Figure 4.
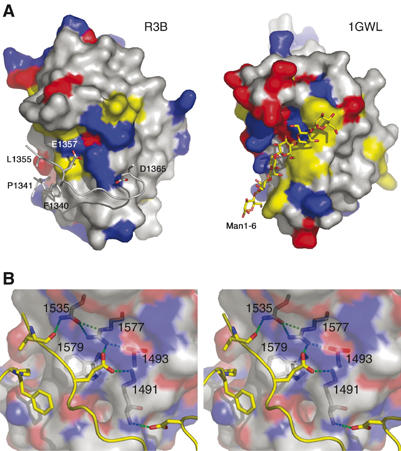
Similarity between the reelin subrepeat and the CBM. (A) Reelin subrepeat B (R3B) and the ligand-binding domain of bacterial cellulase (1GWL), in surface presentation, viewed from the same orientation. Their surfaces are color-coded by the type of residue: red for acidic, blue for basic, and yellow for aromatic residues. In 1GWL, its bound ligand oligomannose is shown in a stick model, whereas in R3B the ‘ligand-like' inserted loop from the subrepeat A, with important residues making direct side-chain contacts, is shown. (B) Stereo presentation of the close-up view at the subrepeat A–B interface. R3B residues involved in the recognition of R3A loop are shown in stick models inside the half-transparent molecular surface and labeled. Both hydrophobic and hydrogen bonding interactions are evident. The figure was made using PyMol (DeLano, 2002).
