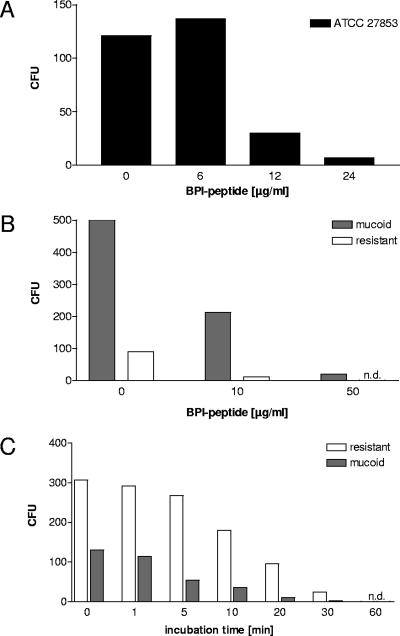
FIG. 5.
Antimicrobial activity of a BPI-derived peptide and kinetics of BPI-mediated killing. A 27-amino-acid peptide from the amino-terminal region of BPI was synthesized and compared to natural BPI isolated from human granulocytes. BPI peptide was used at the indicated concentrations to determine bactericidal activity against P. aeruginosa. BPI peptide was coincubated with the bacteria for 1 h at increasing concentrations (A and B), whereas BPI was applied at 10 μg/ml for time-dependent killing of P. aeruginosa (C) and then plated on blood agar to quantify surviving bacteria (A, B, and C). In panel A, the ATCC 27853 strain was used. In panels B and C, the P. aeruginosa stains used were freshly isolated from the lungs of CF patients, one showing a mucoid phenotype (gray bars) and the other being fully resistant to common antibiotics applied in CF lung infection (white bars). n.d., not detected.