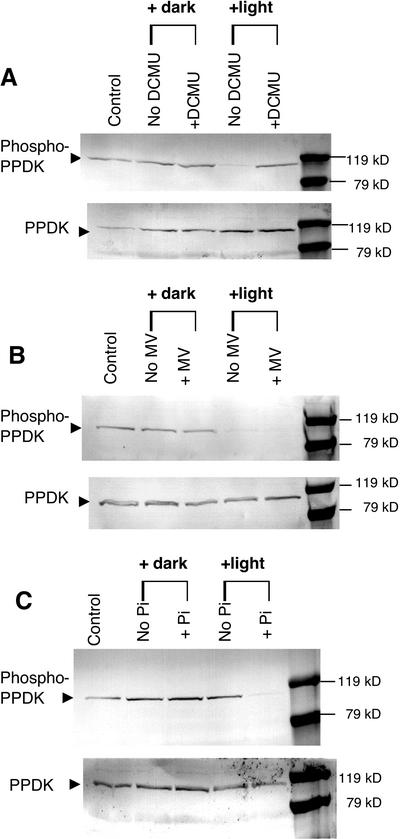
Figure 6.
Effects of a PSII inhibitor, a PSI alternate electron acceptor, and exogenous Pi on light-induced PPDK dephosphorylation in isolated intact spinach chloroplasts. Stromal extracts, fractionated with 35% to 55% saturation ammonium sulfate, were prepared from isolated intact chloroplasts incubated in the presence or absence of 20 μm 3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea (DCMU; A), 100 μm methyl viologen (MV; B), or 2 mm potassium Pi (C). Duplicate immunoblots were probed with either phospho-PPDK antibody (above) or standard PPDK antibody (below). Each lane contained 100 μg of stromal protein. Intact chloroplasts were darkened or illuminated at approximately 600 μmol m−2 s−1 for 10 min at 25°C before freezing in liquid N2. The lanes labeled as “control” represent the PPDK phosphorylation state before experimental manipulation of the intact chloroplasts isolated from the dark-adapted (1.5 h) parent leaves.