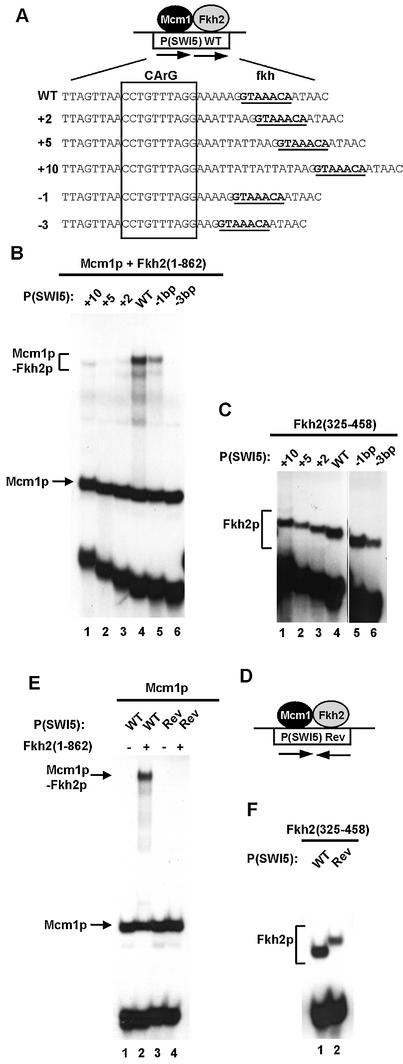
Figure 5.
Influence of binding site spacing on Mcm1p–Fkh2p complex formation. (A) Schematic of the Mcm1p–Fkh2p ternary complex bound to the P(SWI5) site. The sequence of the wild-type site and ‘spacer’ mutants are shown below. The fkh binding motif is shown in bold and underlined and the CArG box Mcm1p binding motif is boxed. (B and C) Gel retardation analysis of Fkh2(1–862) (B) and Fkh2(325–458) (C) in the presence (B) or absence (C) of Mcm1(1–96) bound to the indicated wild-type (WT) and ‘spacer’ mutant binding sites. (D) Schematic of the Mcm1p–Fkh2p complex and the P(SW15)Rev binding site. The arrows represent the relative orientation of the Mcm1p and Fkh2p binding sites. (E and F) Gel retardation analysis of Fkh2(1–862) (E) and Fkh2(325–458) (F) in the presence (E) and absence (F) of Mcm1p on the WT and Rev versions of the P(SWI5) site. The locations of Mcm1p, Fkh2p and Mcm1p–Fkh2p complexes are indicated in each panel.