Figure 3.
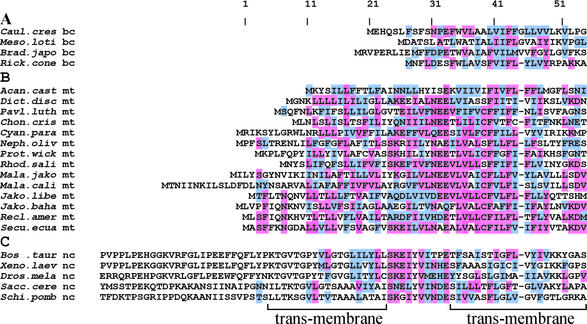
Multiple protein alignments of bacterial AtpF, mitochondrion-encoded Ymf39 and nucleus-encoded ATP4. (A) Bacterial AtpF; (B) mitochondrion-encoded Ymf39; (C) nucleus-encoded ATP4 (also designated ATP5F or PVP). Highlighting of amino acids followed similar rules as in Figure 2. In a given column, an amino acid is highlighted in magenta when four or more residues are identical in alignment B; amino acids with a positive PAM250 value relative to the magenta-labeled residue in a given column are shown in light blue. Sequences used, taxonomy and GenBank accession nos as in legend to Figure 2. Acan.cast., A.castellanii (mycetozoa; NC_001637); Dict.disc., D.discoideum (mycetozoa; NC_000895); Pav.luth., P.lutheri (haptophyte alga; reported here); Chon.cris., C.crispus (rhodophyte alga; NC_1677); Cyan.para., C.paradoxa (glaucocystophyte alga; reported here); Neph.oliv., Nephroselmis oliva (green alga; NC_000927); Prot.wick., P.wickerhamii (green alga; NC_001613); Mala.jako. M.jakobiformis (malawimonad; NC_002553); Mala.cali., M.californiana (malawimonad; reported here). Bos.taur., Bos taurus (chordata; P13619); Xeno.laev., Xenopus laevis (chordata; AAF31360); Sacc.cere., Saccharomyces cerevisiae (fungi; NP_015247); Schi.pomb., Schizosaccharomyces pombe (fungi; CAA22340).