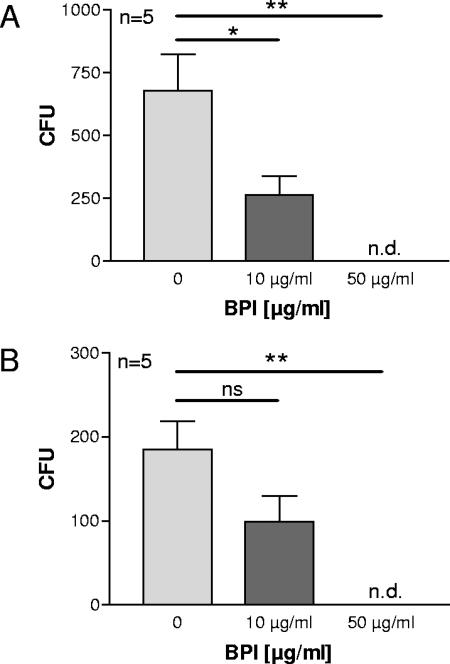
FIG. 6.
Mucoid and antibiotic-resistant clinical P. aeruginosa isolates are killed by BPI. Natural BPI isolated from human granulocytes was used at the indicated concentrations to determine bactericidal activity. The experiments were performed as described in the legend for Fig. 5. All bacteria shown are clinical P. aeruginosa isolates from CF patients. (A) P. aeruginosa strains with a mucoid phenotype, three of which have resistance to up to four antibiotics. (B) P. aeruginosa strains that are multiresistant to antibiotics. Two of the strains are fully resistant to all antibiotics applied. Statistically significant differences are given as P values (*, P <0.05; **, P <0.01). ns, not significant. Error bars indicate standard deviations.