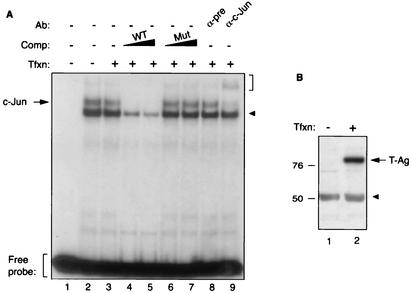
FIG. 3.
T-Ag inhibits c-Jun binding to its target sequences in an electrophoretic mobility shift assay. (A) Band shift assay. A double-stranded synthetic oligonucleotide containing JCV AP-1 binding site (5′-CAAGCATGAGCTCATACCTA-3′) spanning nucleotides 155 to 162 of JCV Mad-1 regulatory region was end labeled with [γ-32P]ATP with T4 polynucleotide kinase and gel purified. Nuclear extracts (10 μg/lane) prepared from U-87MG cells and untransfected (lane 2) or transfected with a T-Ag expression plasmid (lane 3) were incubated with labeled probe (40,000 cpm/lane) in a binding buffer, as described in Materials and Methods. In addition, probe plus nuclear extract from T-Ag-transfected cells was also incubated with either unlabeled wild-type oligonucleotide (WT) (lanes 4 and 5) or 25- or 150-fold molar excesses of its mutant variant competitor oligonucleotides (Mut) (5′-CAAGCATTAGCTTGTACCTA-3′; bold indicates base substitutions relative to the wild type) (lanes 6 and 7, respectively). Probe plus nuclear extract mixture was also incubated either with a preimmune (α-pre; 2 μg) (lane 8) or an anti-c-Jun (α-c-Jun, KM-1; 2 μg) (lane 9) antibody. Formed DNA-protein complexes were then resolved on a 6% polyacrylamide gel under native conditions and visualized by autoradiography. The specific DNA-protein complexes are indicated by an arrow, and nonspecific complexes are indicated by a solid arrowhead. A bracket indicates antibody supershifted complexes. (B) Western blot analysis. Nuclear extracts prepared from either untransfected U-87MG cells (lane 1) or U-87MG cells transfected with CMV-T-Ag expression plasmid (lane 2) were analyzed by Western blotting using an anti-SV40 T-Ag antibody (Ab-2 416) which is cross-reactive with JCV T-Ag. Comp, competitor; Ab, antibody; Tfxn, transfection.