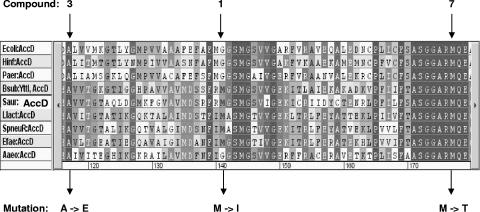
FIG. 2.
Part of the multiple amino acid sequence alignment of carboxyltransferase β-subunits (AccD) of bacterial acetyl-CoA carboxylases. The amino acid exchanges caused by mutations obtained by serial passaging of S. aureus 133 in the presence of the pyrrolidinedione variants 1, 3, and 7 are indicated below the alignment. The accD mutations are G400-A (compound 1), C332-A (compound 3), and T509-C (compound 7). The mutation isolated with compound 1 (the natural product moiramide B) was found in a strain with a fourfold increased MIC compared to that of the corresponding wild type. The mutation isolated with compound 3 was associated with a 16-fold elevated MIC, while the mutation isolated with compound 7 was identified in a mutant with a 256-fold increased MIC (see Results). Sequences of the following bacteria are included: Ecoli, E. coli; Hinf, Haemophilus influenzae; Paer, Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Bsub, B. subtilis (YttI is a synonym for AccD); Saur, S. aureus; Llact, Lactobacillus lactis; Spneu, S. pneumoniae; Efae, Enterococcus faecalis; and Aaeo, Aquifex aeolicus.