Abstract
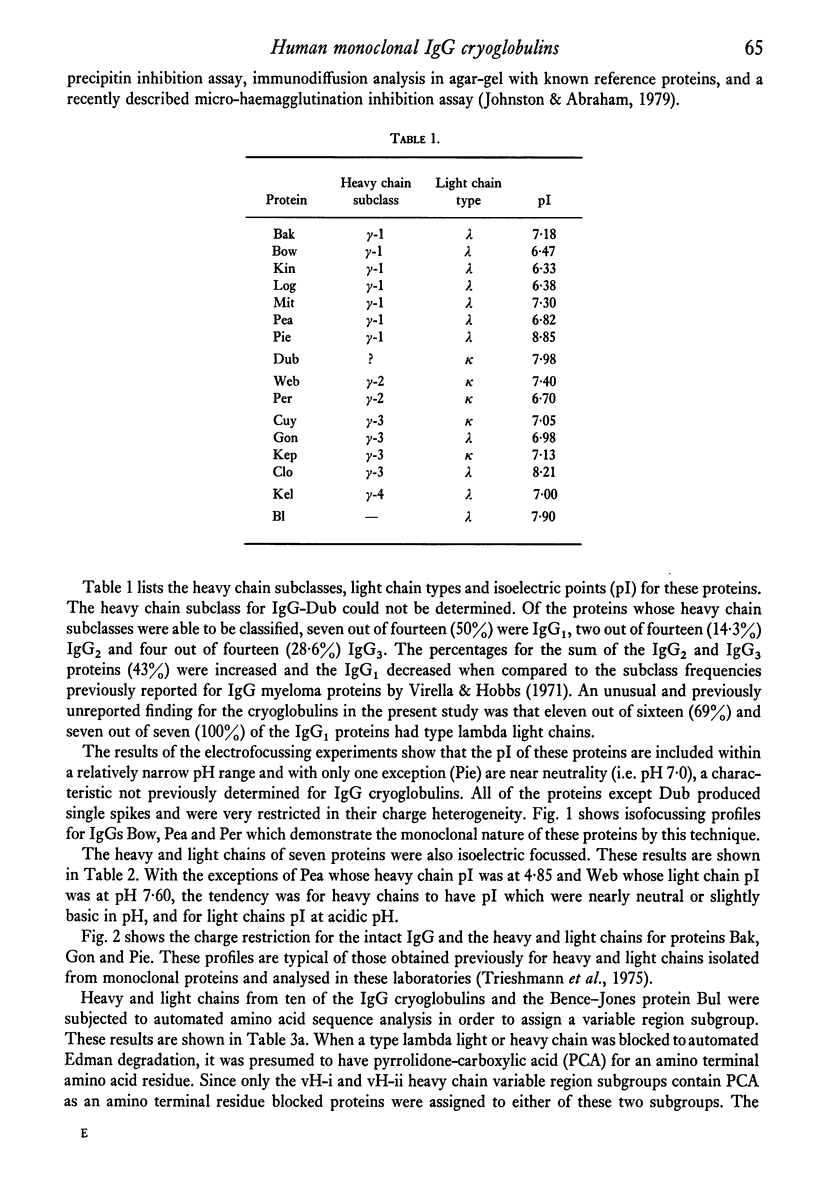
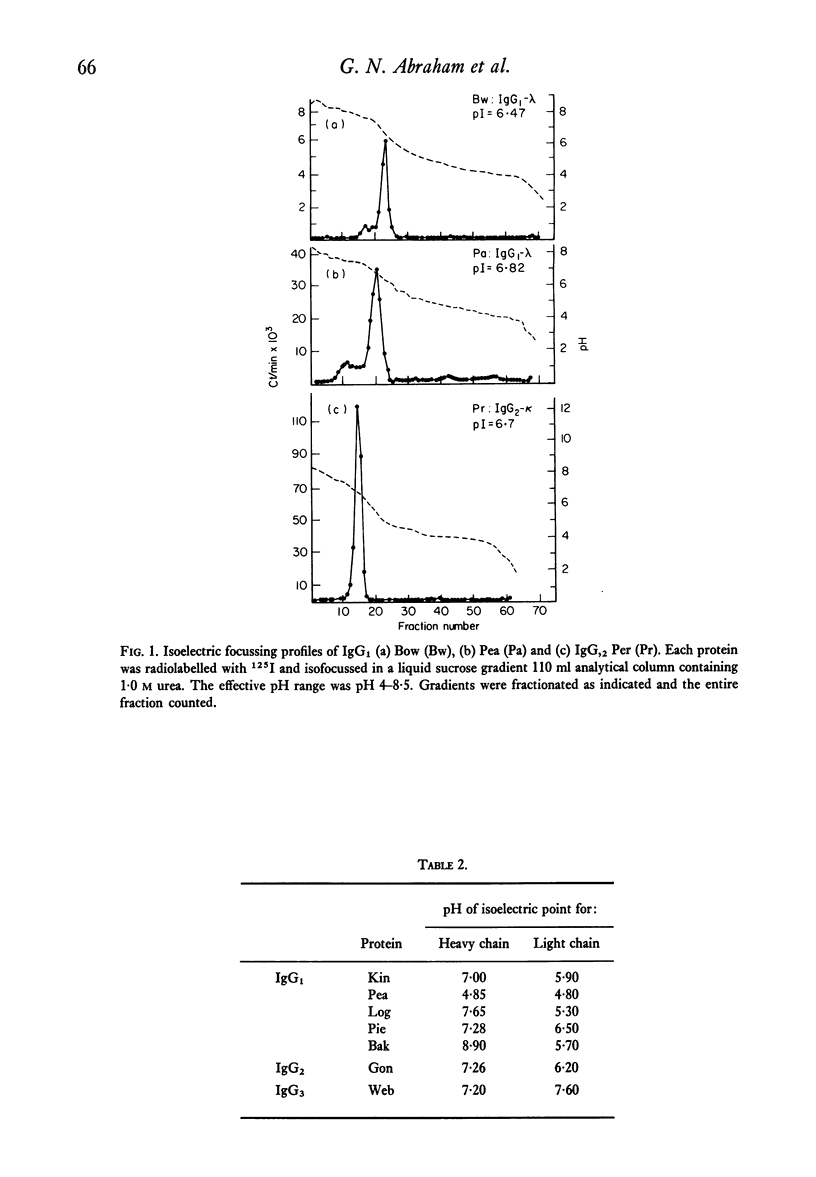
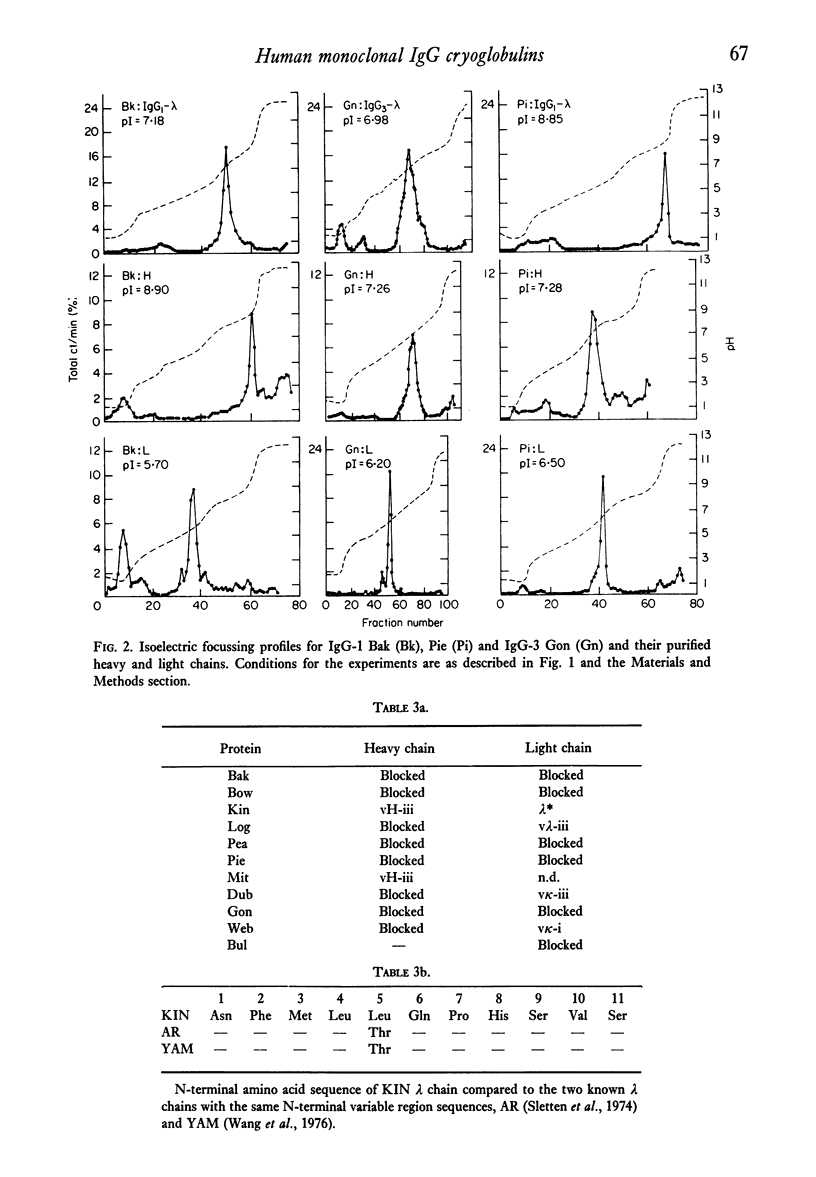
Structural and immunological properties were determined for sixteen IgG and one Bence-Jones, human monoclonal cryoglobulins. The heavy chain subclass percentages were 47% IgG1, 14% IgG2 and 29% IgG3, and were different from previously reported distributions of myeloma proteins. In addition, 69% (eleven out of fifteen) of the cryoglobulins and 100% (seven out of seven) of the IgG1 cryos contained type lambda light chains. Electrofocussing of the cryoproteins by analytical liquid gradient column showed the isoelectric points to be included in the range of pH 6.3--8.9. The pI of six light chains and five out of six heavy chains were at acidic and slightly basic pH, respectively. The pI of the intact cryoglobulins were thus close to those of their constituent heavy chains. Six out of seven of the heavy chains were subjected to automated Edman degradation and were classified as containing vH-i or vH-ii variable region subgroups on the basis of their blocked amino termini. One type lambda light chain was unusual in that it contained an amino terminal sequence initially described in an amyloid fibril protein and is the first instance in which light chains with this sequence have been isolated from IgG. The data support the notion that the cryoglobulins are IgGs with unique structural and immunological properties which separate them from non-cryoprecipitable IgGs.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham G. N., Brown P., Johnston S. L., Nellis L., Marks S., Welch E. H. Human triclonal anti-IgG gammopathy. III. Determination of the clonal persistence of the IgM autoantibody for a four and one-half year period. Immunology. 1978 Sep;35(3):447–453. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham G. N., Clark R. A., Vaughan J. H. Characterization of an IgA rheumatoid factor: finding properties and reactivity with the subclasses of human G globulin. Immunochemistry. 1972 Mar;9(3):301–315. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90094-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham G. N. Human triclonal anti-IgG gammopathy. I. Iso-electric focusing characteristics of the IgG, IgA and IgM anti-IgG and their heavy and light chains. Immunology. 1978 Sep;35(3):429–436. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bale W. F., Helmkamp R. W., Davis T. P., Izzo M. J., Goodland R. L., Contreras M. A., Spar I. L. High specific activity labeling of protein with I-131 by the iodine monochloride method. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Jun;122(2):407–414. doi: 10.3181/00379727-122-31148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brouet J. C., Clauvel J. P., Danon F., Klein M., Seligmann M. Biologic and clinical significance of cryoglobulins. A report of 86 cases. Am J Med. 1974 Nov;57(5):775–788. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90852-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forre O., Natvig J. B., Kunkel H. G. Serological detection of variable region (Vh) subgroups of Ig heavy chains. J Exp Med. 1976 Oct 1;144(4):897–905. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.4.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston S. L., Abraham G. N., Welch E. H. Structural studies of monoclonal human cryoprecipitable immunoglobulins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Sep 16;66(2):842–847. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90586-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer M., Franklin E. C. Cryoglobulinemia--a study of twenty-nine patients. I. IgG and IgM cryoglobulins and factors affecting cryoprecipitability. Am J Med. 1966 Jun;40(6):828–836. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(66)90199-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sletten K., Husby G., Natvig J. B. N-terminal amino acid sequence of amyloid fibril protein AR, prototype of a new lambda-variable subgroup, V lambda V. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(6):833–836. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01319.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trieshmann H. W., Jr, Abraham G. N., Santucci E. A. The characterization of human anti-IgG autoantibodies by liquid isoelectric focussing. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 1):176–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virella G., Hobbs J. R. Heavy chain typing in IgG monoclonal gammopathies with special reference to cases of serum hyperviscosity and cryoglobulinaemia. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Jun;8(6):973–980. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. C., Fudenberg H. H., Wang I. Y., Watanabe A. Chemical and genetic characterization of a monoclonal IgA(lambda) protein with both cryo- and pyro-precipitability. Scand J Immunol. 1976;5(4):311–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb00284.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. C., Wells J. V., Fudenberg H. H. Chemical analyses of cryoglobulins. Immunochemistry. 1974 Jul;11(7):341–345. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(74)90186-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


