Abstract
Lymphoid cells from twenty-four untreated Hodgkin's disease biopsies were examined for spontaneous sheep erythrocyte and sensitized ox erythrocyte rosette formation for the identification of T cell and cells with Fc and C3 receptors and surface immunoglobulin. Compared with normal tissues mean T-lymphocytes values were elevated in both involved lymph nodes and uninvolved spleens from Hodgkin's patients. Lymphocytes bearing C3 receptors were correspondingly reduced in these tissues. Involved spleen T-cell values fell within the normal range. In normal tissues the sum of lymphocytes with surface immunoglobulin and sheep erythrocyte receptors fell in the range 89-108%. In six biopsies of Hodgkin's tissue the sum was outside the normal range (121-142%). This observation is compatible with surface immunoglobulin-coated T cells. Surface marker characteristics and intracellular immunoglobulin studies of small lymphocytes, lymphoblasts and Hodgkin's cells suggested that the neoplastic cells were of B lymphocyte origin.
Full text
PDF

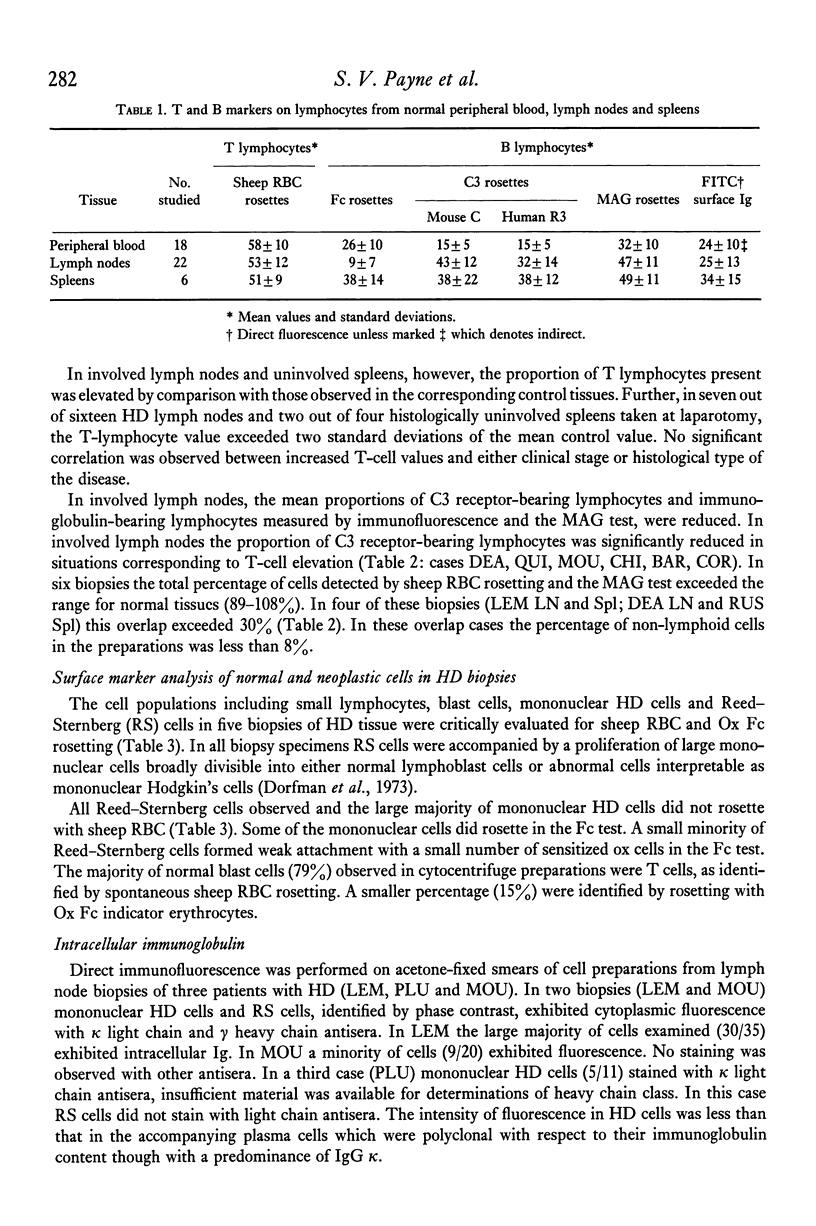


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AISENBERG A. C. Studies on delayed hypersensitivity in Hodgkin's disease. J Clin Invest. 1962 Nov;41:1964–1970. doi: 10.1172/JCI104654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen E. Depletion of thymus dependent lymphocytes in Hodgkin's disease. Scand J Haematol. 1974;12(4):263–269. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1974.tb00208.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianco C., Patrick R., Nussenzweig V. A population of lymphocytes bearing a membrane receptor for antigen-antibody-complement complexes. I. Separation and characterization. J Exp Med. 1970 Oct 1;132(4):702–720. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.4.702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braylan R. C., Jaffe E. S., Berard C. W. Letter: Surface characteristics of Hodgkin's lymphoma cells. Lancet. 1974 Nov 30;2(7892):1328–1329. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90198-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catovsky D., Galetto J., Okos A., Galton D. A., Wiltshaw E., Stathopoulos G. Prolymphocytic leukaemia of B and T cell type. Lancet. 1973 Aug 4;2(7823):232–234. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)93135-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin A. H., Saiki J. H., Trujillo J. M., Williams R. C., Jr Peripheral blood T- and B-lymphocytes in patients with lymphoma and acute leukemia. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1973 Jul;1(4):499–510. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(73)90006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins R. D., Smith J. L., Clein G. P., Barker C. R. Absence of B- and T-cell markers on acute lymphoblastic leukaemic cells and persistence of the T-cell marker on mitogen-transformed T-lymphocytes. Br J Haematol. 1974 Apr;26(4):615–625. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1974.tb00505.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton P. M. Immune responsiveness in Hodgkin's disease. Br J Cancer Suppl. 1973 Aug;1:119–127. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorfman R. F., Rice D. F., Mitchell A. D., Kempson R. L., Levine G. Ultrastructural studies of Hodgkin's disease. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1973 May;36:221–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froland S. S., Natvig J. B. Identification of three different human lymphocyte populations by surface markers. Transplant Rev. 1973;16:114–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1973.tb00119.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvin A. J., Spicer S. S., Parmley R. T., Munster A. M. Immunohistochemical demonstration of IgG in Reed-Sternberg and other cells in Hodgkin's disease. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1077–1083. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gergely P., Szegedi G., Berényi E., Petrányi G. Lymphocyte surface immunoglobulins in Hodgkin's disease. N Engl J Med. 1973 Jul 26;289(4):220–220. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197307262890421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grifoni V., Del Giacco G. S., Manconi P. E., Tognella S., Mantovani G. Letter: Lymphocytes in spleen in Hodgkin's disease. Lancet. 1975 Feb 8;1(7902):332–333. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91238-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallberg T., Haegert D., Clein G. P., Coombs R. R., Feinstein A., Gurner B. W. Observations on the mixed antiglobulin reaction as a test for immunoglobulin-bearing lymphocytes in normal persons and in patients with chronic lymphatic leukaemia. J Immunol Methods. 1974 Mar;4(2):317–332. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90074-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Holm G., Wigzell H. Surface markers on human T and B lymphocytes. I. A large population of lymphocytes forming nonimmune rosettes with sheep red blood cells. J Exp Med. 1972 Aug 1;136(2):207–215. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN H. S., SMITHERS D. W. Auto-immunity in man and homologous disease in mice in relation to the malignant lymphomas. Lancet. 1959 Jul 4;2(7088):1–4. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)92106-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadin M. E., Newcom S. R., Gold S. B., Stites D. P. Letter: Origin of Hodgkin's cell. Lancet. 1974 Jul 20;2(7873):167–168. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91602-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaur J., Spiers A. S., Catovsky D., Galton D. A. Increase of T lymphocytes in the spleen in Hodgkin's disease. Lancet. 1974 Oct 5;2(7884):800–802. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMB D., PILNEY F., KELLY W. D., GOOD R. A. A comparative study of the incidence of anergy in patients with carcinoma, leukemia, hodgkin's disease and other lymphomas. J Immunol. 1962 Oct;89:555–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang J. M., Oberling F., Bigel P., Mayer S., Waitz R. Lymphocyte reactivity to phytohaemagglutinin and allogeneic lymphocytes in 32 untreated patients with Hodgkin's disease. Biomedicine. 1974 Sep 20;21(9):372–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leech J. Immunoglobulin-positive Reed Sternberg cells in Hodgkin's disease. Lancet. 1973 Aug 4;2(7823):265–266. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)93173-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R., Kaplan H. S. Impaired lymphocyte function in untreated Hodgkin's disease. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jan 24;290(4):181–186. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197401242900402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Order S. E., Hellman S. Pathogenesis of Hodgkin's disease. Lancet. 1972 Mar 11;1(7750):571–573. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90360-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. L., Clein G. P., Barker C. R., Collins R. D. Characterisation of malignant mediastinal lymphoid neoplasm (Sternberg sarcoma) as thymic in origin. Lancet. 1973 Jan 13;1(7794):74–77. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90469-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. L., Haegert D. B- and T-lymphocyte markers on transformed lymphocytes from mitogen-stimulated cultures of normal and CLL lymphocytes and on tonsil blasts. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Aug;17(4):547–560. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithers D. W. Hodgkin's disease. II. Br Med J. 1967 May 6;2(5548):337–341. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5548.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMSON A. D. The thymic origin of Hodgkin's disease. Br J Cancer. 1955 Mar;9(1):37–50. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1955.4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. R., Burns J. The demonstration of plasma cells and other immunoglobulin-containing cells in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues using peroxidase-labelled antibody. J Clin Pathol. 1974 Jan;27(1):14–20. doi: 10.1136/jcp.27.1.14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tindle B. H., Parker J. W., Lukes R. J. "Reed-Sternberg cells" in infectious mononucleosis? Am J Clin Pathol. 1972 Dec;58(6):607–617. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/58.6.607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


