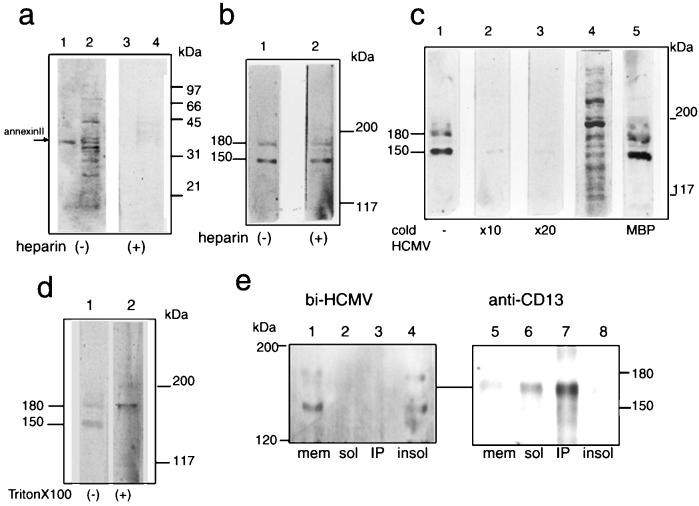
FIG. 1.
The radiolabeled HCMV probe specifically bound to two host proteins with molecular masses of 150 and 180 kDa. (a) The membrane fractions of MRC-5 (lanes 2 and 4) and authentic annexin II (lanes 1 and 3) were separated in SDS-12% PAGE gels and subjected to the virus overlay assay as described in Materials and Methods in the absence (lanes 1 and 2) and the presence (lanes 3 and 4) of heparin (100 μg/ml). (b to e) The membrane fraction was separated in SDS-5% PAGE gels, transferred to a PVDF membrane under strong conditions, and a virus overlay assay was carried out as for panel a. (b) Assay in the absence (lane 1) and the presence (lane 2) of heparin. (c) Assay in the absence (lane 1) and the presence of cold virions at a 10-fold excess (lane 2) and a 20-fold excess (lane 3) or in the presence of myelin basic protein (MBP; lane 5). Lane 4, protein pattern of the membrane fraction stained by amido black. (d) Virus overlay assay performed in the absence (lane 1) and the presence (lane 2) of Triton X-100 (0.5%, final concentration). (e) The membrane fraction (mem) was solubilized with 1% Triton X-100 in PBS for 30 min on ice and centrifuged to separate the soluble (sol) and insoluble (insol) fractions. Then immunoprecipitation with a MAb against CD13 (WM15) was carried out, followed by either a virus overlay assay (lanes 1 to 4) or immunostaining by WM15 (lanes 5 to 8). Shown are the membrane fraction of MRC-5 cells prior to solubilization (lanes 1 and 5), the Triton X-100-soluble fraction (lanes 2 and 6), the immunoprecipitates (IP) with WM15 (lanes 3 and 7), and the Triton X-100-insoluble fraction (lanes 4 and 8). bi-HCMV, biotinylated HCMV.