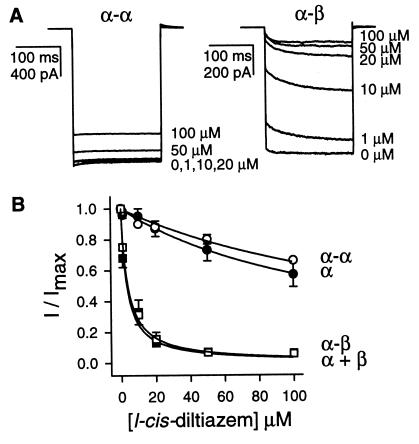
Figure 1.
l-cis-diltiazem blocks channels formed from α-β heterodimers more effectively than those from α-α homodimers. (A) Current traces elicited by saturating cGMP (1 mM) and different concentrations of l-cis-diltiazem in patches expressing α-α (Left) and α-β (Right) channels. Currents were evoked by −50 mV pulses from a holding potential of 0 mV. (B) l-cis-diltiazem sensitivities of homomeric and heteromeric channels formed from both monomers and dimers. The response to 1 mM cGMP in the presence of l-cis-diltiazem divided by the response in the absence of l-cis-diltiazem (I/Imax) is plotted against l-cis-diltiazem concentration. The smooth curves are fits to the data with the equation: I/Imax = KI/([l-cis-diltiazem] + KI), where KI is the concentration of l-cis-diltiazem that causes half-maximal inhibition. α monomers, KI = 135 μM (n = 4); α-α dimers, KI = 185 μM (n = 4); α + β monomers (■), KI = 3.3 μM (n = 5); α-β dimers (□), KI = 3.8 μM (n = 4).