Abstract
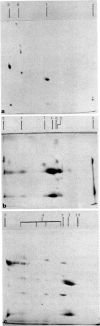
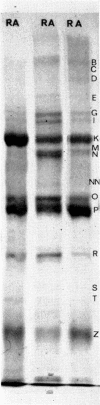
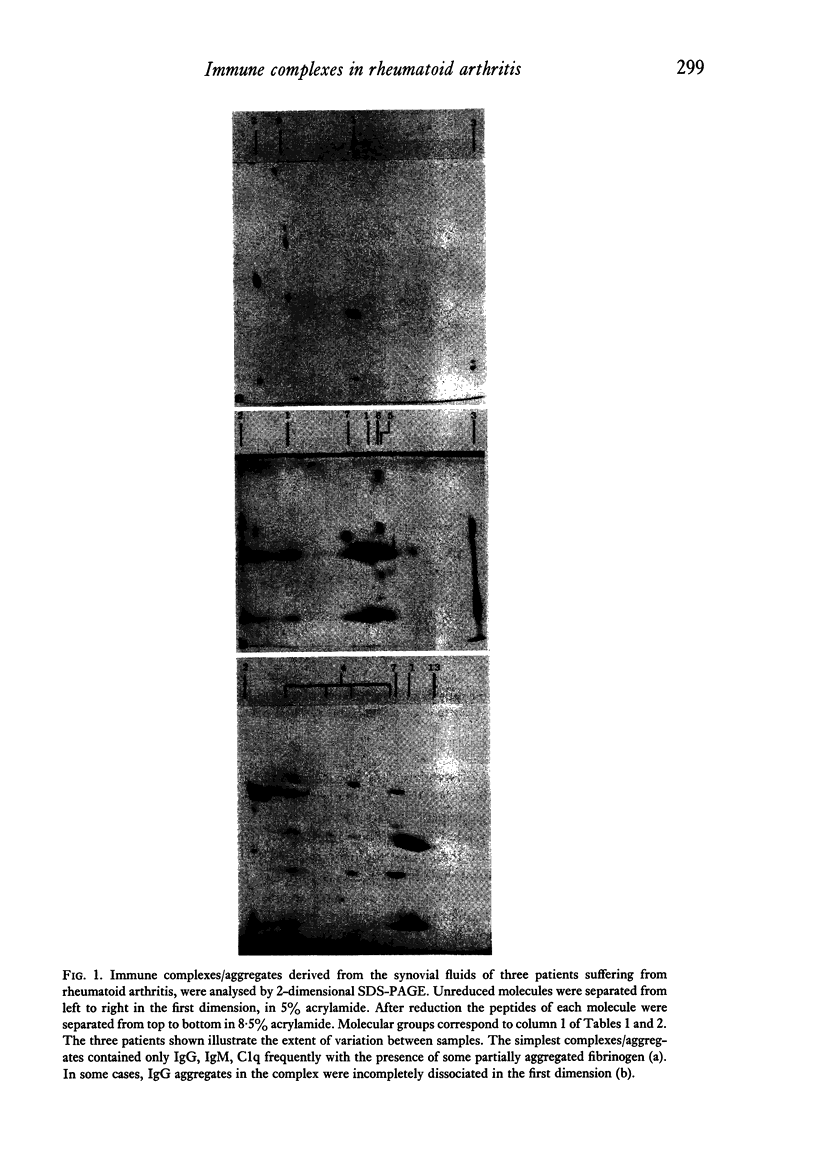
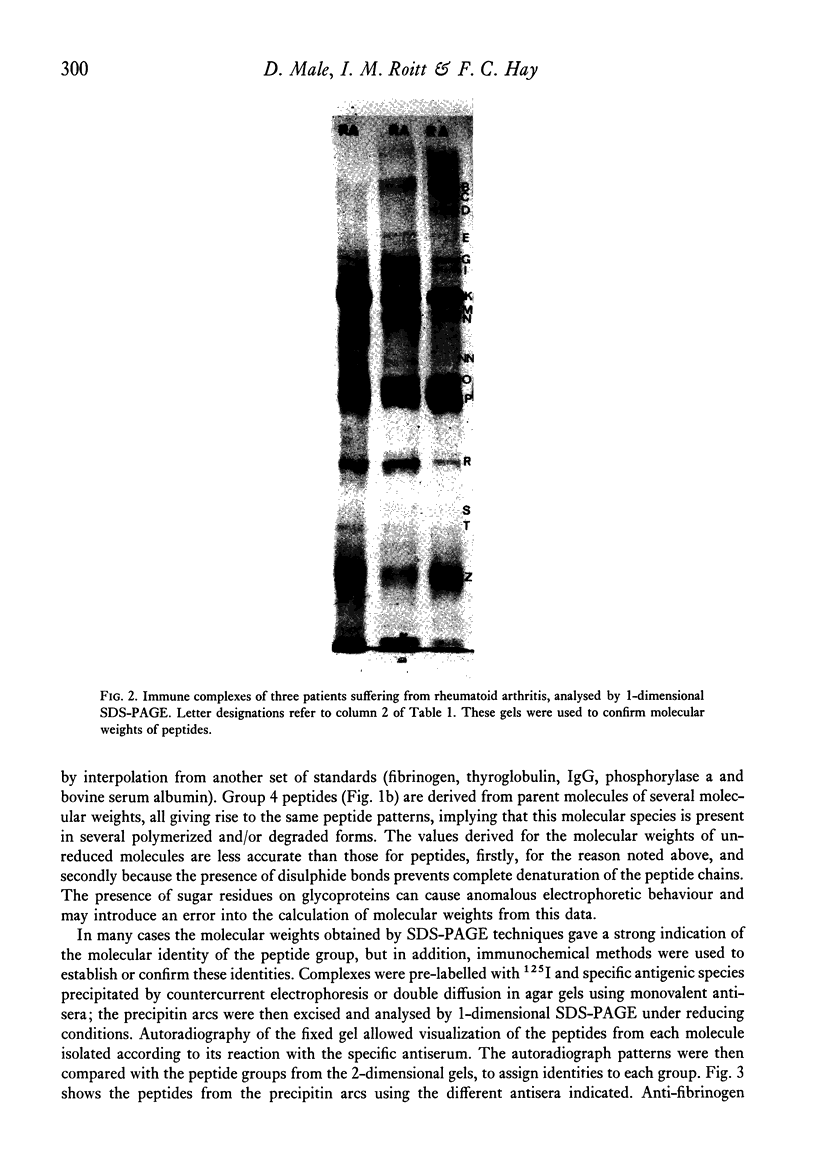
Immune complexes were isolated from the synovial effusions of patients with seropositive definite or classical rheumatoid arthritis by centrifugation over a sucrose-polyethylene glycol gradient. Physiochemical and immunochemical analysis showed IgG and IgM to be the predominant molecular species with lesser amounts of Clq and moderate amounts of IgA and activated C4 and C3. Very low concentrations of Clr, Cls, factor B and beta 2-microglobulin were detected. Trace amounts of four other components totalling less than 4% of the total protein, were seen and their molecular weights established. Reasons were advanced for thinking that fibrinogen, human serum albumin and alpha 2-macroglobulin were only secondarily associated with the complexes. The data are consistent with the hypothesis that IgG is the main, if not the only antigen, responsible for provoking and maintaining the pathological changes in rheumatoid arthritis.
Full text
PDF

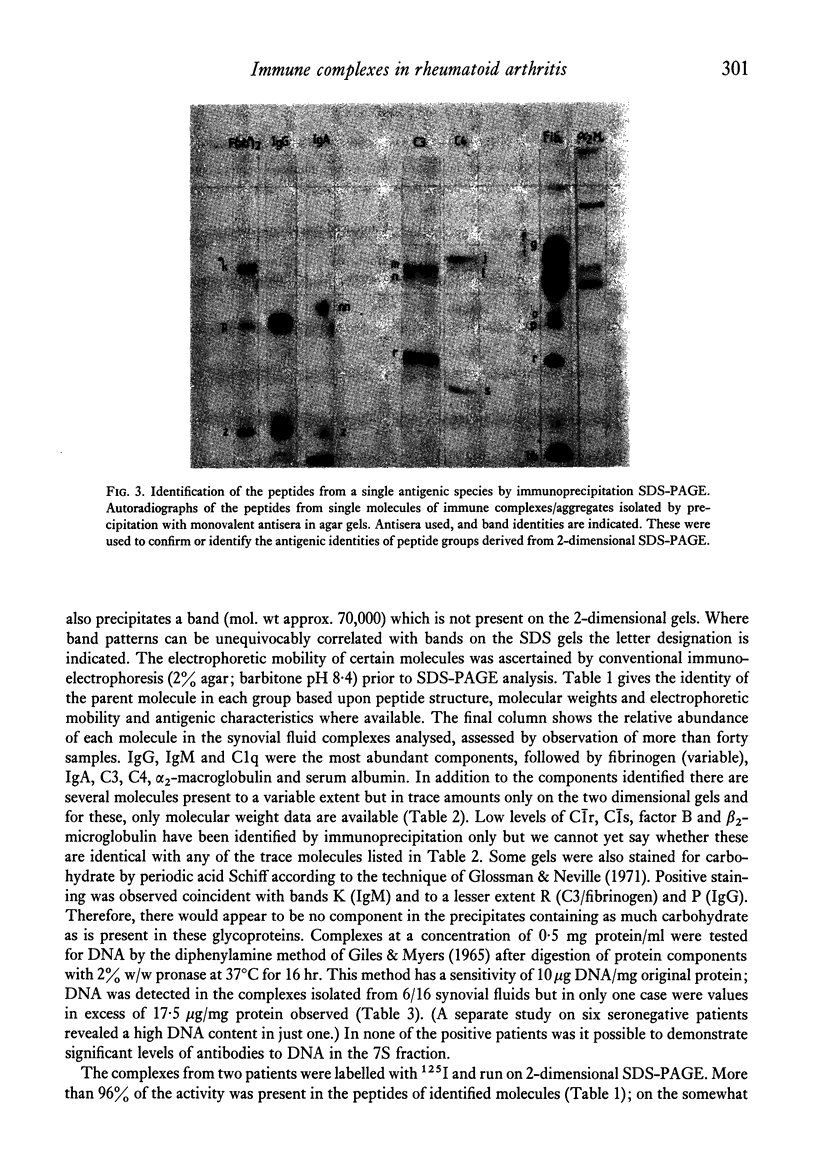
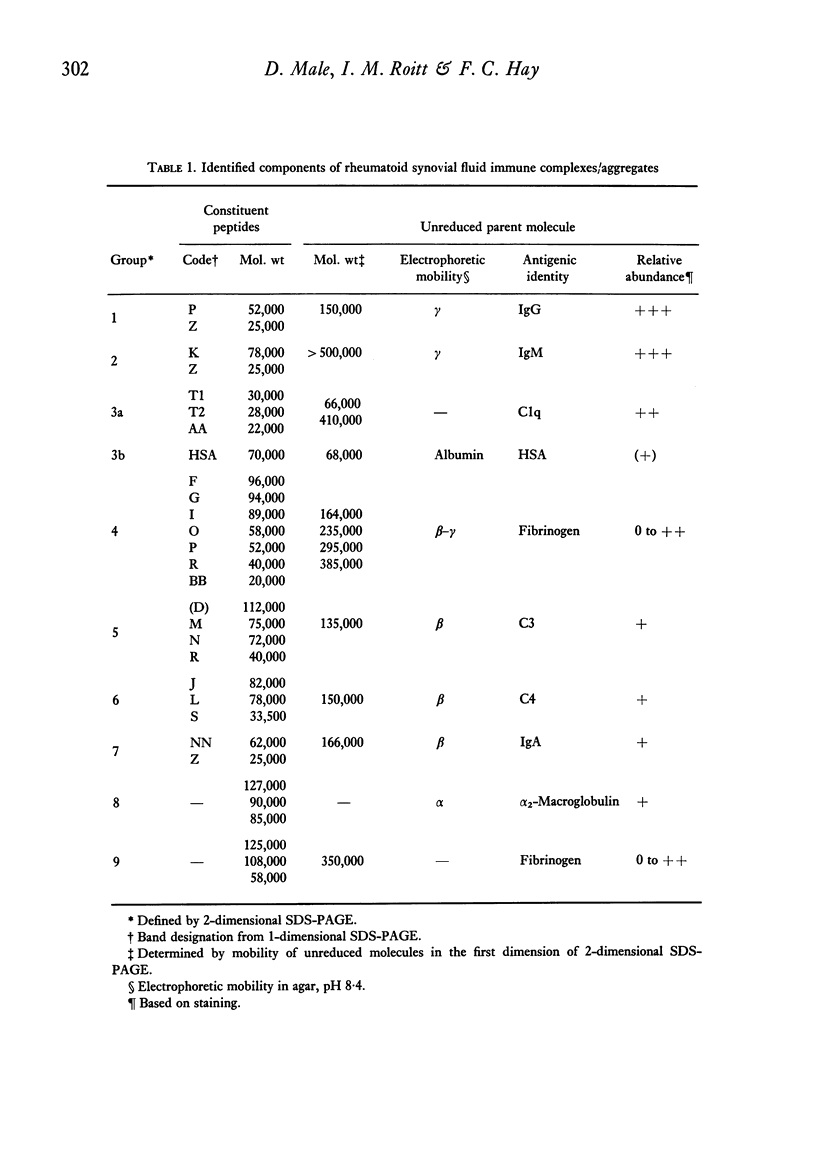
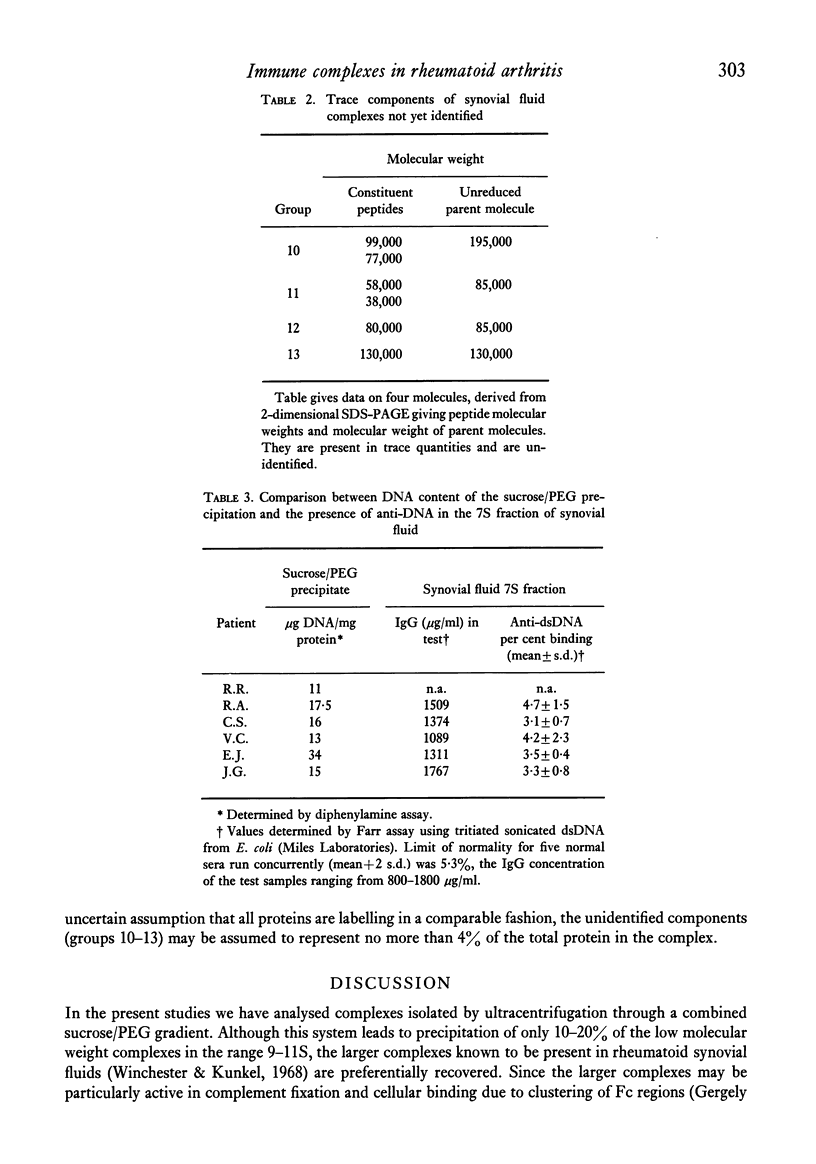



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cracchiolo A., Goldberg L. S., Barnett E. V., Bluestone R. Studies of cryoprecipitates from synovial fluid of rheumatoid patients. Immunology. 1971 Jun;20(6):1067–1077. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer N. E., Hurwitz D., Quismorio F. P., Lennette E. H., Friou G. J. Antiviral antibodies in rheumatoid synovial fluid and cryoprecipitates. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Sep;18(1):27–37. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glossmann H., Neville D. M., Jr Glycoproteins of cell surfaces. A comparative study of three different cell surfaces of the rat. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6339–6346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P. K., Roberts R. C. Physical and chemical properties of human plasma alpha2-macroglobulin. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 1;173(1):27–38. doi: 10.1042/bj1730027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrold A. J. Elimination of fibrinogen from synovial joints. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973 Jan;32(1):29–34. doi: 10.1136/ard.32.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASTER R. W. POSSIBLE SYNTHESIS OF POLYRIBONUCLEOTIDES OF KNOWN BASE-TRIPLET SEQUENCES. Nature. 1965 Apr 3;206:93–93. doi: 10.1038/206093b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Male D., Roitt I. M. Analysis of the components of immune complexes. Mol Immunol. 1979 Mar;16(3):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(79)90146-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellbye O. J., Munthe E. Specific binding of immunoconglutinin in tissues and synovial fluids from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 May;8(5):713–722. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellbye O. J., Natvig J. B. Evidence for immune complexes containing antibody to the pepsin site of IgG in rheumatoid synovial fluids. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Jun;8(6):889–899. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munthe E., Natvig J. B. Characterization of IgG complexes in eluates from rheumatoid tissue. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Feb;8(2):249–262. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munthe E., Natvig J. B. Immunglobulin classes, subclasses and complexes of IgG rheumatoid factor in rheumatoid plasma cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Sep;12(1):55–70. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natvig J. B., Munthe E. Self-associating IgG rheumatoid factor represents a major response of plasma cells in rheumatoid inflammatory tissue. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 13;256:88–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb36038.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nineham L. J., Hay F. C., Roitt I. M. Laboratory diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis: a solid phase radioassay for IgG and IgM antiglobulins. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Dec;29(12):1121–1126. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.12.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowoslawski A., Brzosko W. J. Immunopathology of rheumatoid arthritis. II. The rheumatoid nodule (the rheumatoid granuloma). Pathol Eur. 1967;2(3):302–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope R. M., Mannik M., Gilliland B. C., Teller D. C. The hyperviscosity syndrome in rheumatoid arthritis due to intermediate complexes formed by self-association of IgG-rheumatoid factors. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 Mar-Apr;18(2):97–106. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddy S., Austen K. F. The complement system in rheumatoid synovitis. I. An analysis of complement component activities in rheumatoid synovial fluids. Arthritis Rheum. 1970 Nov-Dec;13(6):713–723. doi: 10.1002/art.1780130601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen C., Ludwig H., Knapp W., Thumb N., Eberl R., Frank O., Freilinger H. Collagen antibodies and collagen- anticollagen immune complexes in rheumatoid arthritis. Z Rheumatol. 1975 Nov-Dec;34(11-12):391–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl L. M., Wahl S. M., Mergenhagen S. E., Martin G. R. Collagenase production by lymphokine-activated macrophages. Science. 1975 Jan 24;187(4173):261–263. doi: 10.1126/science.163038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Agnello V., Kunkel H. G. Gamma globulin complexes in synovial fluids of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Partial characterization and relationship to lowered complement levels. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 May;6(5):689–706. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J. Characterization of IgG complexes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 13;256:73–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb36036.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolley D. E., Crossley M. J., Evanson J. M. Collagenase at sites of cartilage erosion in the rheumatoid joint. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Jul-Aug;20(6):1231–1239. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]