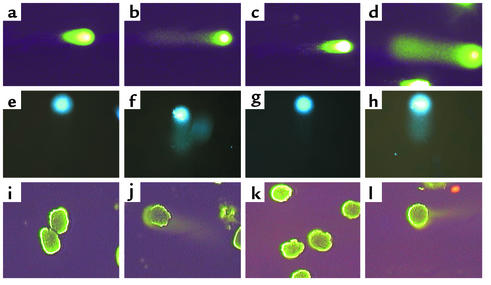
Figure 2.
Comet assay. DNA damage was measured in rat (a–d) and mouse (e–h) podocytes in vitro using the comet assay. (a and e) DNA damage was not detected in normal podocytes not exposed to Ab or a complement source. (b and f) In podocytes exposed to Ab and complement, the characteristic “tail” of damaged DNA is seen migrating away from the nucleus. (c and g) In contrast, DNA damage was not detected in control cells exposed to Ab without a complement source. (d and h) In UV-irradiated cells, used as a positive control, DNA damage was detected. The comet assay was also performed on glomeruli isolated from control and PHN rats. (i–l) DNA damage was not detected in control rats injected with normal sheep serum (i) nor in PVG C– rats injected with anti-Fx1A Ab (k). DNA damage was detected in Sprague-Dawley PHN (j) and in PVG C+ (l) rats injected with anti-Fx1A Ab.