Abstract
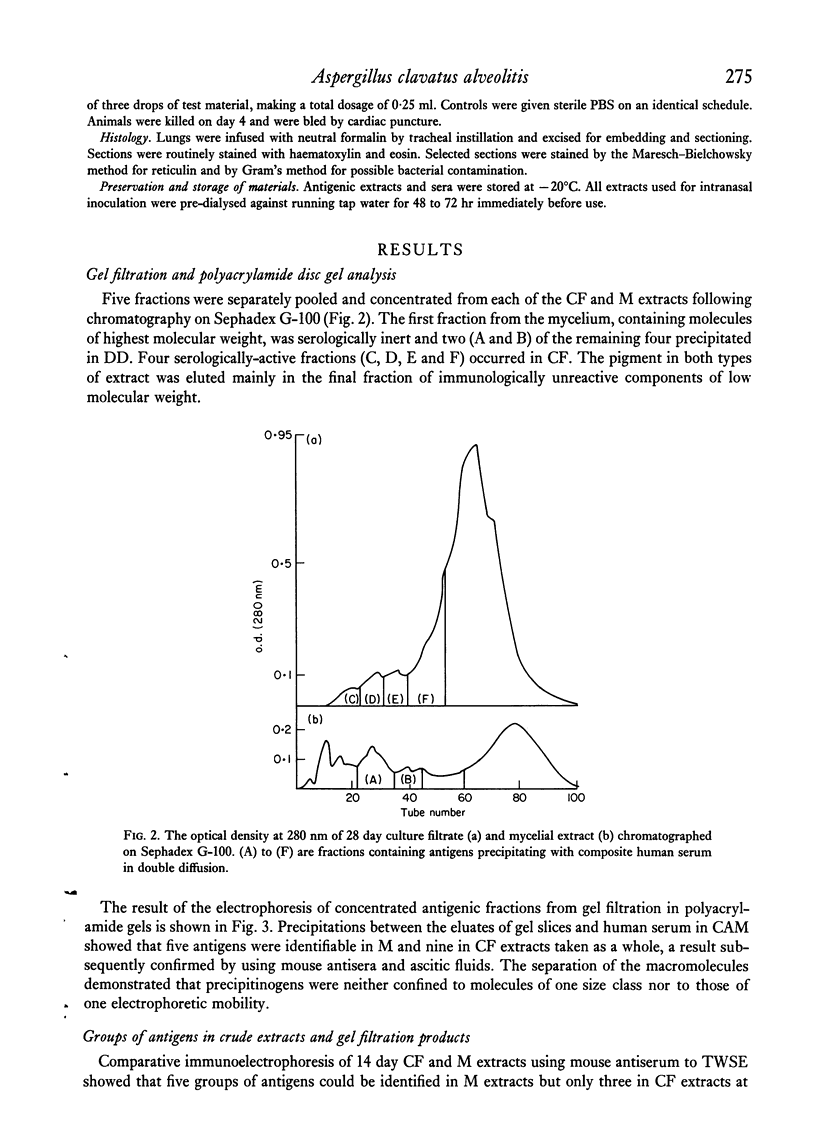
Five groups of antigens were identified in culture filtrates and extracts from spores and mycelia of Aspergillus clavatus fractionated by gel filtration, affinity chromatography, electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gels and chemical analysis. Some particulate and soluble fractions given by nasal inoculation provoked murine allergic alveolitis in non-sensitized and sensitized precipitin-negative, and sensitized, precipitin-positive, animals. Alveolitis-inducing substances appeared to be glycoprotein precipitinogens, which withstood proteolysis, were preferentially adsorbed by concanavalin A, but which were rendered almost inert by sodium periodate oxidation. Spore walls were particularly rich in allergenic substances extractable by alkaline hydrolysis. Delipidated dead spores provoked more severe disease in all immunological groups of mice than live spores. Polysacchraride extracts and acid hydrolysates of spore walls were unreactive.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aspberg K., Porath J. Group-specific adsorption of glycoproteins. Acta Chem Scand. 1970;24(5):1839–1841. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.24-1839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azuma I., Kimura H., Yamamura Y. Purification and characterization of an immunologically active glycoprotein from Asperigillus fumigatus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jul;96(1):272–273. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.1.272-273.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrowcliff D. F., Arblaster P. G. Farmer's lung: a study of an early acute fatal case. Thorax. 1968 Sep;23(5):490–500. doi: 10.1136/thx.23.5.490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blyth W., Wardrop V. E. Particulate and soluble antigens of Micropolyspora faeni in experimental allergic alveolitis of the mouse. J Med Microbiol. 1977 Aug;10(3):331–346. doi: 10.1099/00222615-10-3-331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boros D. L., Warren K. S. Delayed hypersensitivity-type granuloma formation and dermal reaction induced and elicited by a soluble factor isolated from Schistosoma mansoni eggs. J Exp Med. 1970 Sep 1;132(3):488–507. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.3.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boros D. L., Warren K. S. The bentonite granuloma. Characterization of a model system for infectious and foreign body granulomatous inflammation using soluble mycobacterial, histoplasma and schistosoma antigens. Immunology. 1973 Mar;24(3):511–529. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Channell S., Blyth W., Lloyd M., Weir D. M., Amos W. M., Littlewood A. P., Riddle H. F., Grant I. W. Allergic alveolitis in maltworkers. A clinical, mycological, and immunological study. Q J Med. 1969 Oct;38(152):351–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. H. A quantitative study on the activation of the alternative pathway of complement by mouldy hay dust and thermophilic actinomycetes. Clin Allergy. 1976 Jan;6(1):19–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1976.tb01408.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. H., Wagner J. C., Seal R. M. Pulmonary responses to particulate materials capable of activating the alternative pathway of complement. Clin Allergy. 1976 Mar;6(2):155–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1976.tb01893.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. R. The production of farmer's lung antigens. Med Lab Technol. 1971 Apr;28(2):172–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gander J. E. Fungal cell wall glycoproteins and peptido-polysaccharides. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1974;28(0):103–119. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.28.100174.000535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghose T., Landrigan P., Killeen R., Dill J. Immunopathological studies in patients with farmer's lung. Clin Allergy. 1974 Jun;4(2):119–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1974.tb01369.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant I. W., Blackadder E. S., Greenberg M., Blyth W. Extrinsic allergic alveolitis in Scottish maltworkers. Br Med J. 1976 Feb 28;1(6008):490–493. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6008.490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- How M. J., Withnall M. T., Cruickshank C. N. Allergenic glucans from dermatophytes. I. Isolation, purification, and biological properties. Carbohydr Res. 1972 Dec;25(2):341–353. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)81644-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richerson H. B. Acute experimental hypersensitivity pneumonitis in the guinea pig. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 May;79(5):745–757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddle H. F., Channell S., Blyth W., Weir D. M., Lloyd M., Amos W. M., Grant I. W. Allergic alveolitis in a maltworker. Thorax. 1968 May;23(3):271–280. doi: 10.1136/thx.23.3.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seal R. M., Hapke E. J., Thomas G. O., Meek J. C., Hayes M. The pathology of the acute and chronic stages of farmer's lung. Thorax. 1968 Sep;23(5):469–489. doi: 10.1136/thx.23.5.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie B., Pauli B., Gygax M. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: experimental production in guinea pigs with antigens of Micropolyspora faeni. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1973;39(6):393–411. doi: 10.1159/000162686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaidi S. H., Dogra R. K., Shanker R., Chandra S. V. Experimental farmer's lung in guinea-pigs. J Pathol. 1971 Sep;105(1):41–48. doi: 10.1002/path.1711050106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zavala D. C., Rhodes M. L., Richerson H. B., Oskvig R. Light and immunofluorescent study of the Arthus reaction in the rabbit lung. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1975 Dec;56(6):450–463. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(75)90063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]