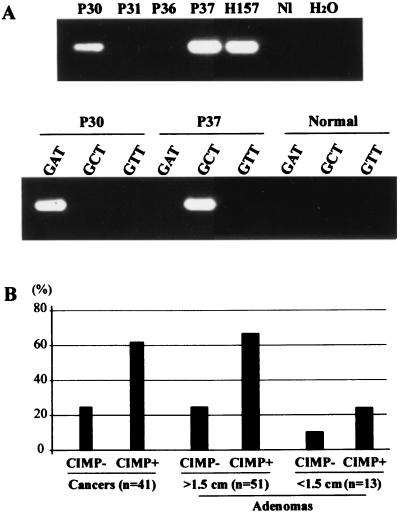
Figure 1.
Mutational analysis of K-RAS in colorectal tumors. Mutations were detected by mutant allele-specific amplification. (A). PCR reactions were first performed by using a primer mixture to detect six different mutations of K-RAS codon 12 (Upper). A second PCR reaction was then performed by using specific primers to detect the exact mutation in each case (Lower). For example, p30 was found to have a mutation by using the primer mix (Upper), and the mutation was determined to be a GGT to GAT change by using specific primers (Lower). P30, P31, P36, and P37, colorectal adenomas; H157, a human lung cancer cell line that has a mutation in codon 12 of K-RAS. “Normal” refers to normal colon (a negative control). (B) Frequencies of K-RAS mutations in colorectal tumors with or without CIMP. The frequencies of K-RAS mutations in each population were expressed as percentages. The number of tumors examined is shown at the bottom. The adenomas were divided into <1.5 cm and ≥1.5 cm.