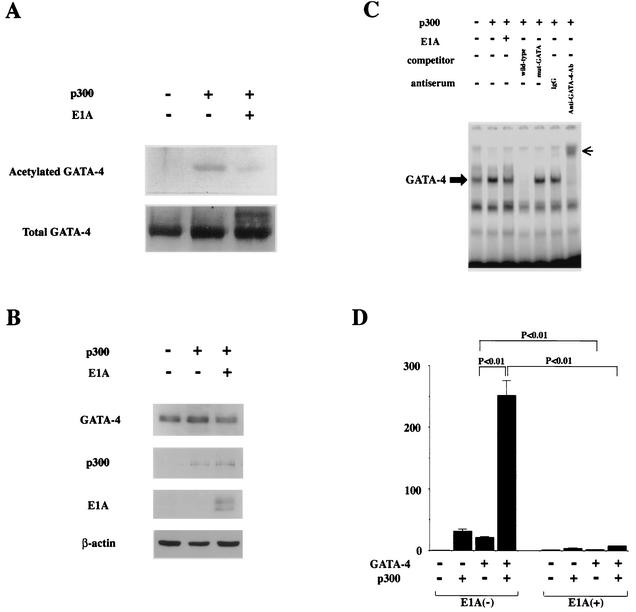
FIG. 2.
p300 acetylates lysine residues of GATA-4, enhances its DNA-binding activity, and is involved in GATA-4-dependent ET-1 transcription. (A) COS7 cells were transfected with 2 μg of pcDNAG4 or with (+) 9 μg of pCMVwtp300 (p300) and/or 1 μg of pwtE1A (E1A) as indicated. The total amount of DNA was kept constant by cotransfecting pCMVβ-gal. Nuclear extracts (300 μg of protein) from these cells were immunoprecipitated with anti-GATA-4 antibody, followed by sequential Western blotting with anti-acetylated lysine antibody and with anti-GATA-4 antibody. (B) The nuclear extracts used for panel A before immunoprecipitation were subjected to Western blotting using the anti-GATA-4 antibody, anti-p300 antibody, anti-E1A antibody, or anti-β-αctin antibody. (C) The same nuclear extracts were probed with a radiolabeled double-stranded oligonucleotide containing the GATA-4 site in the ET-1 promoter. Ab, antibody; small arrow, supershifted band of GATA-4. (D) COS7 cells were transfected with 2.0 μg of pETCAT, 0.1 μg of pRSVluc, 0.5 μg of pcDNAG4 or pCMVβ-gal, 2.5 μg of pCMVwtp300 or pCMVβ-gal, and 0.3 μg of pwtE1A or pCMVβ-gal. The results are expressed as n-fold activation of the normalized CAT activity (CAT/luc) relative to that resulting from transfection with 3.3 μg of pCMVβ-gal without pcDNAG4, pCMVwtp300, or pwtE1A. The data shown are the means and standard errors of the mean from three independent experiments.