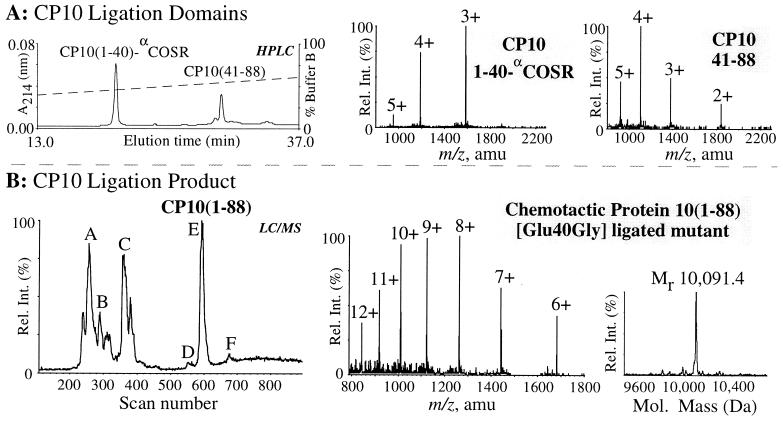
Figure 5.
Total synthesis of [Glu40Gly]CP10 by native chemical ligation. (A) Analytical RP-HPLC of the synthetic peptide fragments [Glu40Gly]CP10(1–40)-αCOSR and CP10(41–88) dissolved at 6 mg/ml in 0.1 M Tris⋅HCl buffer (pH 8.2) containing 6 M guanidine⋅HCl at t = 0. (Center and Right) Electrospray mass spectra show the m/z ratios of the [Glu40Gly]CP10(1–40)-αCOSR peptide (3rd to 5th ionized states) with an observed molecular mass of 4749.8 ± 0.5 Da (calc. 4750.2 Da, average isotope composition), and the CP10(41–88) peptide (2nd to 5th ionized states) with an observed molecular mass of 5518.6 ± 0.9 Da (calc. 5518.2 Da, average isotope composition). (B) LC-MS analysis of the ligation reaction after t = 3 h. Peaks A, B, and C represent unreacted [Glu40Gly]CP10(1–40)-αCOSR, [Glu40Gly]CP10(1–40) as the free C-terminal acid, and [Glu40Gly]CP10(1–40)-αCOS-C6H5, respectively. Peaks D and F had a mass indicating the presence of CP10(1–88) esterified through the Cys-41 by CP10(1–40) (14,665 Da), and the CP10(1–88)[Cys-41-thiophenol] mixed disulfide (10,199 Da), respectively. ES-MS of purified [Glu40Gly]CP10 (6th to 12th ionized states), peak E, had an observed molecular mass of 10,091.4 ± 1.1 Da; (calc. 10,091.3 Da, average isotope composition).