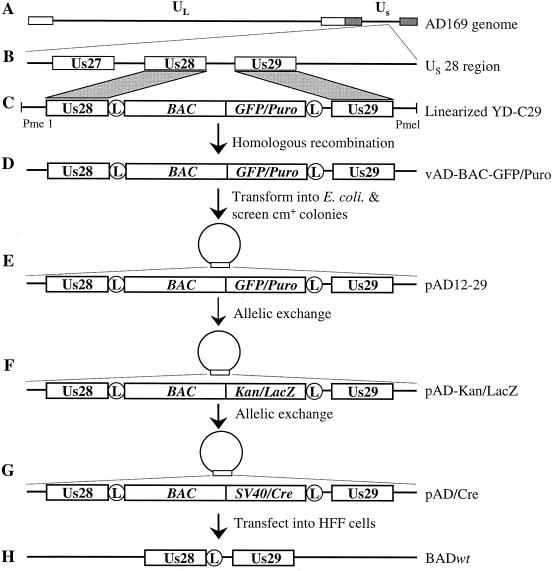
FIG. 1.
Strategy used to clone the genome of HCMV strain AD169 into a BAC. The HCMV genome (A) and a detail showing the ORFs present in the Us28 region (B) are diagrammed. AD169 viral DNA and PmeI-linearized recombination plasmid pYD-C29 (C) were cotransfected into HFF cells to generate the recombinant virus vAD-BAC-GFP/Puro (D). Circular vAD-BAC-GFP/Puro DNA was electroporated into E. coli DH10B cells to generate the BAC clone pAD12-29 (E). pAD12-29 was electroporated into the recA+ derivative of DH10B cells, GS500, where allelic exchange replaced the GFP/Puro cassette in the BAC plasmid with the kan/lacZ cassette (F) and subsequently with the SV40/Cre cassette to construct self-excisable BAC plasmid pAD/Cre (G). Transfection of pAD/Cre alone into HFF cells generated BAD wt (H), a phenotypically wild-type AD169 virus with a single LoxP site remaining that is located after the Us28 ORF. The circle enclosing an L represents the LoxP site.