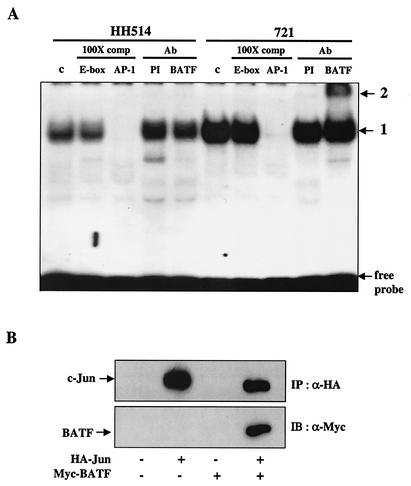
FIG. 7.
BATF is a component of AP-1 DNA binding activity in B cells. (A) Nuclear extracts were prepared from HH514 (BATF−) and 721 (BATF+) B cells as described in Materials and Methods and used for EMSA with a 32P-labeled AP-1 DNA probe. The major complex formed in the control (c) reactions (1) was competed by the addition of unlabeled AP-1 DNA but not by adding an unrelated DNA sequence (E-box). Addition of PI or anti-BATF antiserum (BATF) to the reaction resulted in a supershift (2) only in the extracts from 721 cells. Ab, antibody. (B) Coimmunoprecipitation of BATF:c-Jun complexes from B cell extracts. DG75 cells were electroporated as described in Materials and Methods with 10 μg of an expression plasmid for HA-tagged c-Jun, 10 μg of an expression plasmid for a Myc-tagged BATF, both plasmids, and empty vector DNA (where needed) to adjust the total DNA to 20 μg. After 36 h, the cells were lysed and protein complexes were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-HA antiserum (α-HA). The proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted (IB) initially with α-HA and then with anti-Myc antiserum (α-Myc) to detect BATF. Results indicate the presence of coimmunoprecipitated BATF only in extracts from DG75 cells expressing both proteins.