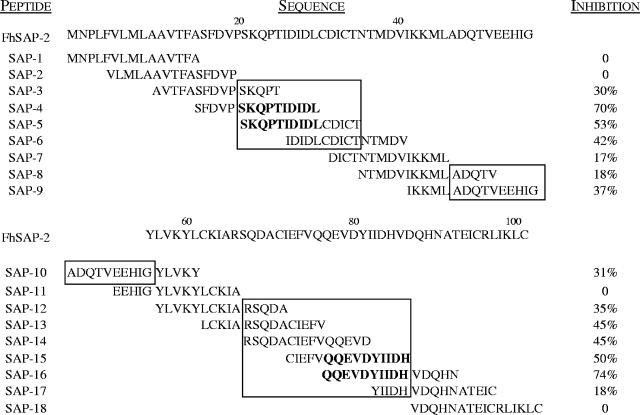
FIG. 3.
Inhibition percentage obtained when peptides were individually added at 20 μg/ml to sera from rabbits at 12 weeks postinfection with F. hepatica. For this assay two pools of peptides were prepared. Pool 1 included the N terminus peptides (SAP-1 to SAP-9), and pool 2 included the C terminus peptides (SAP-10 to SAP-18). Microtiter plates were coated with 20 μg/ml of each pool of peptides. Serum diluted 1:200 was mixed with 20 μg/ml of a single peptide and incubated for 1 h at 37°C to favor peptide-antibody complex formation. After incubation, a serum-peptide mixture was added to the plates and incubated for 1 h at 37°C. Conjugate was then added, followed by the substrate solution as previously described (9). Percent inhibition (I) was calculated as follows: I = [1− (OD at 492 nm of serum-peptide mixture/OD at 492 nm of serum-PBS-Tween mixture)] × 100. Peptides that inhibited the binding capacity of antibodies to antigen-coated plates by >50% were considered distinctive of dominant B-cell epitopes. The three antigenic regions identified within the FhSAP-2 protein are enclosed in a box. The amino acid residues that were considered to contain dominant B-cell epitopes are in bold type.