillip T. W. A simple method for liquid scintillation counting of 125-iodine and 51-chromium used in antigen binding and cytotoxicity studies. J Immunol Methods. 1974 Mar;4(2):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90068-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor F. S. Infection, anergy and cell-mediated immunity. N Engl J Med. 1975 Mar 20;292(12):629–634. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197503202921210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz S. I., DeBetz B. H., Zaias N. Production of macrophage inhibitory factor by patients with leprosy. Arch Dermatol. 1971 Apr;103(4):358–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimpel G. R., Henney C. S. BCG-induced suppressor cells. I. Demonstration of a macrophage-like suppressor cell that inhibits cytotoxic T cell generation in vitro. J Immunol. 1978 Feb;120(2):563–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. C., Kay J., Wong M. Separation of functionally distinct subpopulations of Corynebacterium parvum-activated macrophages with predominantly stimulatory or suppressive effect on the cell-mediated cytotoxic T cell response. Cell Immunol. 1979 Jan;42(1):28–41. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90218-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim S. D., Jacobson R. R., Park B. H., Good R. A. Leprosy XII. Quantitative analysis of thymus-derived lymphocyte response to phytohemagglutinin in leprosy. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1975 Apr-Jun;43(2):95–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murahata R. I., Zighelboim J. Inhibition of memory cell-mediated cytotoxic response by systemic administration of Corynebacterium parvum. Cell Immunol. 1979 Feb;42(2):289–297. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90194-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. S., Nelson M., Thurston J. M., Waters M. F., Pearson J. M. Phytohaemagglutinin-induced lymphocyte transformation in leprosy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Jul;9(1):33–43. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson T. W., Roelants G. E., Lundin L. B., Mayor-Withey K. S. Immune depression in trypanosome-infected mice. I. Depressed T lymphocyte responses. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Oct;8(10):723–727. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830081010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rea T. H., Levan N. E. Variations in dinitrochlorobenzene responsivity in untreated leprosy: evidence of a beneficial role for anergy. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1980 Jun;48(2):120–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rea T. H., Quismorio F. P., Harding B., Nies K. M., Di Saia P. J., Levan N. E., Friou G. J. Immunologic responses in patients with lepromatous leprosy. Arch Dermatol. 1976 Jun;112(6):791–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley D. S., Jopling W. H. Classification of leprosy according to immunity. A five-group system. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1966 Jul-Sep;34(3):255–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley D. S., Waters M. F. Significance of variations within the lepromatous group. Lepr Rev. 1969 Jul;40(3):143–152. doi: 10.5935/0305-7518.19690026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelants G. E., Pearson T. W., Tyrer H. W., Mayor-Withey K. S., Lundin L. B. Immune depression in trypanosome-infected mice. II. Characterization of the spleen cell types involved. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Mar;9(3):195–199. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saha K., Whittingham S., Ray D., Mittal M. M., Beohar P. C. Impairment of Jones-Mote hypersensitivity and specific antibody response against depolymerized flagellin in lepromatous leprosy. Scand J Immunol. 1979;10(1):31–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1979.tb01331.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salazar Mallén M., Chévez Zamora A., Montes Montes J., Escobar A., Mitrani Levy D., Amezcua M. E. Estudios sobre la inmunidad de la lepra. Alergia. 1971 May;18(4):185–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheagren J. N., Block J. B., Trautman J. R., Wolff S. M. Immunologic reactivity in patients with leprosy. Ann Intern Med. 1969 Feb;70(2):295–302. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-70-2-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard C. C. Immunologic suppression in leprosy and its relation to lepromatous disease. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1968 Jan-Mar;36(1):87–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talwar G. P., Krishnan A. D., Mehra V. L., Blum E. A., Pearson J. M. Evaluation of cell mediated immune responses in untreated cases of leprosy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Oct;12(2):195–203. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J. L., Bryceson A. D. Immunological phenomena in leprosy and related diseases. Adv Immunol. 1971;13:209–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60185-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich M., de Salas B., Convit J. Lymphocyte transformation with phytomitogens in leprosy. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1972 Jan-Mar;40(1):4–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldorf D. S., Sheagren J. N., Trautman J. R., Block J. B. Impaired delayed hypersensitivity in patients with lepromatous leprosy. Lancet. 1966 Oct 8;2(7467):773–776. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)90366-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


