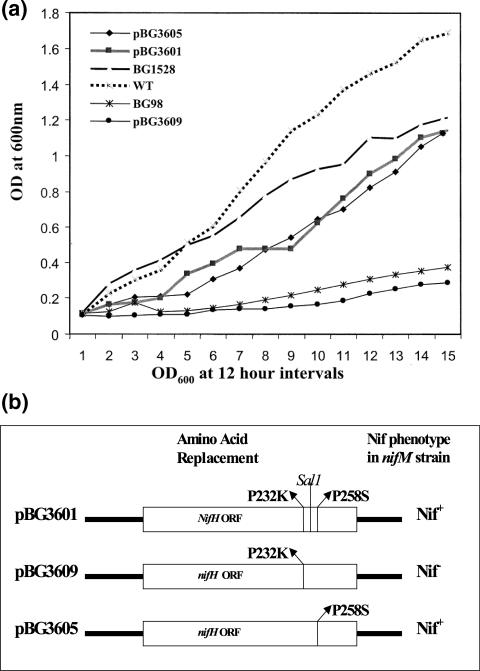
FIG. 3.
The P258S mutation is sufficient to confer NifM independence on NifH. (a) Growth curves of the nifM A. vinelandii BG98 and its derivatives carrying different plasmids harboring different nifH mutants in BN− medium compared with the growth curve of A. vinelandii BG1528 and wild-type A. vinelandii (WT). BG1528 is the A. vinelandii strain that was transformed with pBG1528, the pCR2.1TOPO vector derivative carrying the nifH mutant with two amino acid changes, P232K and P258S. Since this plasmid is not a broad-host-range plasmid, it cannot replicate in A. vinelandii. Therefore A. vinelandii BG1528 was generated via homologous recombination and subsequent rescuing of the mutant nifH gene that can confer NifM independence on the chromosome. OD600, optical density at 600 nm. (b) Amino acid changes in the nifH mutants present in plasmids pBG3601, -3605, and -3609. The SalI site (at position 754) present between the mutations (CCG→AAG at positions C697 and C698, resulting in a P232K amino acid change, and CCG→TCG at position C775, resulting in a P258S amino acid change) is marked. Since these plasmids are broad-host-range plasmids, they replicated in nifM A. vinelandii BG98. The growth curves show the Nif phenotypes conferred by these plasmids on nifM A. vinelandii BG98, and they are marked in panel b.