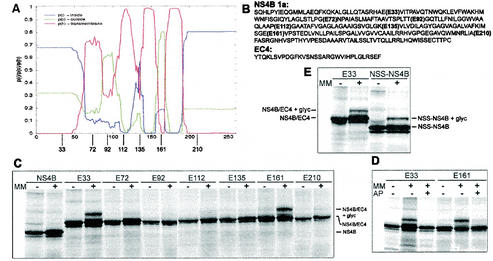
FIG. 5.
TMHMM analysis of NS4B genotype 1a and glycosylation patterns of mutants derived from the same sequence (A) Graphical output of the TMHMM analysis, with the 261 amino acid residues of NS4B indicated on the x axis. The red line describes the probability of that part of the protein to be a transmembrane domain, the blue line describes the probability of it being inside the membrane (cytoplasmic), and the green line describes the probability of it being outside the membrane (lumenal). The approximate sites of the EC4 insertions are depicted below the graph. (B) Amino acid sequences of NS4B genotype 1a and the EC4 loop. The different insertion sites of the EC4 loops in the NS4B sequence are indicated. (C to E) Glycosylation patterns of different constructs that had been in vitro transcribed and translated in the absence or presence of microsomal membranes (MM). The identities of the bands are indicated. An explanation for the weak bands below the main bands is given in the legend to Fig. 4. (C) NS4B and the seven glycosylation mutants containing the EC4 loop. (D) E33 and E161 translated in the presence of an acceptor peptide (AP) that competes for the glycosylation. (E) Control of the N-tail glycosylation. An NSS sequence was put directly in the N-terminal tail of the original NS4B sequence, changing the amino acids HLP to NSS.