Abstract
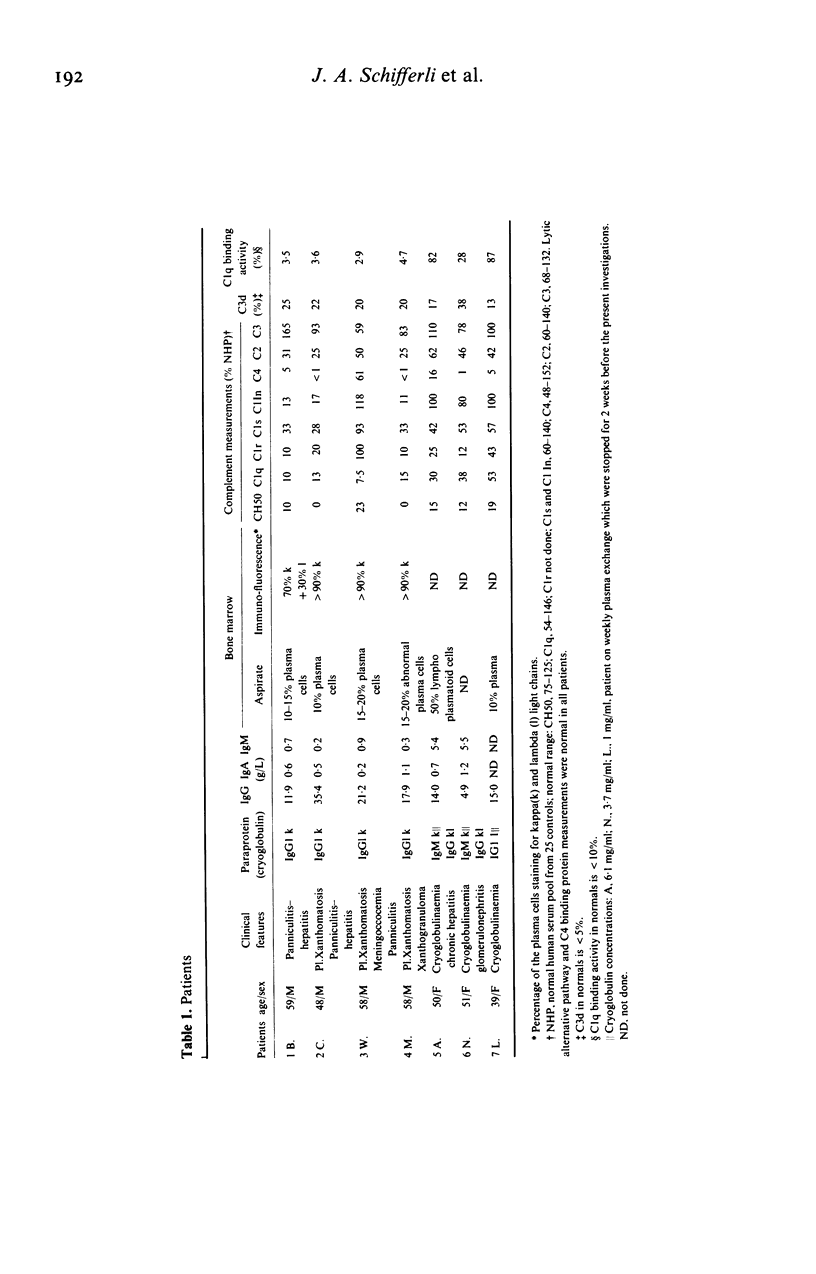
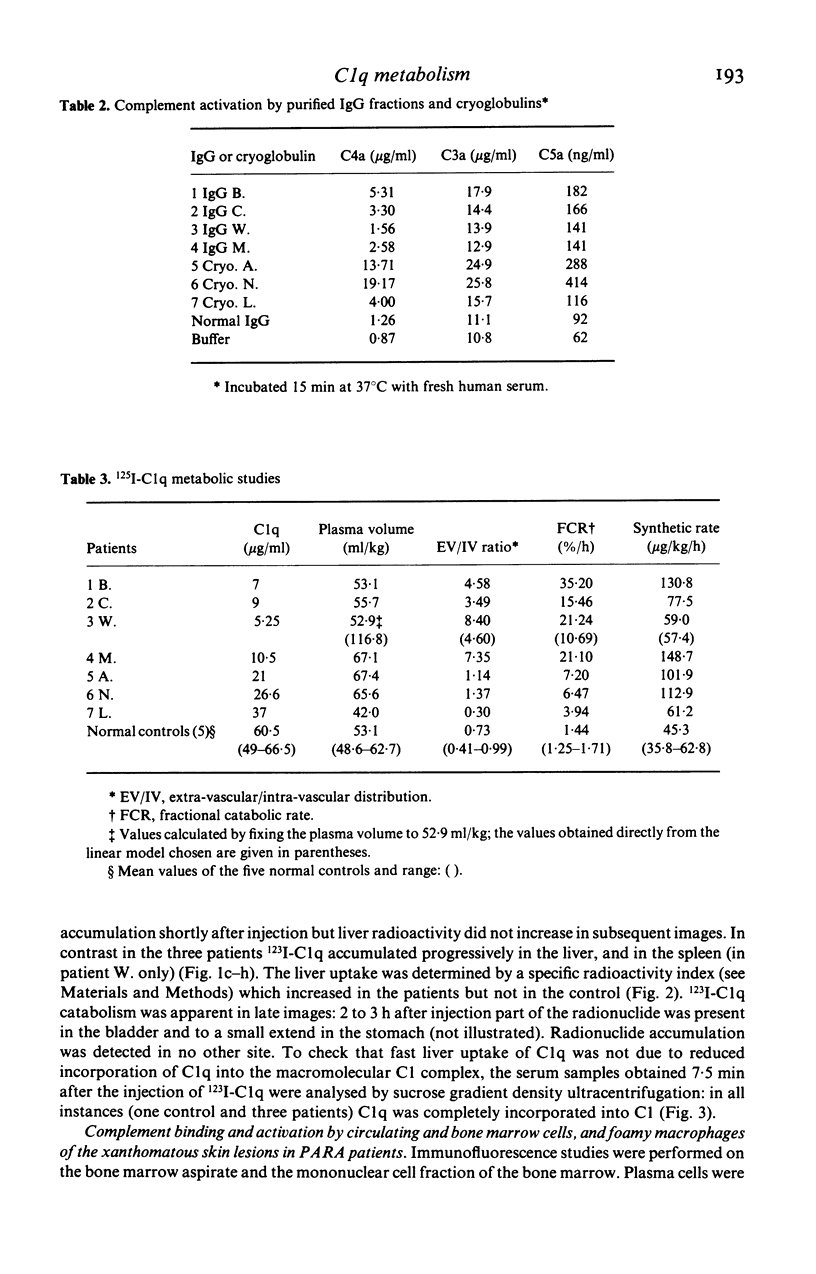
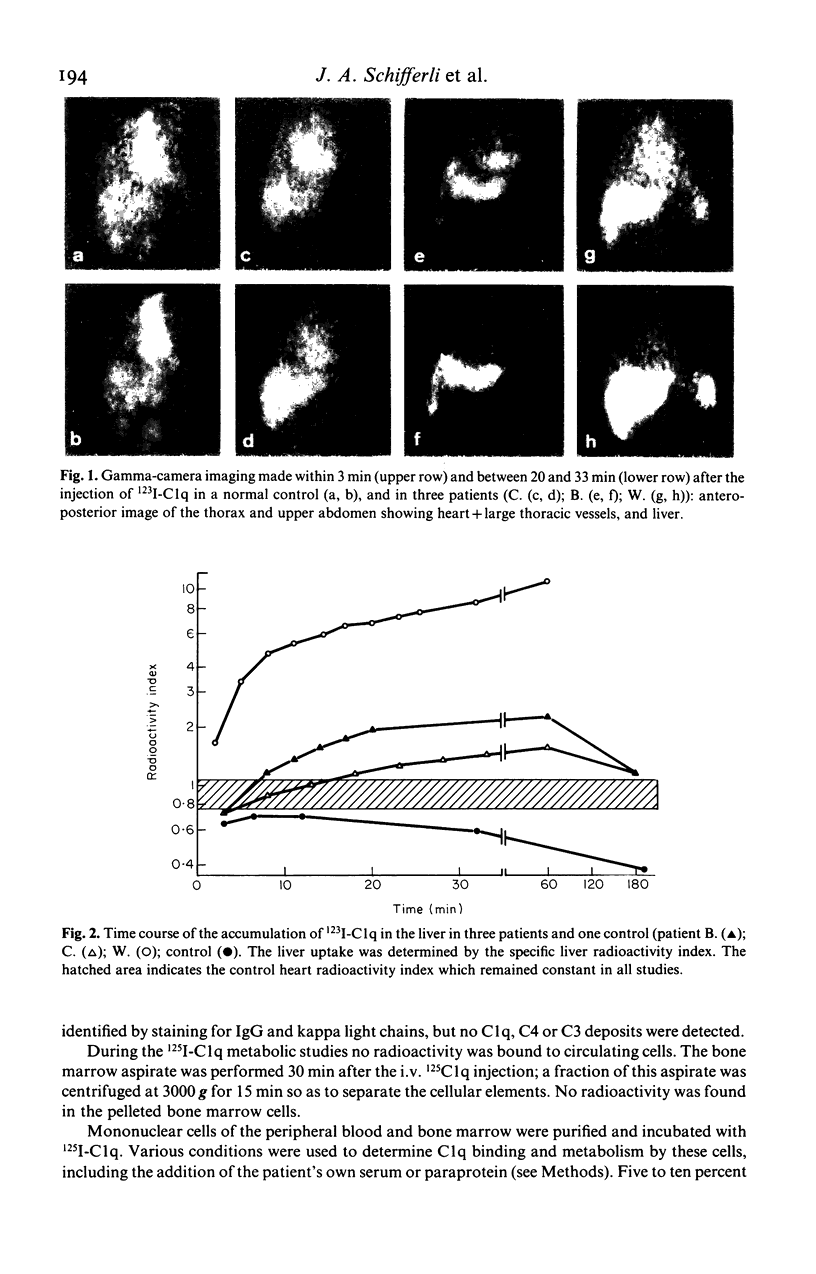
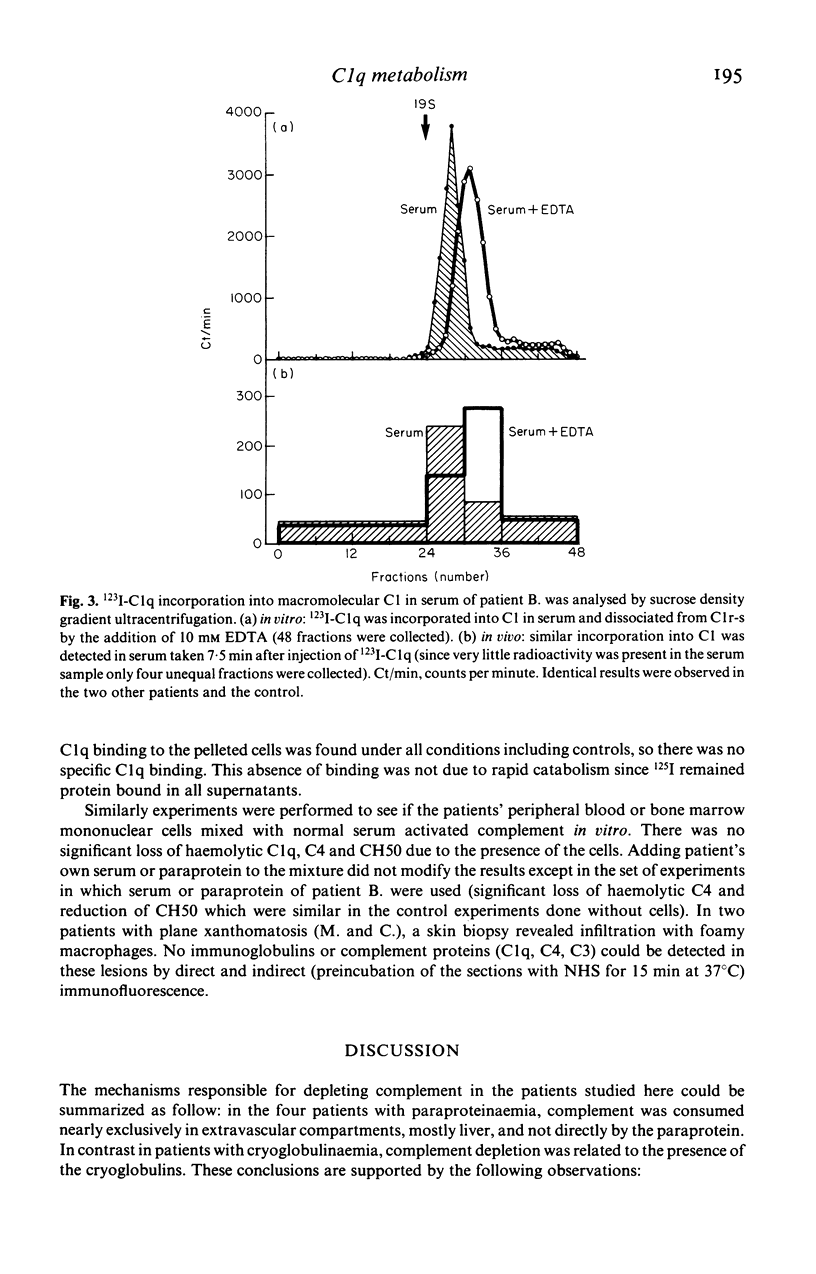
The main clinical features in four patients with IgG1k paraproteinaemia and acquired complement deficiency included xanthomatous skin lesions (in three), panniculitis (in three) and hepatitis (in two). Hypocomplementaemia concerned the early classical pathway components--in particular C1q. Metabolic studies employing 125I-C1q revealed a much faster catabolism of this protein in the four patients than in five normal controls and three patients with cryoglobulinaemia (mean fractional catabolic rates respectively: 23.35%/h; 1.44%/h; 5.84%/h). Various experiments were designed to characterize the mechanism of the hypocomplementaemia: the patients' serum, purified paraprotein, blood cells, bone marrow cells, or xanthomatous skin lesions did not produce significant complement activation or C1q binding. When three of the patients (two with panniculitis and hepatitis) were injected with 123I-C1q, sequential gamma-camera imaging demonstrated rapid accumulation of the radionuclide in the liver, suggesting that complement activation takes place in the liver where it could produce damage.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnello V., Winchester R. J., Kunkel H. G. Precipitin reactions of the C1q component of complement with aggregated gamma-globulin and immune complexes in gel diffusion. Immunology. 1970 Dec;19(6):909–919. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costanzi J. J., Coltman C. A., Jr, Donaldson V. H. Activation of complement by a monoclonal cryoglobulin associated with cold urticaria. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Dec;74(6):902–910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day N. K., Winfield J. B., Gee T., Winchester R., Teshima H., Kunkel H. G. Evidence for immune complexes involving anti-lymphocyte antibodies associated with hypocomplementaemia in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL). Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Nov;26(2):189–195. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estreicher J., Revillard C., Scherrer J. R. Compartmental analysis--I: LINDE, a program using an analytical method of integration with constituent matrices. Comput Biol Med. 1979;9(1):49–65. doi: 10.1016/0010-4825(79)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geha R. S., Quinti I., Austen K. F., Cicardi M., Sheffer A., Rosen F. S. Acquired C1-inhibitor deficiency associated with antiidiotypic antibody to monoclonal immunoglobulins. N Engl J Med. 1985 Feb 28;312(9):534–540. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198502283120902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand J. A., Boss G. R., Conley C. L., Reinhart R., Frank M. M. Acquired C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency and angioedema: a review. Medicine (Baltimore) 1979 Jul;58(4):321–328. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197907000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauptmann G., Petitjean F., Lang J. M., Oberling F. Acquired C1 inhibitor deficiency in a case of lymphosarcoma of the spleen. Reversal of complement abnormalities after splenectomy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Sep;37(3):523–531. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordon R. E., McDuffie F. C., Good R. A., Day N. K. Diffuse normolipaemic plane xanthomatosis. An abnormal complement component profile. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Nov;18(3):407–415. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler P. F., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Complement-immunoglobulin relation: deficiency of C'1q associated with impaired immunoglobulin G synthesis. Science. 1969 Jan 31;163(3866):474–475. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3866.474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler P. F., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Metabolism of human C1q. Studies in hypogammaglobulinemia, myeloma, and systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1972 Apr;51(4):868–875. doi: 10.1172/JCI106881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kövary P. M., Cassuto J. P., Dujardin P., Maiolini R., Campagni J. P., Herzberg J. J., Schwartzkopff W., Gebhart W., Audoly P. Hypocomplémie des premières fractions de la voie classique au cours de xanthomes plans, normolipémiques, avec immunoglobulines monoclonales IgG1 (6 cas). Rev Med Interne. 1981 Oct;2(3):275–279. doi: 10.1016/s0248-8663(81)80026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder R. J., Burch F. X., Schmid F. R., Zeiss C. R., Gewurz H. Low molecular weight C1q-precipitins in hypocomplementemic vasculitis-urticaria syndrome: partial purification and characterization as immunoglobulin. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):613–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDuffie F. C., Sams W. M., Jr, Maldonado J. E., Andreini P. H., Conn D. L., Samayoa E. A. Hypocomplementemia with cutaneous vasculitis and arthritis. Possible immune complex syndrome. Mayo Clin Proc. 1973 May;48(5):340–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin L. H., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Complement breakdown products in plasma from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and patients with membranoproliferative or other glomerulonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jul;56(1):165–176. doi: 10.1172/JCI108065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Praz F., Roque Antunes Barreira M. C., Lesavre P. A one-step procedure for preparation of classical pathway (C1q) and alternative pathway (factor D) depleted human serum. J Immunol Methods. 1982;50(2):227–231. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferli J. A., Pascual M., Deleamont P., Hirschel B., Perrin L. Meningococcemia in a patient with acquired complement deficiency and myeloma. N Engl J Med. 1984 Nov 22;311(21):1381–1382. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198411223112118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferli J. A., Steiger G., Hauptmann G., Spaeth P. J., Sjöholm A. G. Formation of soluble immune complexes by complement in sera of patients with various hypocomplementemic states. Difference between inhibition of immune precipitation and solubilization. J Clin Invest. 1985 Dec;76(6):2127–2133. doi: 10.1172/JCI112217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferli J. A., Steiger G., Polla L., Didierjean L., Saurat J. H. Activation of the alternative pathway of complement by skin immune deposits. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Nov;85(5):407–411. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12277069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. D., Zweiman B., Atkins P., Goldwein F., Pietra G., Atkinson B., Abdou N. I. Acquired angioedema with lymphoproliferative disorder: association of C1 inhibitor deficiency with cellular abnormality. Blood. 1976 Oct;48(4):567–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenner A. J., Cooper N. R. Analysis of receptor-mediated C1q binding to human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1658–1664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenner A. J., Lesavre P. H., Cooper N. R. Purification and radiolabeling of human C1q. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):648–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziccardi R. J., Cooper N. R. The subunit composition and sedimentation properties of human C1. J Immunol. 1977 Jun;118(6):2047–2052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubler R. H., Lange G., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Detection of immune complexes in unheated sera by modified 125I-Clq binding test. Effect of heating on the binding of Clq by immune complexes and application of the test to systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):232–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


