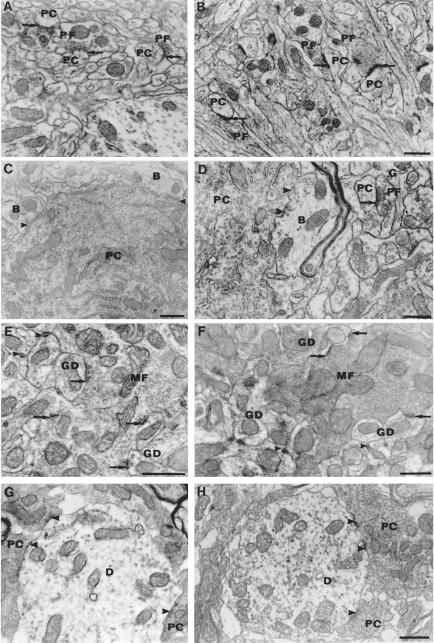
Figure 4.
The cerebella of wild-type and Atm−/− mice have analogous subcellular and synaptic ultrastructure. Asymmetric synapses (arrows) made by parallel fibers (PF) on PC spines in the molecular layer of wild-type (A) and Atm−/− (B) mice (magnification: ×24,000). (C and D) Symmetric synapses (arrowheads) made on PC soma by presumptive basket cell axon terminals (B) from wild-type (C) and Atm−/− (D) mice. A parallel fiber bouton (PF) with presynaptic vesicles makes an asymmetric synapse (arrow) on a postsynaptic dendritic PC spine in the deep molecular layer [glia (G); magnification: ×24,000]. (E and F) Glomerular synapses made by mossy fiber (MF) terminals (arrows) on granule cell dendrites (GD) in the internal granular layer of the wild-type (E) and Atm−/− (F) cerebellum. Arrowheads show tight junctions between GDs (magnification: E, ×36,000; F, ×27,000). (G and H) Synapses made by PC axon terminals (arrows) on the dendrites (D) of neurons in the fastigial nucleus of wild-type (G) and Atm−/− (H) cerebellum (magnification: ×27,000).