Abstract
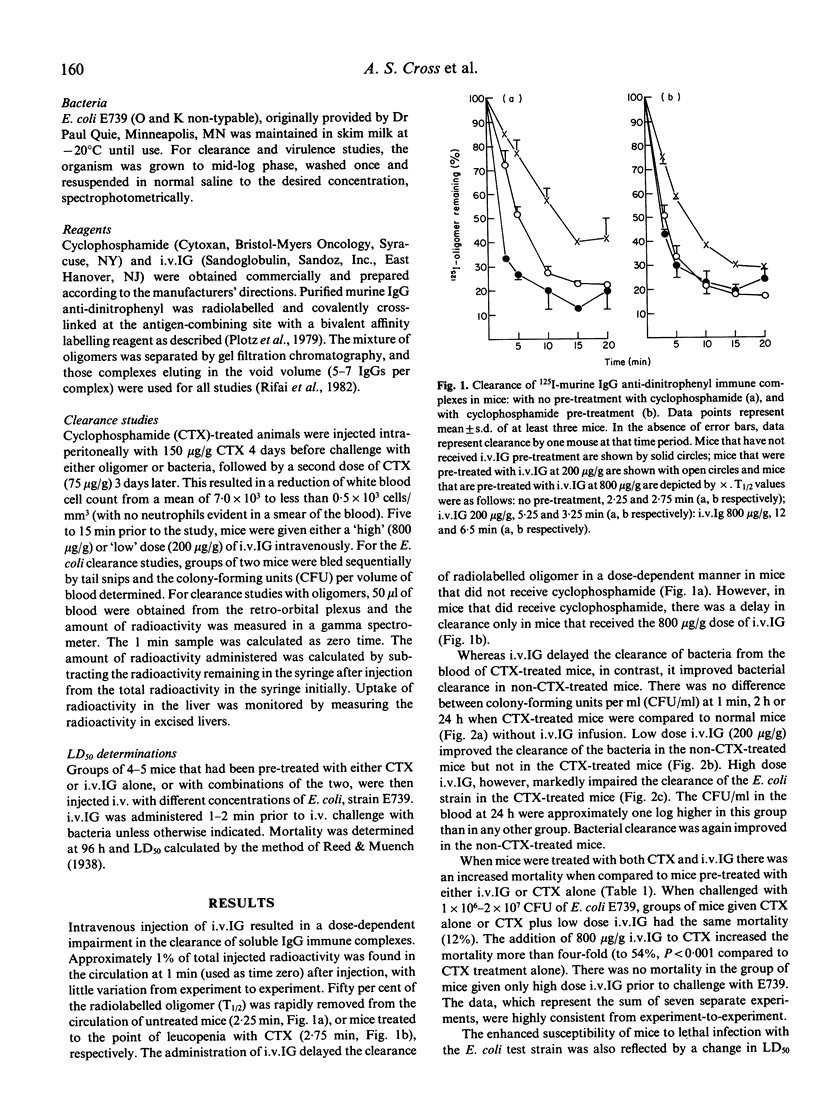
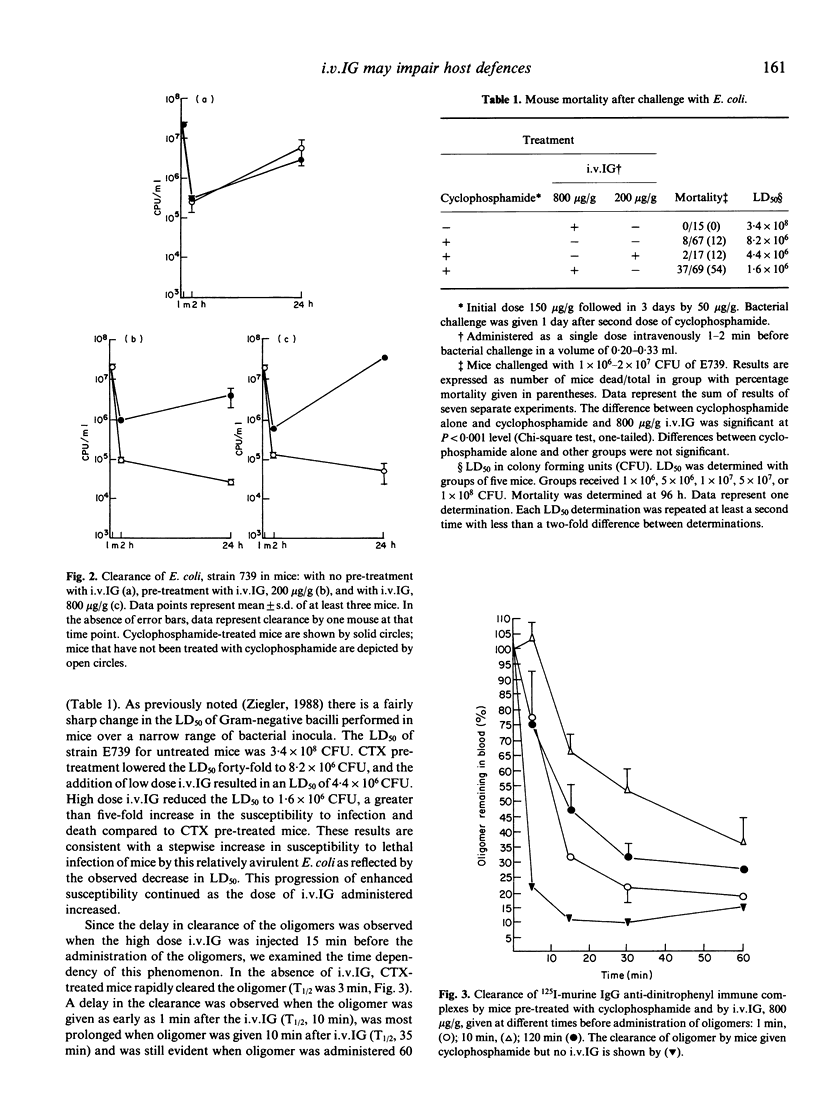
Since intravenous immune globulin (i.v.IG) could impair the clearance of autologous IgG-coated erythrocytes by the reticuloendothelial system (RES), we speculated that a patient with leucopenia who died of candida septicaemia following high dose i.v.IG may have had an impairment of his RES function. We therefore studied the ability of intact i.v.IG to impair the clearance of both soluble immune complexes and a relatively avirulent strain of E. coli from the blood of mice made leucopenic with cyclophosphamide. In the presence of leucopenia, 800 micrograms/g i.v.IG prolonged the time to clear 50% of the administered IgG anti-dinitrophenyl immune complex (T1/2) from 2.7 min to 12 min, impaired the clearance of E. coli and lowered the LD50 of the strain five-fold. This impaired clearance of soluble complexes and increased mortality (8/67 versus 37/69, P less than 0.001) following bacterial challenge was present for up to 120 and 60 min, respectively, following the administration of i.v.IG. In contrast, no significant impairment in RES function was noted when 200 micrograms/g i.v.IG was administered to leucopenic mice, or when cyclophosphamide alone was given to mice before challenge with either soluble complexes or bacteria. In addition, no change in LD50 was found when mice were pretreated with 800 micrograms/g i.v.IG alone. These data suggest that high doses of i.v.IG may impair anti-microbial defences of a leucopenic host and thereby convert a relatively avirulent organism into a pathogen.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arsura E. L., Bick A., Brunner N. G., Namba T., Grob D. High-dose intravenous immunoglobulin in the management of myasthenia gravis. Arch Intern Med. 1986 Jul;146(7):1365–1368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussel J. B., Kimberly R. P., Inman R. D., Schulman I., Cunningham-Rundles C., Cheung N., Smithwick E. M., O'Malley J., Barandun S., Hilgartner M. W. Intravenous gammaglobulin treatment of chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 1983 Aug;62(2):480–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussel J., Lalezari P., Hilgartner M., Partin J., Fikrig S., O'Malley J., Barandun S. Reversal of neutropenia with intravenous gammaglobulin in autoimmune neutropenia of infancy. Blood. 1983 Aug;62(2):398–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavanet P., Portier H., Escalier F., Courtois B. Intravenous gammaglobulin for adult Kawasaki disease. Lancet. 1985 Nov 23;2(8465):1184–1185. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92703-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen K. K., Christensen P., Bucher H. U., Duc G., Kind C. H., Mieth D., Müller B., Seger R. A. Intravenous administration of human IgG to newborn infants: changes in serum antibody levels to group B streptococci. Eur J Pediatr. 1984 Dec;143(2):123–127. doi: 10.1007/BF00445799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clauvel J. P., Vainchenker W., Herrera A., Dellagi K., Vinci G., Tabilio A., Lacombe C. Treatment of pure red cell aplasia by high dose intravenous immunoglobulins. Br J Haematol. 1983 Oct;55(2):380–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1983.tb01260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. S., Alving B. M., Sadoff J. C., Baldwin P., Terebelo H., Tang D. Intravenous immune globulin: a cautionary note. Lancet. 1984 Apr 21;1(8382):912–912. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91376-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DERBY B. M., ROGERS D. E. Studies on bacteriemia. V. The effect of simultaneous leukopenia and reticuloendothelial blockade on the early blood stream clearance of staphylococci and Escherichia coli. J Exp Med. 1961 Jun 1;113:1053–1066. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.6.1053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finbloom D. S., Plotz P. H. Studies of reticuloendothelial function in the mouse with model immune complexes. II. Serum clearance, tissue uptake, and reticuloendothelial saturation in NZB/W mice. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1600–1603. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez E. B., Guernsey B. G., Ingrim N. B., Ichikawa Y., Daniels J. C. Intravenous immune globulin therapy. Treatment of a patient with severe immunodeficiency, chronic malabsorption, and fulminant septicemia. Arch Intern Med. 1985 May;145(5):945–946. doi: 10.1001/archinte.145.5.945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haughton G. Specific immunosuppression by passive antibody. V. Participation of macrophages in reversal of suppression by peritoneal exudate cells from immune animals. Cell Immunol. 1974 Aug;13(2):230–240. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90241-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imbach P., Barandun S., d'Apuzzo V., Baumgartner C., Hirt A., Morell A., Rossi E., Schöni M., Vest M., Wagner H. P. High-dose intravenous gammaglobulin for idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in childhood. Lancet. 1981 Jun 6;1(8232):1228–1231. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92400-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. H., Nusbacher J., Anderson C. L. Fc receptor-mediated binding and endocytosis by human mononuclear phagocytes: monomeric IgG is not endocytosed by U937 cells and monocytes. J Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;100(2):558–564. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.2.558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kekomäki R., Elfenbein G., Gardner R., Graham-Pole J., Mehta P., Gross S. Improved response of patients refractory to random-donor platelet transfusions by intravenous gamma globulin. Am J Med. 1984 Mar 30;76(3A):199–203. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90342-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelton J. G., Singer J., Rodger C., Gauldie J., Horsewood P., Dent P. The concentration of IgG in the serum is a major determinant of Fc-dependent reticuloendothelial function. Blood. 1985 Sep;66(3):490–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Via M. F., La Via D. S. Studies on Fc receptor function. I. IgG-mediated inhibition of B lymphocyte activation by T-dependent and T-independent antigens. Cell Immunol. 1978 Sep;39(2):297–306. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newland A. C., Treleaven J. G., Minchinton R. M., Waters A. H. High-dose intravenous IgG in adults with autoimmune thrombocytopenia. Lancet. 1983 Jan 15;1(8316):84–87. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91738-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plotz P. H., Kimberly R. P., Guyer R. L., Segal D. M. Stable model immune complexes produced by bivalent affinity labeling haptens: in-vivo survival. Mol Immunol. 1979 Sep;16(9):721–729. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(79)90013-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifai A., Finbloom D. S., Magilavy D. B., Plotz P. H. Modulation of the circulation and hepatic uptake of immune complexes by carbohydrate recognition systems. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2269–2275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roifman C. M., Lederman H. M., Lavi S., Stein L. D., Levison H., Gelfand E. W. Benefit of intravenous IgG replacement in hypogammaglobulinemic patients with chronic sinopulmonary disease. Am J Med. 1985 Aug;79(2):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuller E., Govaerts A. First results of immunotherapy with immunoglobulin G in multiple sclerosis patients. Eur Neurol. 1983;22(3):205–212. doi: 10.1159/000115560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tirlapur V. G., Mir M. A. Nocturnal hypoxemia and associated electrocardiographic changes in patients with chronic obstructive airways disease. N Engl J Med. 1982 Jan 21;306(3):125–130. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198201213060301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Epps D. E., Brown S. L. Inhibition of formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine-stimulated neutrophil chemiluminescence by human immunoglobulin A paraproteins. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):864–870. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.864-870.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Epps D. E., Reed K., Williams R. C., Jr Suppression of human PMN bactericidal activity by human IgA paraproteins. Cell Immunol. 1978 Mar 15;36(2):363–376. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90280-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler E. J. Protective antibody to endotoxin core: the emperor's new clothes? J Infect Dis. 1988 Aug;158(2):286–290. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.2.286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


