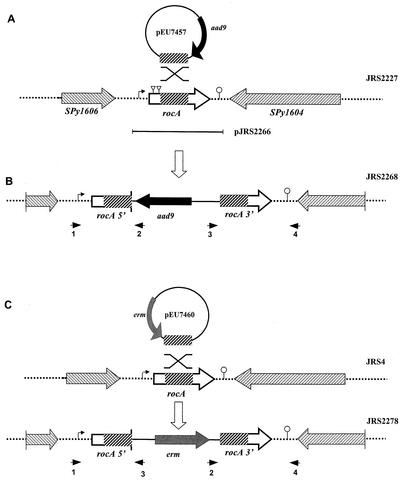
FIG. 2.
Construction of a rocA null mutant. (A) Region surrounding rocA in the chromosome of GAS. Plasmid pEU7457 (circle), which was used for insertional inactivation, contains a region internal to the rocA ORF (thick hatched box) and contains aad9, which encodes spectinomycin resistance (thick black arrow). The direction of transcription of the ORFs flanking rocA is indicated by striped arrowheads. The region of rocA that was cloned in complementing plasmid pJRS2266 is indicated by a bar below the chromosome. (B) JRS2268 was produced by homologous recombination (indicated by the X above the representation of the chromosome in panel A), which inserted pEU7457 into the wild-type rocA gene in the JRS2227 chromosome. (C) JRS2278 was produced by a similar targeted insertion in JRS4 by using integrational plasmid pEU7460, which contains erm, encoding erythromycin resistance (gray box), and a region internal to the rocA ORF (thick hatched box) as shown. Symbols: dotted lines, chromosome; striped boxes, coding regions with the directions of transcription indicated by the arrowheads; bent arrow, putative promoter; triangles, ISS1 insertion sites; lollipop, putative rho-independent transcription terminator. Small arrowheads below the chromosome represent primers used to confirm plasmid insertion into the chromosome (see Materials and Methods). The figure is not drawn to scale.