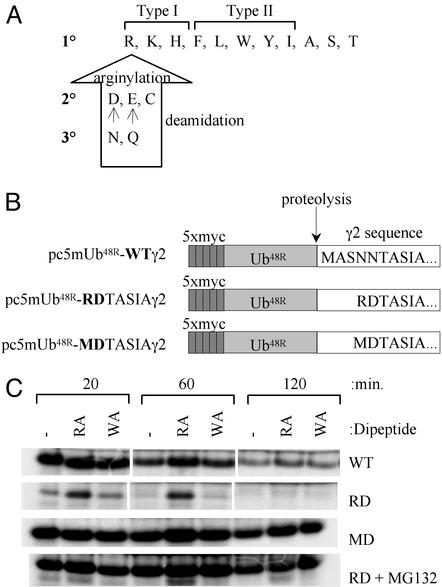
Figure 2.
N-terminal variant of γ2 undergoes proteasome-dependent degradation. (A) Destabilizing N-terminal amino acids of the N-end rule pathway. Primary destabilizing amino acids can be subdivided into the type I (basic) residues or type II (bulky hydrophobic) residues. Secondary destabilizing amino acids require N-terminal arginylation, whereas tertiary amino acids are modified by deamidation and arginylation before N-end degradation (14). (B) The ubiquitin-fusion constructs used to generate γ2 in reticulocyte coupled transcription/translation system with varying N termini. Ub48R, ubiquitin containing K48R substitution, which does not support formation of multiubiquitin chains. (C) Accumulation of γ2 or its N-terminal variants after translation in rabbit reticulocyte lysate. Dipeptide inhibitors of the N-end ubiquitin ligase (type 1 inhibitor, RA; type 2 inhibitor, WA) are included in the indicated reactions.