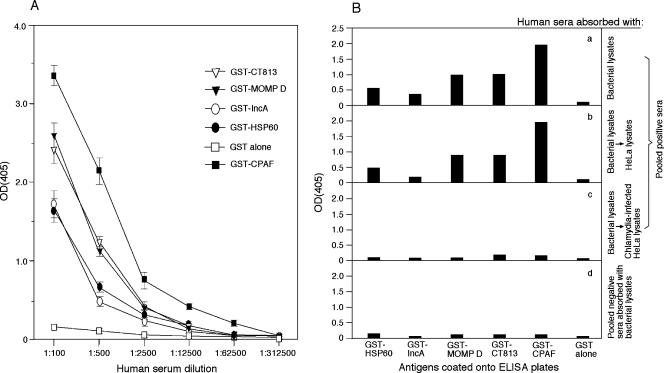
FIG. 6.
Results of an ELISA of human antibody responses to the CT813 protein. (A) Detection of titers of antibody in individual patients. Serum samples from 10 women diagnosed with urogenital tract infection with C. trachomatis were each serially diluted as shown along the x axis and reacted with GST-CT813, GST-MOMP from serovar D, GST-IncA, GST-HSP60, GST alone, and GST-CPAF immobilized onto the ELISA plates. All dilutions of each serum sample were measured in duplicate. The OD values obtained at the wavelength of 405 nm were expressed as means ± standard deviations, as shown along the y axis. Note that the titers of anti-CT813 were as high as those of anti-MOMP antibody. (B) Specificity of human antibody binding. The same 10 patient sera were pooled together at equal ratios to make the pooled positive sera, while sera from 8 normal individuals were pooled similarly to make the pooled negative sera. Both of the pooled serum samples were subjected to absorption with the bacterial lysates (a and d), while the positive serum samples were further absorbed with either HeLa alone (b) or C. trachomatis serovar D-infected HeLa lysates (c). After a dilution of 1:500 (relative to the initial serum volume), the processed serum samples were reacted with the ELISA plate-immobilized fusion proteins (in duplicate) as indicated along the horizontal axis and the ODs were expressed as the mean values from the duplicate wells as shown along the vertical axis. Note that the pooled positive sera variably reacted with all fusion proteins but not GST alone (a) and that reactivity was blocked by a further absorption with the infected cell lysates (c) but not the uninfected cell lysates (b). The pooled negative sera failed to significantly react with any fusion proteins (d).