Abstract
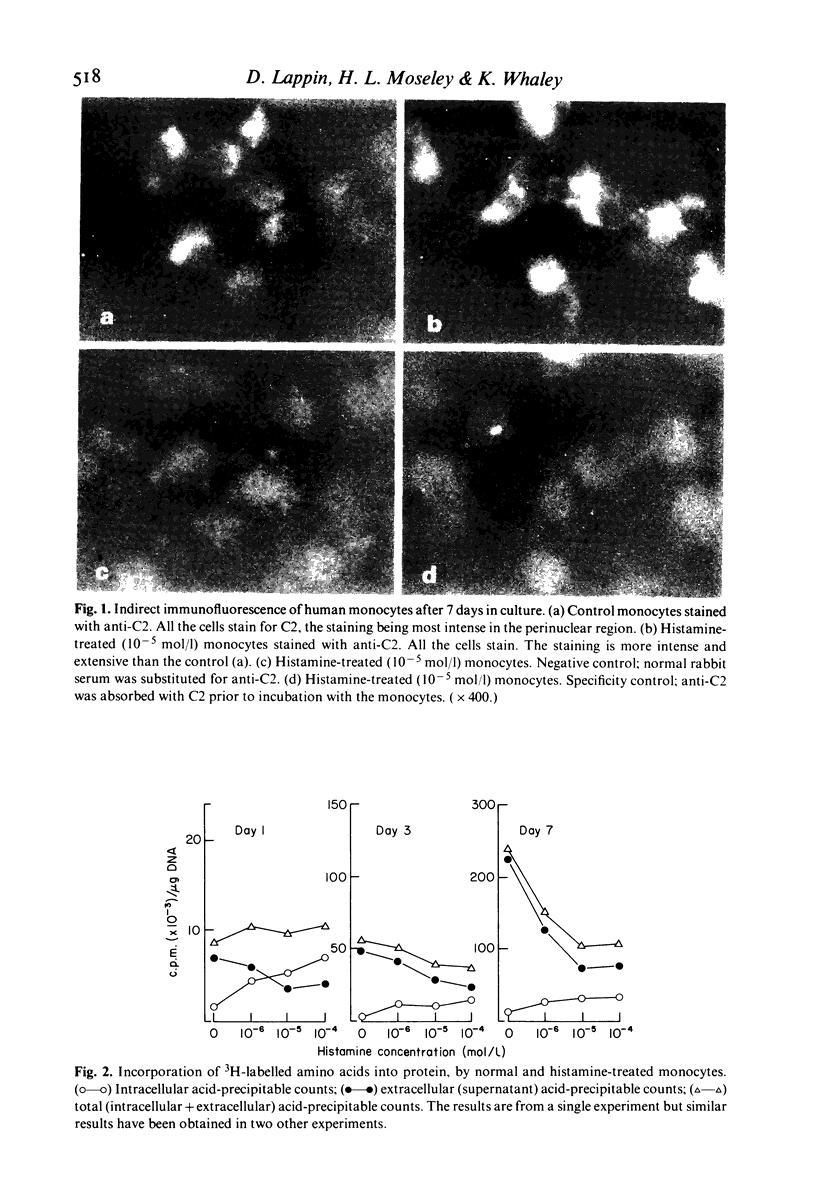
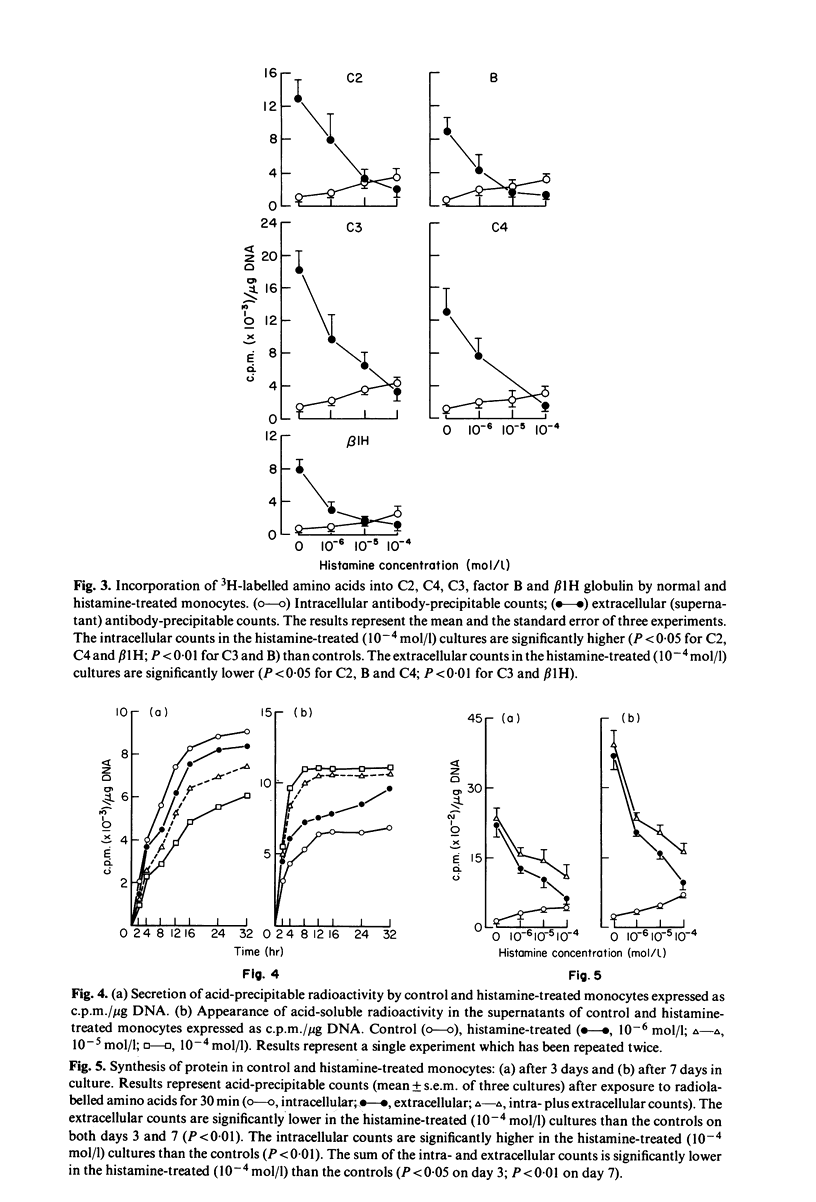
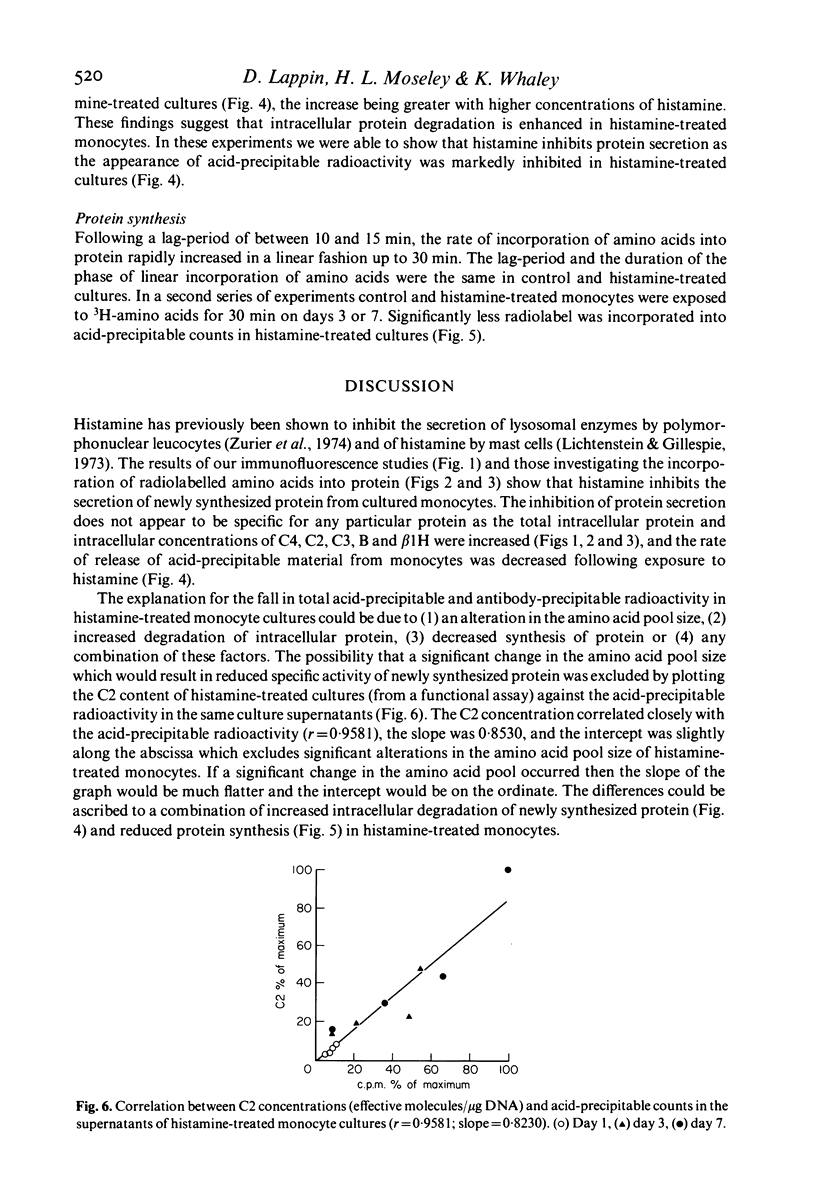
Using immunofluorescence and pulse-label studies with 3H-labelled amino acids, histamine was shown to inhibit the secretion of newly synthesized C2, C4, C3, factor B and beta 1H globulin by monocytes in culture. The findings suggested that protein synthesis was decreased, and that the degradation of newly synthesized intracellular protein was increased in histamine-treated monocytes. The observations that all monocytes in cultures containing histamine stained for C2, C4, and C3, factor B and beta 1H, when secretion was impaired, shows that all monocytes synthesize these proteins. These results demonstrate a negative feedback loop on C3 and C5 cleavage. The anaphylotoxins, C3a and C5a, formed as a result of C3 and C5 cleavage, release histamine from mast cells and basophils. Histamine, by inhibiting the production of C4, C2, and C3 and factor B by mononuclear phagocytes, inhibits further C3 and C5 cleavage by restricting the formation of C42, C423b and C3bBbP.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dean R. T. Macrophage protein turnover. Evidence for lysosomal participation in basal proteolysis. Biochem J. 1979 May 15;180(2):339–345. doi: 10.1042/bj1800339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einstein L. P., Schneeberger E. E., Colten H. R. Synthesis of the second component of complement by long-term primary cultures of human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Jan 1;143(1):114–126. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. E., Colten H. R. Cell-free synthesis of the fourth component of guinea pig complement (C4): identification of a precursor of serum C4 (pro-C4). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1707–1710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunsicker L. G., Ruddy S., Austen K. F. Alternate complement pathway: factors involved in cobra venom factor (CoVF) activation of the third component of complement (C3). J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):128–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lappin D., Whaley K. Effects of histamine on monocyte complement production. I. Inhibition of C2 production mediated by its action on H2 receptors. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Sep;41(3):497–504. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein L. M., Gillespie E. Inhibition of histamine release by histamine controlled by H2 receptor. Nature. 1973 Aug 3;244(5414):287–288. doi: 10.1038/244287a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddy S., Austen K. F. A stoichiometric assay for the fourth component of complement in whole human serum using EAC'la-gp and functionally pure human second component. J Immunol. 1967 Dec;99(6):1162–1172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tack B. D., Prahl J. W. Third component of human complement: purification from plasma and physicochemical characterization. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 5;15(20):4513–4521. doi: 10.1021/bi00665a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whaley K. Biosynthesis of the complement components and the regulatory proteins of the alternative complement pathway by human peripheral blood monocytes. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):501–516. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whaley K., Ruddy S. Modulation of the alternative complement pathways by beta 1 H globulin. J Exp Med. 1976 Nov 2;144(5):1147–1163. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.5.1147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurier R. B., Weissmann G., Hoffstein S., Kammerman S., Tai H. H. Mechanisms of lysosomal enzyme release from human leukocytes. II. Effects of cAMP and cGMP, autonomic agonists, and agents which affect microtubule function. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jan;53(1):297–309. doi: 10.1172/JCI107550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


