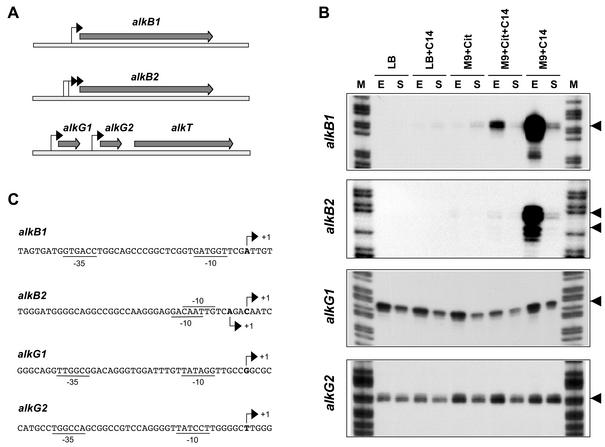
FIG. 1.
Promoters for alkB1, alkB2, alkG1, and alkG2 genes. (A) The genes encoding the two membrane-bound alkane hydroxylases, alkB1 and alkB2, are located on different sites of the chromosome. The genes encoding the two rubredoxins (alkG1 and alkG2) and the rubredoxin reductase (alkT) are clustered and map at a different site. Arrows indicate the promoters identified in this work. (B) Identification and expression of the promoters for the alkB1, alkB2, alkG1, and alkG2 genes in cells grown either in rich LB medium or in M9 minimal salts medium in the absence or presence of tetradecane (C14) or citrate (Cit). Cells were collected at either the exponential (A550 of 1.5) or stationary (A550 of 5) phase of growth (indicated as E and S, respectively). Transcripts originating upstream of the genes under study were analyzed by S1 nuclease protection assays; the 5′ ends of the probes used hybridized at positions +89, +56, +87, and +152 relative to the transcription start sites observed for promoters PalkB1, PalkB2, PalkG1, and PalkG2, respectively. Lane M, DNA size ladder. Arrows indicate the transcription start sites observed. No other bands were detected in the gels in addition to those shown. (C) Sequences of the promoters identified in P. aeruginosa strain RR1. The transcription start sites observed in panel B are indicated with arrows. Sequences at the −10 and −35 regions showing similarity (at least three matches) to those recognized by the vegetative RNA polymerase are underlined. The ATG translation start sites of alkB1, alkB2, alkG1, and alkG2 are located at positions +36, +35, +36, and +101, respectively.