Figure 1.
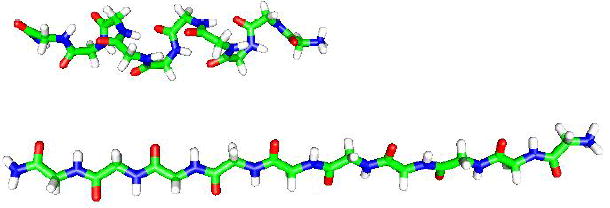
A picture (generated using gOpenMol) of the peptide subjected to external forces (in the horizontal direction in the picture) of K=2 and 100 kcal/(mol·Å). For K=2 the molecule is still approximately helical with end-to-end distance of R=21.7 Å. For K=100 kcal/(mol·Å) the helix becomes an extended structure that is stretched significantly to R=36.8 Å with decreased conformational freedom. This is a pictorial illustration for the results of Δαk (Table 1), which are shown to decrease as the external force increases. Similar figures for the forces K=8, 20 and 40 are not provided because the corresponding extensions are close to that of K=100 (see Table 4).
