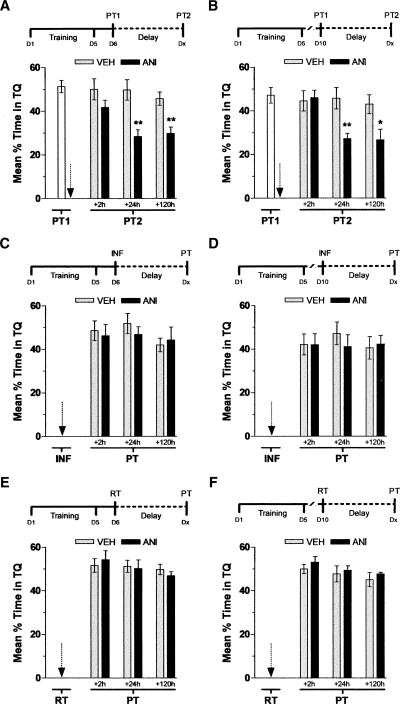
Figure 2.
Inhibition of hippocampal protein synthesis immediately after nonreinforced retrieval hinders spatial memory retention. (A) Animals with infusion cannulae implanted in the CA1 region of the dorsal hippocampus were trained during 5 d in the spatial version of the MWM (D1–D5). Twenty-four hours later (D6), animals were randomly assigned to one out of six experimental groups and submitted to a 60-sec probe test in the absence of the escape platform (PT1). Immediately after PT1, animals received intra-CA1 infusions of anisomycin (160 μg/side; ANI) or vehicle (VEH). The black arrow indicates the moment of infusion. Memory retention was assessed in a second 60-sec probe test (PT2) carried out either at 2, 24, or 120 h after PT1. Data are expressed as mean (±SEM) percentage of time swimming in the target quadrant (TQ); **P < 0.01 vs. VEH during PT2 carried out at 24 h (+24 h; t[12] = 3.80) or 120 h (+120 h; t[12] = 3.73) after PT1; P > 0.1 vs. VEH during PT2 carried out 2 h after PT1 (+2 h; t[12] = 1.41). In all cases n = 7 per group. (B) Animals were treated exactly as in A except that PT1 was carried out 120 h (D10) after the last training session. **P < 0.01 vs. VEH during PT2 carried out 24 h after PT1 (+24 h; t[12] = 3.38); *P < 0.05 vs. VEH during PT2 carried out 120 h after PT1 (+120 h; t[12] = 2.51); P > 0.05 vs. VEH during PT2 carried out 2 h after PT1 (+2 h; t[12] = 0.25). In all cases n = 7 per group. (C) Animals with infusion cannulae implanted in the CA1 region of the dorsal hippocampus were trained during 5 d in the spatial version of the MWM (D1–D5). Twenty-four hours later (D6), animals were randomly assigned to one out of six experimental groups and received intra-CA1 infusions (INF) of anisomycin (160 μg/side; ANI) or vehicle (VEH). The black arrow indicates the moment of infusion. Memory retention was assessed in a 60-sec probe test (PT) carried out at either 2 h (+2 h; P > 0.1 vs. VEH, t[12] = 0.33), 24 h (+24 h; P > 0.1 vs. VEH, t[12] = 0.85), or 120 h (+120 h; P > 0.1 vs. VEH, t[12] = 0.34) after INF. Data are expressed as mean (±SEM) percentage of time swimming in the target quadrant (TQ). In all cases n = 7 per group. (D) Animals were treated exactly as in C except that INF was carried out 120 h (D10) after the last training session; P > 0.1 vs. VEH during a PT carried out at 2 h (+2 h; t[12] = 0.02), 24 h (+24 h; t[12] = 0.79), or 120 h (+120 h; t[12] = 0.26) after INF. In all cases n = 7 per group. (E) Animals with infusion cannulae implanted in the CA1 region of the dorsal hippocampus were trained during 5 d in the spatial version of the MWM (D1–D5). Twenty-four hours later (D6), animals were randomly assigned to one out of six experimental groups and submitted to a retraining test (RT) in the presence of the escape platform. Immediately after RT, animals received intra-CA1 infusions of anisomycin (160 μg/side; ANI) or vehicle (VEH). The black arrow indicates the moment of infusion. Memory retention was assessed in a probe test (PT) carried out either at 2 h (+2 h; P > 0.1 vs. VEH, t[14] = 0.42), 24 h (+24 h; P > 0.1 vs. VEH, t[14] = 0.01), or 120 h (+120 h; P > 0.1 vs. VEH, t[14] = 1.44) after RT. Data are expressed as mean (±SEM) percentage of time swimming in the target quadrant (TQ). In all cases n = 8 per group. (F) Animals were treated exactly as in E except that RT was carried out 120 h (D10) after the last training session; P > 0.1 vs. VEH during a PT carried out at 2 h (+2 h; t[14] = 0.81), 24 h (+24 h; t[14] = 0.20), or 120 h (+120 h; t[14] = 0.28) after INF. In all cases n = 8 per group.