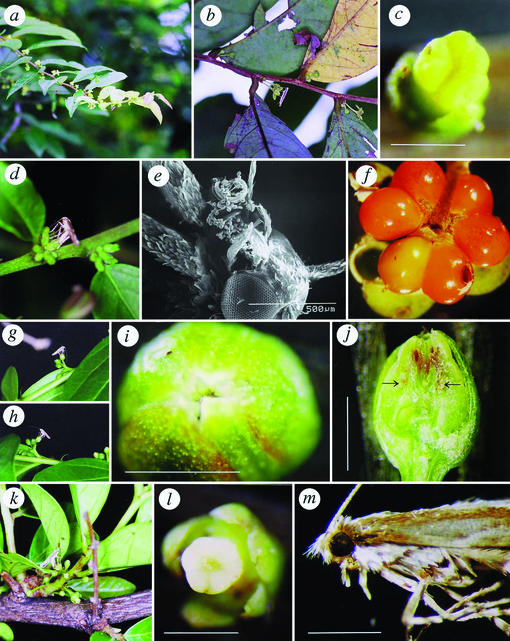
Figure 1.
Flowers and pollinators of G. acuminatum (a–f), G. zeylanicum (g–j), and G. obovatum (k–m). (a) A branch bearing many male and female flowers, one of which is visited by a moth, Epicephala sp. 1. (b) A female moth visiting a male flower. (c) Pollinated stigma. (d) An ovipositing Epicephala moth. (e) Pollen-loaded proboscis of a female moth. (f) A fruit with two seeds infested by a moth larva, which had emerged from the hole. (g) An Epicephala sp. 2 moth actively pollinating a female flower. (h) An ovipositing Epicephala moth. (i) Dorsal view of a female flower, showing the pollinated cryptic stigma. (j) Cross section of a female flower with two eggs (shown by arrows). (k) An ovipositing Epicephala sp. 3 moth. (l) Pollinated stigma. (m) Lateral view of a female moth, whose proboscis is loaded with pollen. [Scale bars, 1 mm (except in e).]