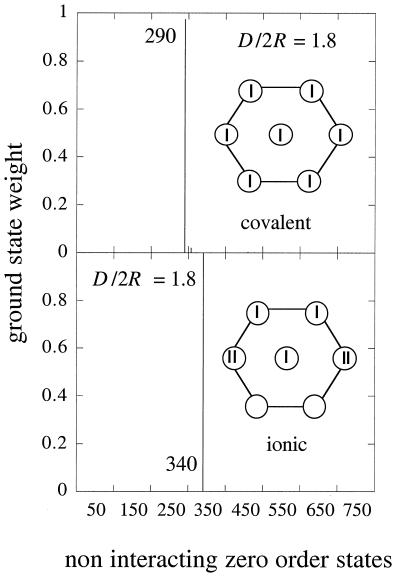
Figure 4.
The weights of the ground electronic state on the states of the noninteracting dots. These zero-order states have each electron assigned to a particular site as, for example, in Eq. 4 above. Computed at large interdot separation (D/2r = 1.8) for a moderate, Δα < I (Upper), and a higher, Δα > I (Lower), disorder . I = 0.3 eV for both Upper and Lower. In Upper, there is 5% fluctuation in sizes and 5% in packing, whereas in Lower, we introduce 15% fluctuation in size and 30% in packing. In Upper, the ground state at large separation is a covalent state with one electron per site, whereas in Lower, where the fluctuations in sizes and in packing overcome the effect of the charging energy, the ground electronic state will be an ionic state. In this example, it is an ionic state with two doubly occupied sites (see Inset).