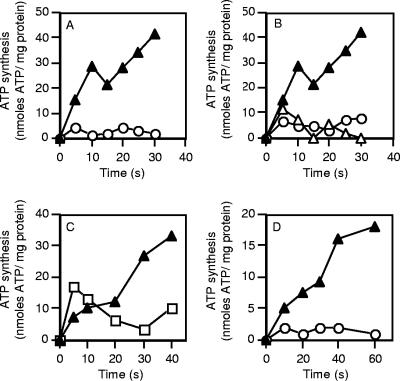
FIG. 6.
ATP synthesis in C. paradoxum membrane vesicles. (A) ATP synthesis in inverted membrane vesicles was energized by a valinomycin (2 μM)-induced potassium diffusion potential (Δψ) (100 mV) applied in the absence of a ΔpNa+ at 40°C (▴). ○, no valinomycin addition. (B) Effect of CCCP (20 μM) (○) or DCCD (50 μM) (▵) on ATP synthesis of inverted membrane vesicles energized by a valinomycin-induced potassium diffusion potential applied in the absence of ΔpNa+ at 40°C (▴). All inhibitors were preincubated with the inverted membrane vesicles for 10 min prior to the addition of valinomycin. (C) Ability of an artificially imposed ΔpNa+ (100 mV) to drive ATP synthesis in the presence of a valinomycin-induced potassium diffusion potential (Δψ, 100 mV) (▴). The experiment was also performed with 5 μM monensin included in the reaction buffer (□). (D) Effect of CCCP (20 μM) on ATP synthesis in the presence of either a ΔpNa+ and Δψ (▴) or Δψ alone (○). ATP synthesis was measured as described in Materials and Methods. For all experiments the values are the means of two to four independent determinations, and the associated experimental error was less than 15%.